As organizations continue to evaluate their infrastructure moving forward, cloud migration is likely a direction most are considering. Microsoft Azure is one of the front runners for cloud migration. Many organizations already have a relationship with Microsoft with traditional on-premises enterprise agreements and familiarity with Microsoft apps and operating systems. Let’s look at the recommended steps to ensure a successful migration to Microsoft Azure for businesses considering a move.
Steps for successful Azure migration from on-premises
Microsoft recommends that there are seven steps or considerations to make sure an Azure migration is successful. Those include the following:
- Plan using the Azure Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF)
- Have a strategy for migrating to Azure
- Assess and evaluate your current on-premises infrastructure
- Prepare and plan for migration
- Execute your migration
- Optimize your workloads after migration
- Continue with ongoing management and governance
1. Plan using the Azure Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF)
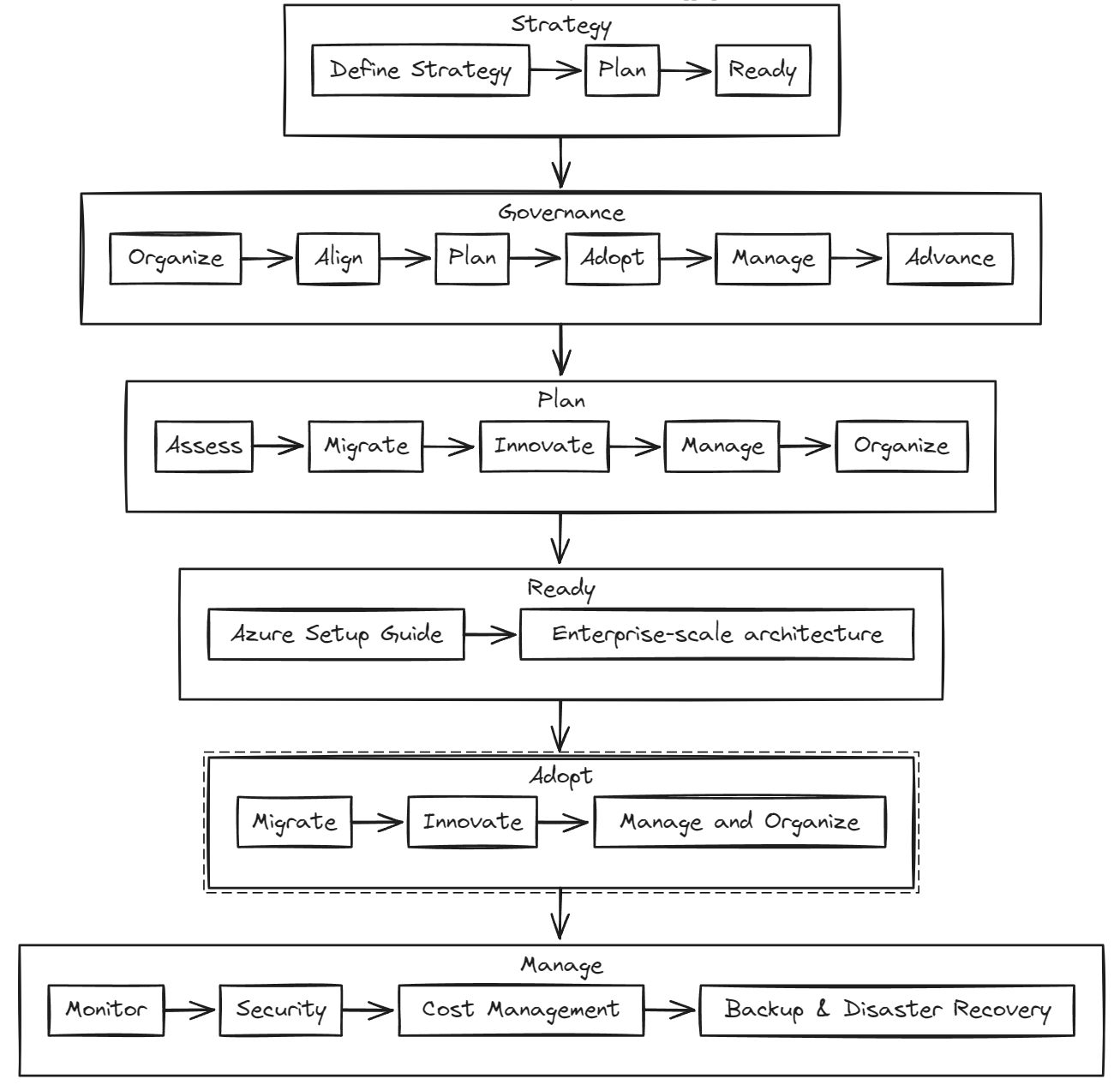
Microsoft’s Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF) helps plan the transition to the cloud. It includes documentation, best practices, and tools admins need through all stages of the cloud adoption process.
