Back-ups, in simple terms, are copies of your data that are usually stored in a different location from your production environment. Backups ensure data redundancy and therefore tend to be a requirement in every IT environment. Doing backups is an important preventative measure against possible data loss or corruption that allows you to restore lost information. There is no one-size-fits-all here, so let’s take a look at some of the different backup types.
Types of Backups
There are generally three main types or strategies of back-ups regardless of the software used:
Full backups: Backups that create image files of the entire dataset every time the backup is run.
Incremental backups: Backups of the changes to a given data set since the last backup was made (whether full or incremental).
Differential backups: Backups of the changes to a given data set since the last full backup was made.
Full Backup
How Does a Full Backup Work?
As the name suggests, a full backup of a data set will copy the original set plus the new changes every time the backup is run. This is the most straightforward backup process since it consists of copying the entire data block regardless of whether changes were made to some or all of the components contained within. It requires the most amount of storage and is therefore suitable for enterprises without a large amount of data to back up. Restoration is very fast. 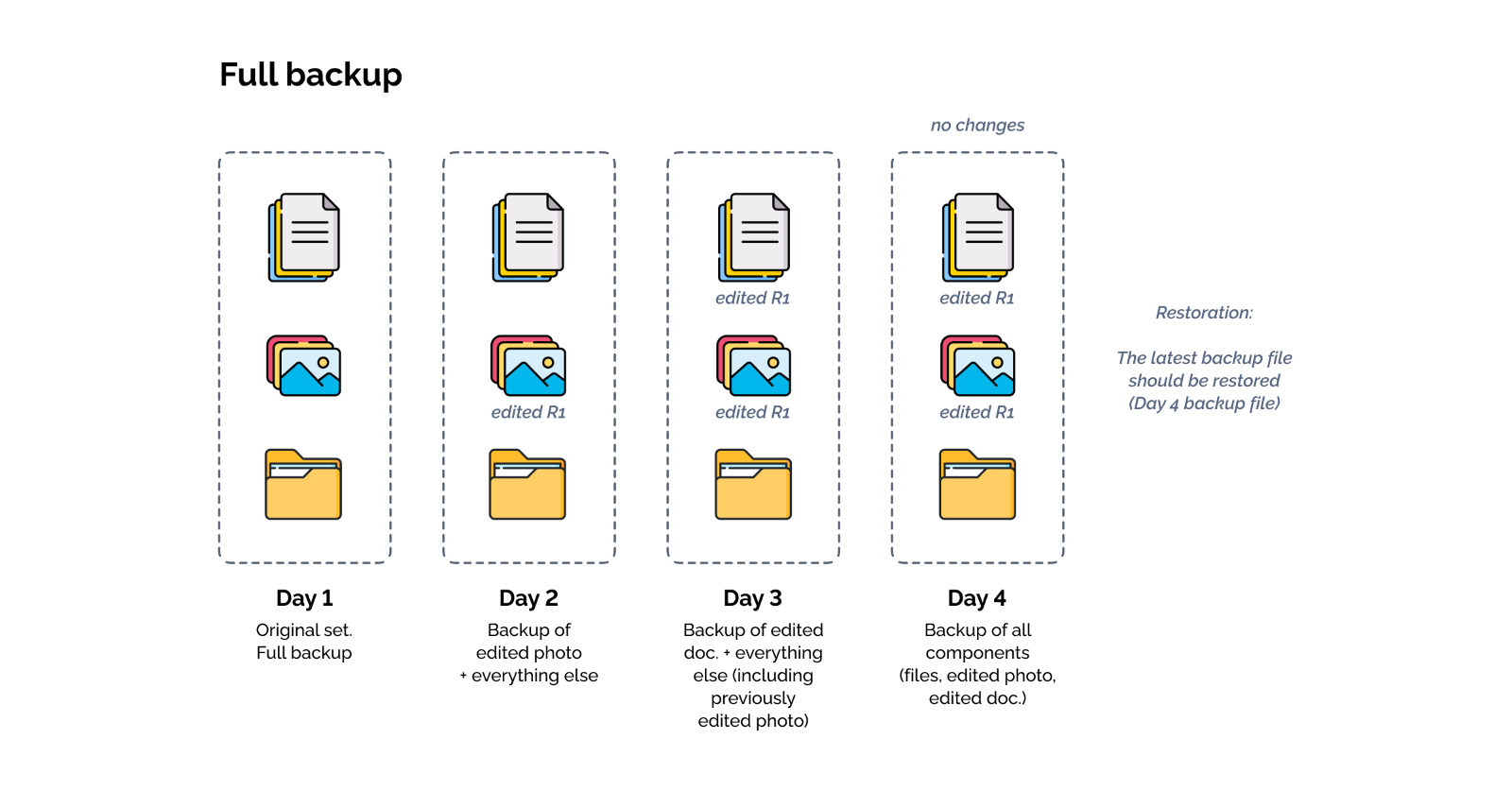
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Quick restoration | Requires a large amount of storage |
| Only the latest backup version should be restored | Backups take a long time |
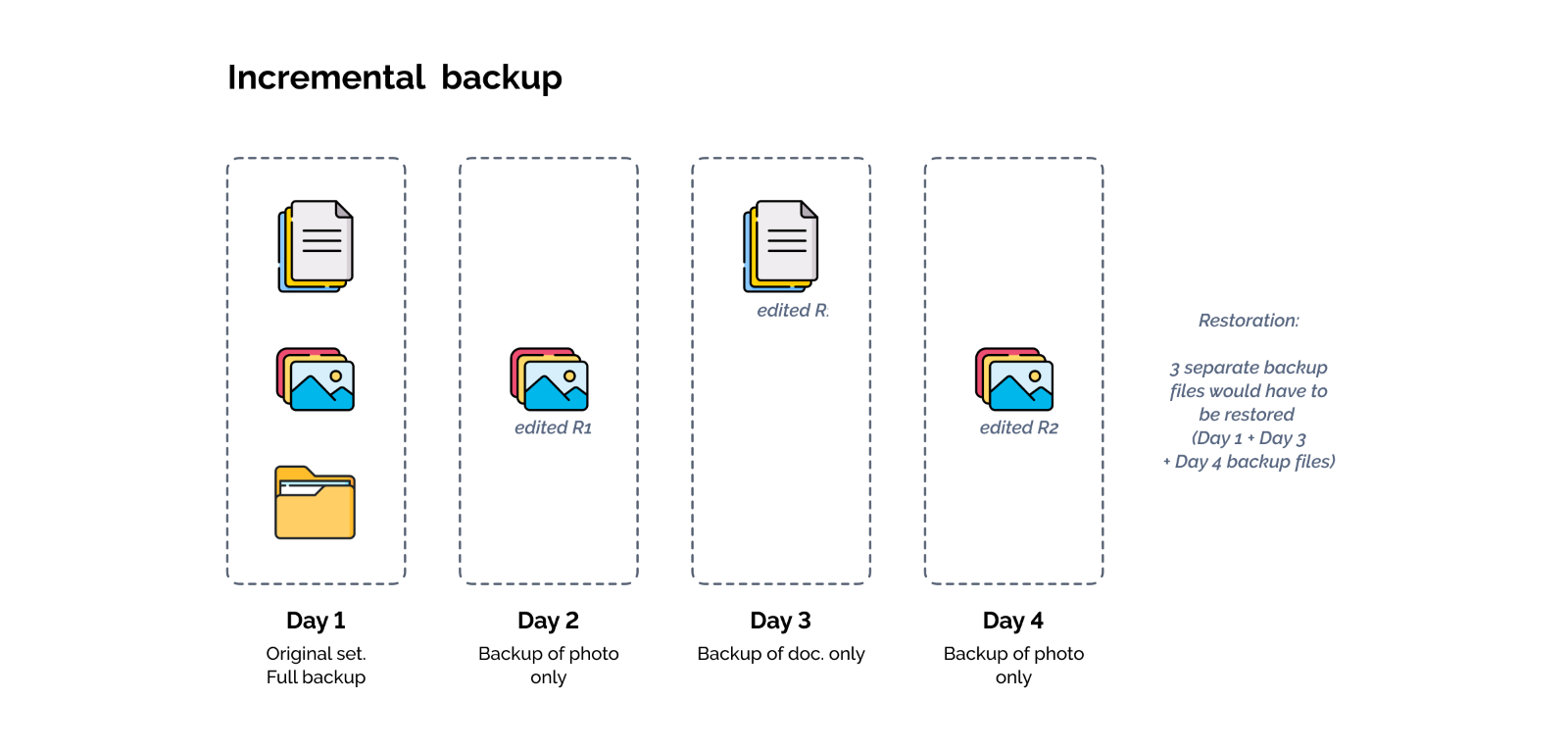
Incremental Backup
How Does an Incremental Backup Work?
