Microsoft has provided a unique option to run the Azure Stack HCI cluster. In a supported way, you can now run Azure Stack HCI on a single server, known as a single-node cluster. In addition, it provides an option to stand up an Azure Stack HCI cluster initially using a single host, which offers some compelling use cases. So what is the Azure Stack HCI single node cluster? Why would you want to use this configuration?
What is Azure Stack HCI?
First, what is Azure Stack HCI? The Azure Stack HCI offering is a new solution from Microsoft that is a cloud-based offering for customers to run HCI clusters enabled from the Microsoft Azure cloud. Azure Stack HCI allows organizations to have a cloud-based subscription model and control plane for their HCI workloads.
Azure Stack HCI is a purpose-built operating system intended to run hyperconverged workloads and benefit from the efficiencies and new technologies enabled through Microsoft Azure. Customers now have the choice when provisioning HCI clusters to “roll their own cluster” using Windows Server and Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) or use Azure Stack HCI, enabled from Azure, to stand up an HCI cluster.
There are additional benefits to using Azure Stack HCI, including the latest features and improvements in functionality, capabilities, and security. We have seen this with many of Microsoft’s “hybrid” offerings. In addition, they often enable those solutions with features from Azure that you can’t get with other traditional on-premises solutions. A great example of this is the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). When you run Azure Stack HCI, you can run containerized apps with AKS on Azure Stack HCI.
Azure Stack HCI hosts appear in the Azure portal as a native Azure resource beside other resources that exist in Azure. Note the following capabilities as part of the solution:
- You can manage and monitor multiple Azure HCI clusters in Azure
- You can manage extensions and use Azure Policies for your Azure HCI clusters
- You can apply Azure Policies to your Azure HCI clusters
- Use Azure-Arc to take advantage of other Azure services like Azure Backup, Microsoft Defender for Cloud, and Azure Site Recovery
- Azure Stack HCI makes use of existing Windows Server and Hyper-V skills to manage the solution
With Azure Stack HCI, you can manage the solution from your Windows Admin Center using the Cluster Manager extension.
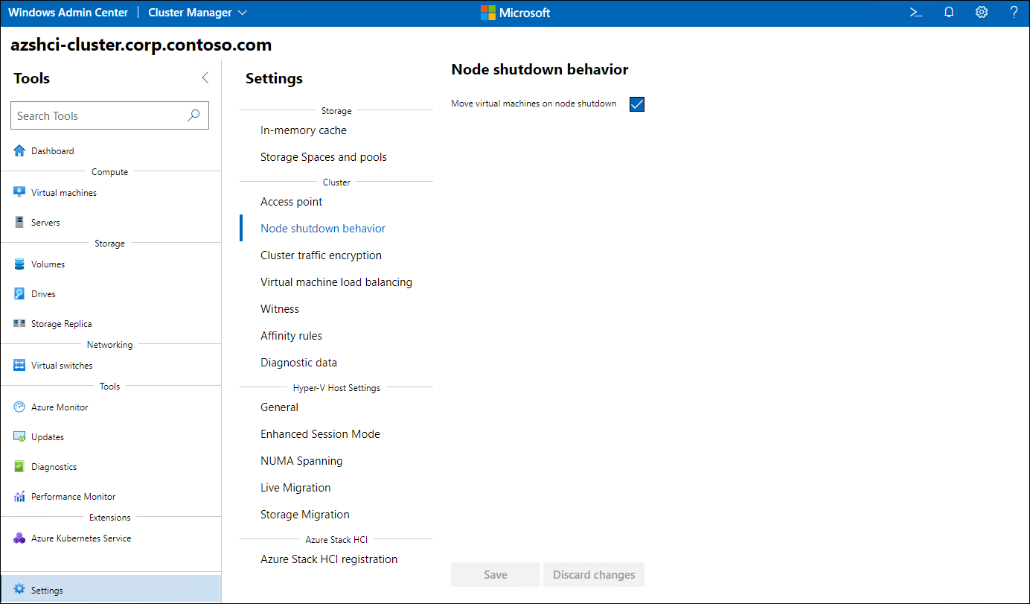 Managing Azure Stack HCI using Windows Admin Center
Managing Azure Stack HCI using Windows Admin Center
Azure Stack HCI general requirements
What are the requirements for Azure Stack HCI? These include:
- A standard Azure Stack HCI cluster requires a minimum of one server and a maximum of 16 servers
- Servers need to be of the same make and model, and processor architecture
- Servers need at least 32 GB of RAM
- Virtualization support is turned on in the BIOS
- It supports any boot device supported by Windows Server
- Direct attached SATA, SAS, NVMe, or persistent memory drives
- At least one network adapter is required to be present in the hosts
Azure Stack HCI vs. Windows Server with Hyper-V
When should you choose to use Azure Stack HCI vs. Windows Server? You should use Azure Stack HCI when you want to have the most modern approach to running workloads in your environment. It is the best approach for organizations that are already pivoting to the cloud for running their critical workloads and want to introduce a hybrid configuration.
Organizations that want to take advantage of running Azure services on-premises can also benefit from Azure Stack HCI since, using the Azure Stack HCI solution, they can run Azure-only services like Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
Azure Stack HCI is built only for running virtual workloads, including virtual machines and containers. However, if you need to run workloads or house resources directly on the server, Windows Server is the option you want to leverage. Windows Server is a multi-purpose operating system that provides direct connections to clients with appropriate CALs.
If you need to run traditional Windows Server roles like Active Directory Domain Services, File and Print services, DNS, DHCP, or IIS, Windows Server allows hosting these roles. Standard Windows Server installations are also the choice needed for bare-metal SQL server installs
Another note is that you can install Windows Server in an Azure Stack HCI virtual machine. So, you can also take advantage of the best of both worlds using both Azure Stack HCI server and Windows Server together.