By using the Azure CAF, businesses can make sure their migration is well-planned and aligned with their goals and security requirements. Also, it helps to stay close to Microsoft’s recommended best practices.
Azure Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF)
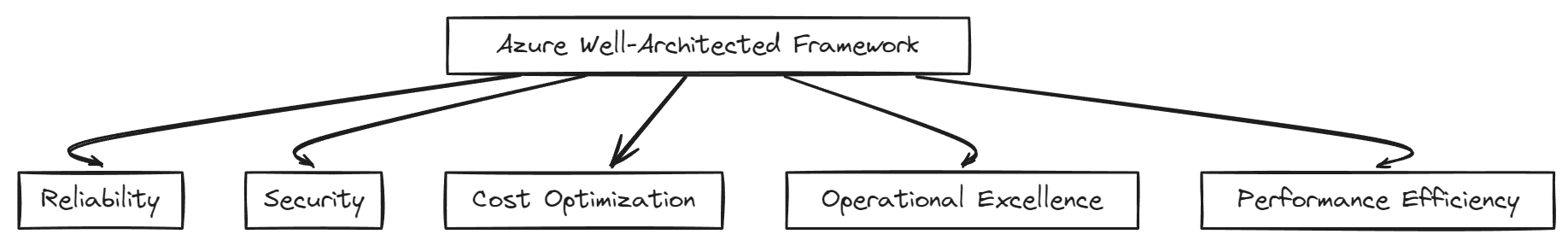
There is also the Azure Well-Architected Framework (WAF), which provides a set of very specific guidance related to Microsoft Azure.
Azure Well-Architected Framework
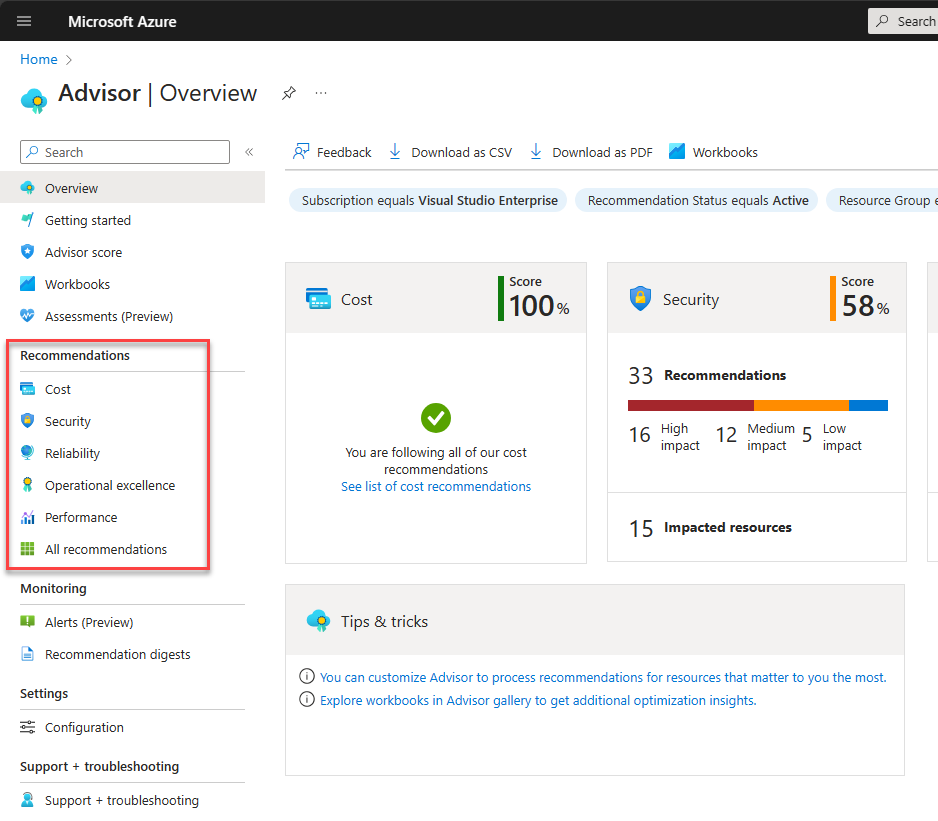
Businesses also have a great resource in Azure Advisor. The Azure Advisor tool is a resource that provides recommendations to help optimize your Azure resources. It gives recommendations on cost, security, reliability, operational excellence, and performance.