Incremental backups work by backing up the changes made to the data since the previous backup. This process takes up less storage and avoids data duplication. Restoration with incremental backups, however, is slower and may be tricky since you would need to restore several files and do so in consecutive order so that you may get the full set of data in the end.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Takes up less storage | Slow restoration |
| Very fast backups | Risk of incomplete data if one of the increments in the series is lost or corrupted |
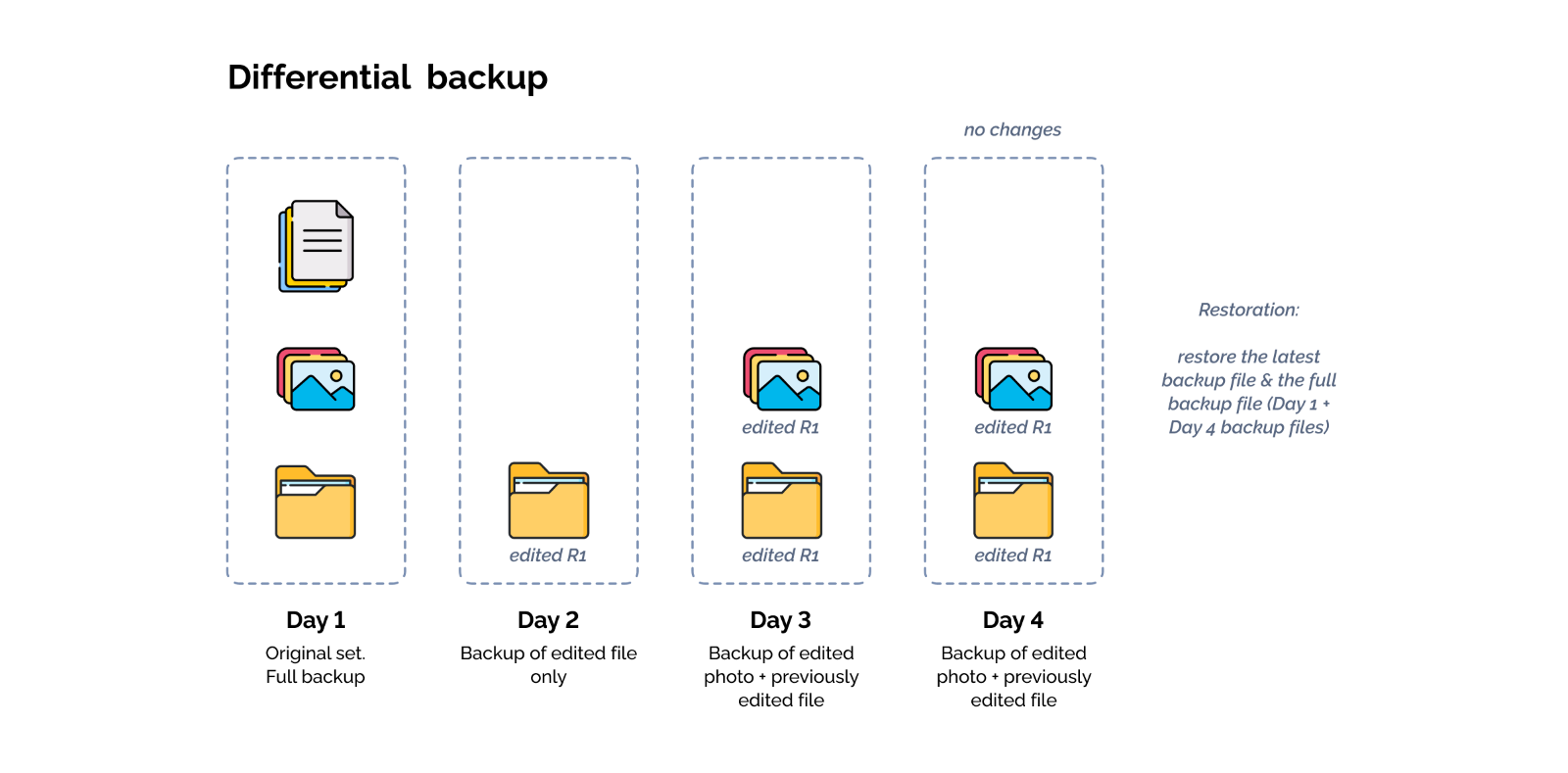
Differential Backup
How Does a Differential Backup Work?
A differential backup is the cumulative result of incremental backups since the last full backup. This is the middle ground between full and incremental backups which makes for a compromise regarding the speed of backups and ease of restoration. In order to restore a backup, you would need to restore the last differential backup plus the original full backup.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Fast backups | Slower restoration than with full backups |
| Takes up less storage than full backups but more than incremental backups | May be heavy on the network bandwidth |
Mirror Backup
Mirror backups function less like backups and more like replicas of everything that is on a given environment – that includes compute resources. The purpose of a mirror backup is to reflect exactly what is going on in the source environment/data set and is therefore the fastest recovery option. However, since this is not quite a backup in the traditional sense, if a file were to be mistakenly deleted on the source datastore, for example, that file would likewise be impossible to recover on the mirror backup.
How to Choose the Right Type of Backup
Ultimately, the right backup strategy varies from enterprise to enterprise. It all depends on the amount of data that requires backup, the available funds (or lack thereof) to provision large amounts of storage and/or manage the backup infrastructure. A no less important consideration is network bandwidth and RTO requirements.
Most companies these days use a combination of backup strategies, opting for a full backup as a starting point with alternating full and incremental/differential backups. The larger the data set, the less likely a full backup strategy is to be used on a day-to-day basis. The more time-sensitive RTOs, the more likely that incremental backups would be most suitable, etc. Eventually, the business needs of an enterprise may evolve and so will the backup strategy along with it.