Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) is a solution that provides additional layers of security on user devices, such as Windows 10. MDE includes an EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response), automated investigation and response, software inventory, and a lot more tools. In this topic, I’d like to talk about web content filtering because, in this period of COVID and remote office, a lot of customers want to filter web content even if the user is not connected to the information system through VPN for example.
MDE is able to filter web content from a blacklist provided by Microsoft but you can also filter URLs / domains, certificates, and IP addresses. In this topic, I’ll show how to use a blacklist and how to block an URL / Domain.
Enable web content filtering feature
By default, the web content filtering feature is not enabled. So, first, we have to enable this feature. To connect to MDE, navigate to https://security.microsoft.com. Then click on Settings and Endpoints.
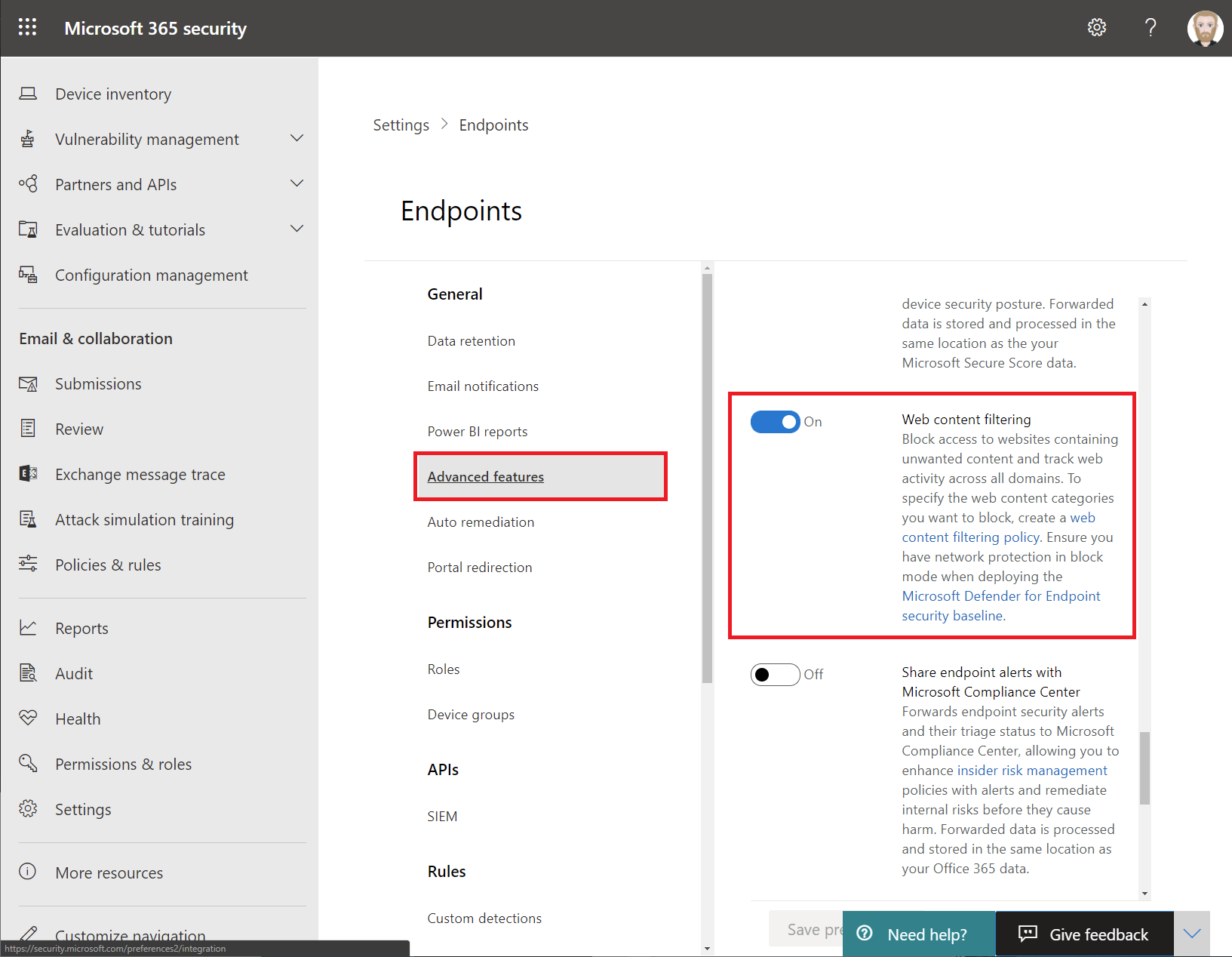
Next, select Advanced features and check if web content filtering is enabled.