Viewing Azure Advisor recommendations
2. Understand your strategy for Azure Migration
Before moving to the cloud in general, not just Azure, businesses must understand their motivation and reasons for doing so. For the most part, it would likely be a “cost” disaster to simply lift and shift all your on-premises VMs to the cloud. However, there may be workloads that are suitable for moving to the cloud and actually make sense to do so.
Many organizations today are looking at refactoring applications from the traditional monolithic application design running in virtual machines to the more modern microservices apps made up of various containerized services.
Before executing a migration, it is important to determine the strategic intent behind moving to the cloud. Considering the objectives is important. These may include cost efficiency and enhanced flexibility. Another common reason for cloud migration is to modernize outdated data centers and take advantage of many of the other Azure services.
The first step in defining your strategy involves thoroughly assessing business impacts and the motivations driving cloud adoption. It helps make sure the move aligns with business strategies.
You can then determine how best to migrate using the right Azure tools like the following:
- Azure migrate
- App migration
- Windows server migration
- SQL server migration
- Linux migration
- Mainframe migration
- Azure Arc
- Azure Data Box
3. Assessment and Evaluation of Current Infrastructure
A detailed inventory of the current IT environment is one of the most important first steps. If organizations don’t understand their current resources, it will be difficult to know what resources they want or can migrate. The identification process needs to include identifying servers, databases, applications, and other critical resources for the business.
Once you know existing resources, it helps determine which workloads are best suited for the cloud. This in itself can help establish a baseline for the migration strategy. Then, you can use tools like Azure Migrate for any workloads you have migrated to streamline these for the cloud cost-effectively.
4. Preparation and Planning for Migration
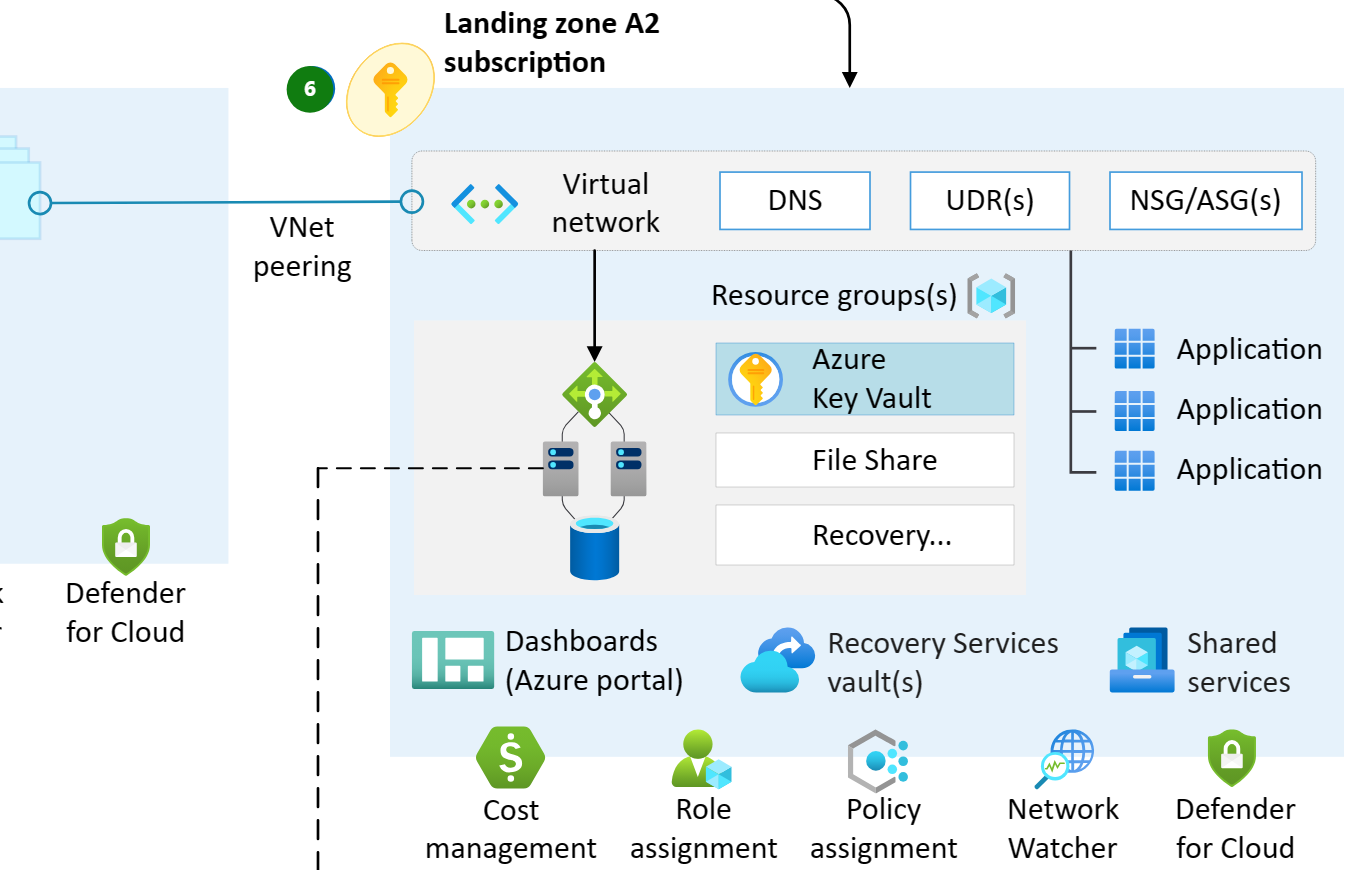
Preparation involves setting up the Azure environment before the actual migration. This step includes configuring the Azure landing zone. The migration landing zone is a special-purpose environment that is prepared ahead of time to host your migration workloads. It creates logical segmentation of the cloud environment where your migrated resources will reside.