Azure Stack HCI on a single server
With Azure Stack HCI, version 21H2, Microsoft has introduced the idea of running Azure Stack HCI on a single server configuration. Microsoft refers to this as a single-node cluster configuration. As a point for consideration, why would you want to use a cluster comprised of a single physical server?
It may seem like it defeats the purpose of a cluster design. Clusters, by design, are generally made up of more than one physical server. This design is for high availability. If you lose a single physical host, you still have a physical host on which to run workloads.
So, why run a single-node cluster configuration using Azure Stack HCI?
- The single-node cluster configuration with Azure Stack HCI allows customers to build out an Azure Stack HCI cluster with a single physical server, saving hardware costs.
- It allows gaining the capabilities afforded by being enabled by Azure, such as running Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
- A single-server solution allows the creation of an initial deployment of Azure Stack HCI and scaling the solution when needed
- You can use the single server Azure Stack HCI solution as a dev, test, or PoC environment for running Azure Stack HCI
- Managing Azure Stack HCI using Windows Admin Center includes creating new virtual machines. You can easily do this from Windows Admin Center.
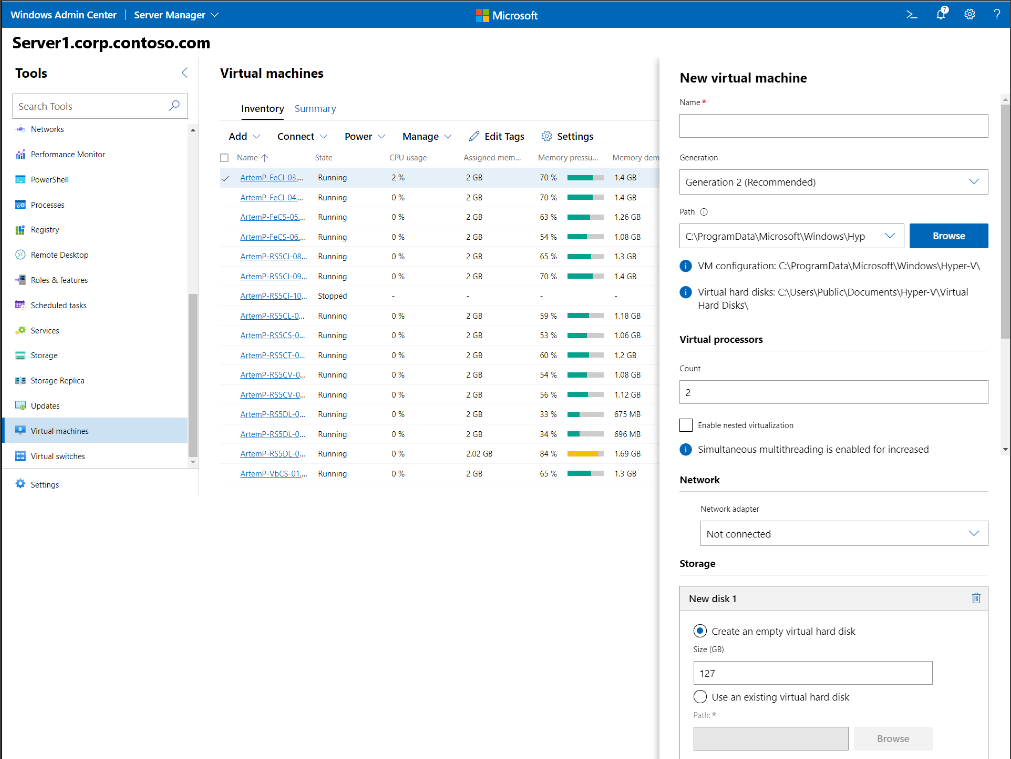 Creating a new virtual machine in Windows Admin Center
Creating a new virtual machine in Windows Admin Center
Azure Stack HCI single-node cluster limitations
While there are significant advantages to leveraging the Azure Stack HCI single-node cluster, there are also limitations.
- The Azure Stack HCI cluster cannot be created using a GUI such as Windows Admin Center. It can only be created using PowerShell
- You need to have drives of a single drive type, including NVMe or Solid-State SSDs
- You can’t create a stretched multi-site cluster using the Azure Stack HCI single-node cluster type
- You can use the Windows Server Server Manager GUI tool to install updates on an Azure Stack HCI single-node cluster
- You can also use PowerShell or SConfig to install updates
- Like any other single-node cluster configuration, you don’t have resiliency for workloads running in the cluster. Any downtime for the single-node host will result in downtime of the virtual machines running in the cluster.
- SBL cache is not supported in single-node Azure Stack HCI clusters
- You can’t pause a single-node cluster configuration with Windows Admin Center since it tries to drain the cluster host
- You must create a volume without “StorageTier” parameter in PowerShell. Only PowerShell can be used for this operation and not Windows Admin Center.
Wrapping up
The new Azure Stack HCI single-node cluster provides many interesting use cases that can make this option interesting for customers deploying Azure Stack HCI in the enterprise. It allows the easy creation of a supported HCI environment using the smallest number of nodes while still benefiting from Azure-enabled services, such as Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
Azure Stack HCI single-node clusters currently do have limitations such as no stretched clustering, the inability to configure and manage the solution using Windows Admin Center, and other quirks. However, Microsoft is continuing to develop and evolve the solution to function similarly to multi-node clusters using the management capabilities in Windows Admin Center. It will be interesting to see what the next few releases bring to the table regarding capabilities and improvements.
Learn more about Azure Stack HCI here: Azure Stack HCI solution overview – Azure Stack HCI | Microsoft Learn