As part of the preparation, you must make sure governance policies, compliance requirements, and security measures are configured in advance to support and protect the migrated workloads.
A landing zone for migrated resources
5. Executing the Migration
Once you have properly planned and prepared, you can execute the Azure migration for selected workloads that you want to move to Microsoft Azure. Azure Migrate is purpose-built to migrate your VMs, servers, databases, and web apps to Microsoft Azure.
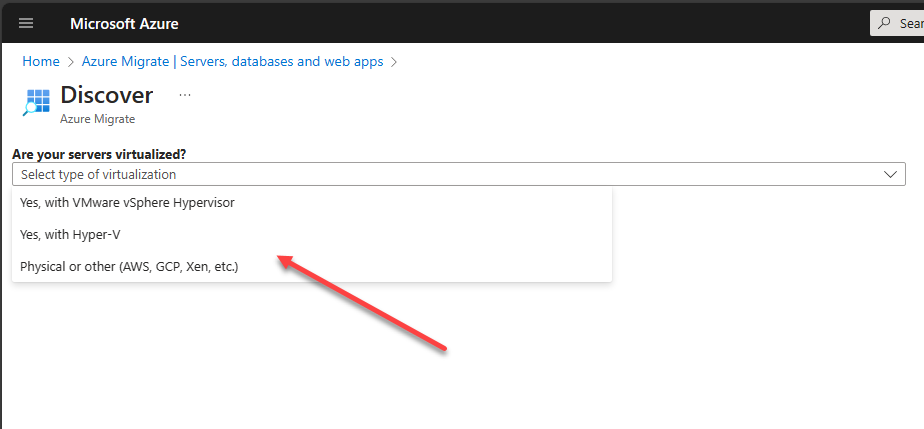
It can assess and migrate Windows, Linux, and SQL Server (physical or virtual) from your data center. Also, you can use it to discover ASP.Net and Java web apps and perform at-scale assessments of ASP.Net web apps from your VMware, Microsoft Hyper-V, and physical environments. It is best practice to start with less critical workloads for beginning the migration process before moving on to more business-critical workloads and applications.
Microsoft makes the process extremely easy for migrating on-premises virtualization solutions, such as VMware vSphere, Hyper-V, physical, or other cloud environments like AWS, GCP, Xen, etc. You can use the Azure Migrate appliance, which you can deploy in your vSphere or Hyper-V environment to take the heavy lifting out of the migration process.
6. Optimization Post-Migration
After the migration, the focus becomes optimizing the workloads running in Azure. This includes optimizing for performance, cost, and security. Most will find Azure Advisor a great resource for shedding light on where optimizations can happen. It provides personalized recommendations based on the well-architected framework and helps to enhance reliability, cost, and operational excellence.
One thing to note about optimization is that it is not a “one-and-done” task. Organizations will benefit from regular reviews and adjustments using Azure Advisor. These help continue to align the cloud services with business needs.
7. Ongoing Management and Governance
Regular management and governance assessments will need to be made to ensure these meet the business’s needs and requirements. In Azure, there are many tools businesses can use to manage and optimize costs, governance, and security. These include:
- Azure Cost Management – this is a free solution that provides information about overall costs and utilization across Azure services
- Azure Defender – Azure Defender is a built-in tool that runs in Azure, on-premises, and other clouds for security
- Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management helps organizations implement role-based access control in Microsoft Entra.
Azure Cost Management
Wrapping up
Migrating from on-premises environments to Microsoft Azure, or any other cloud environment, is not trivial. It requires careful and detailed planning. Microsoft provides many great tools that can be used to get workloads up to the cloud more easily. By following the steps outlined, such as using frameworks like the Cloud Adoption Framework and tools such as Azure Migrate, organizations can successfully migrate to the cloud.
Top of Form