Add a device group
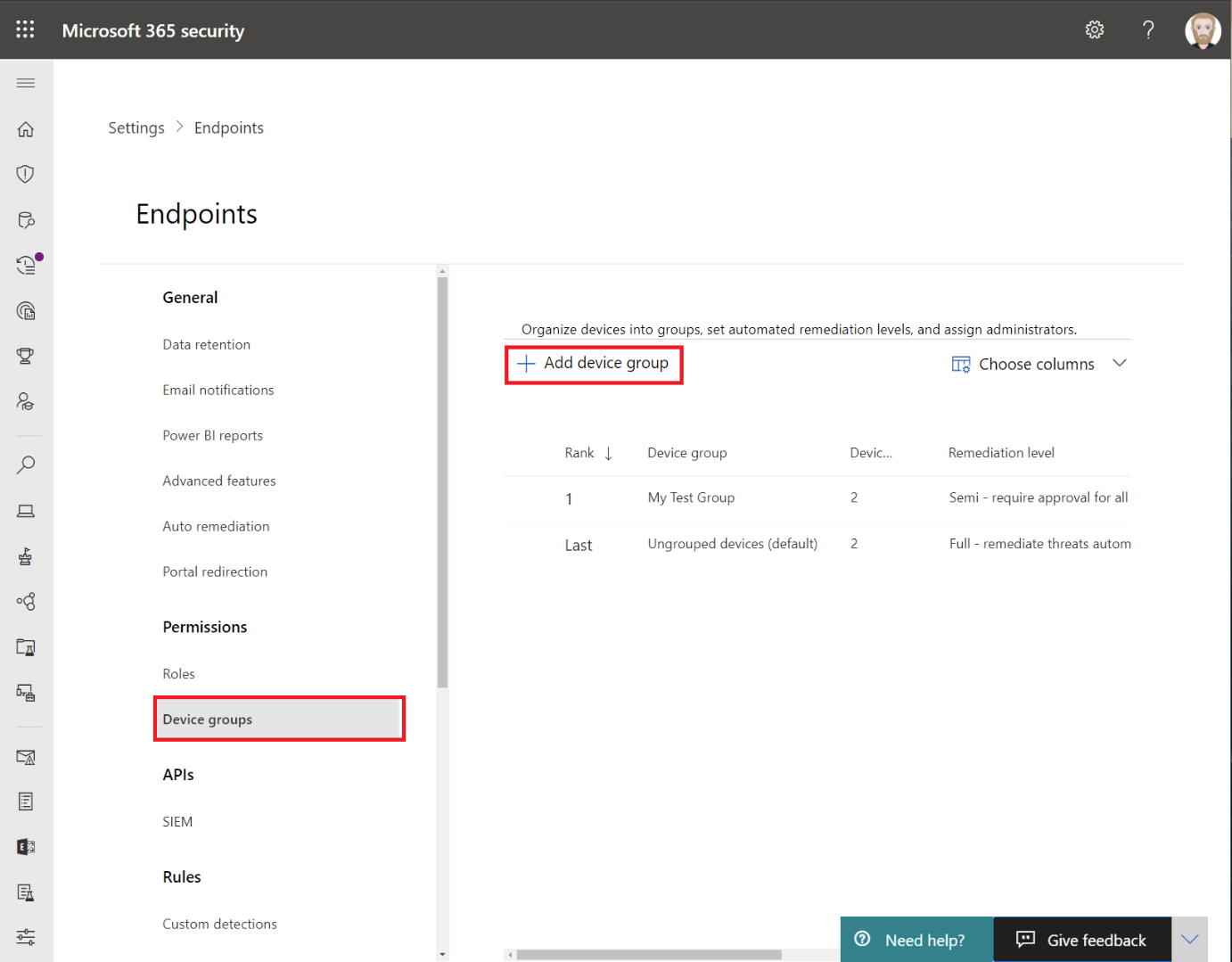
To target specific devices for web content filtering, you can create a device group. To do that, select Device groups and click on Add device group.
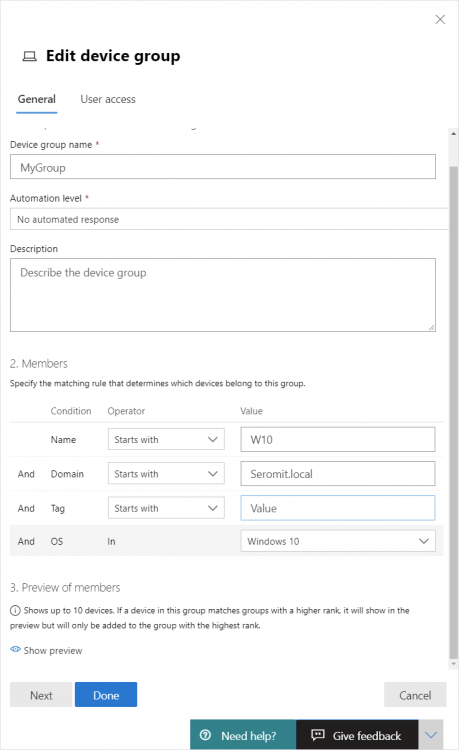
Then provide a device group and an automation level (this setting regards automated investigation and remediation to automate remediation actions). Specify also condition value to fill automatically the device group in the function of the device name, domain tag and/or OS.
Filter web content from Microsoft blacklist
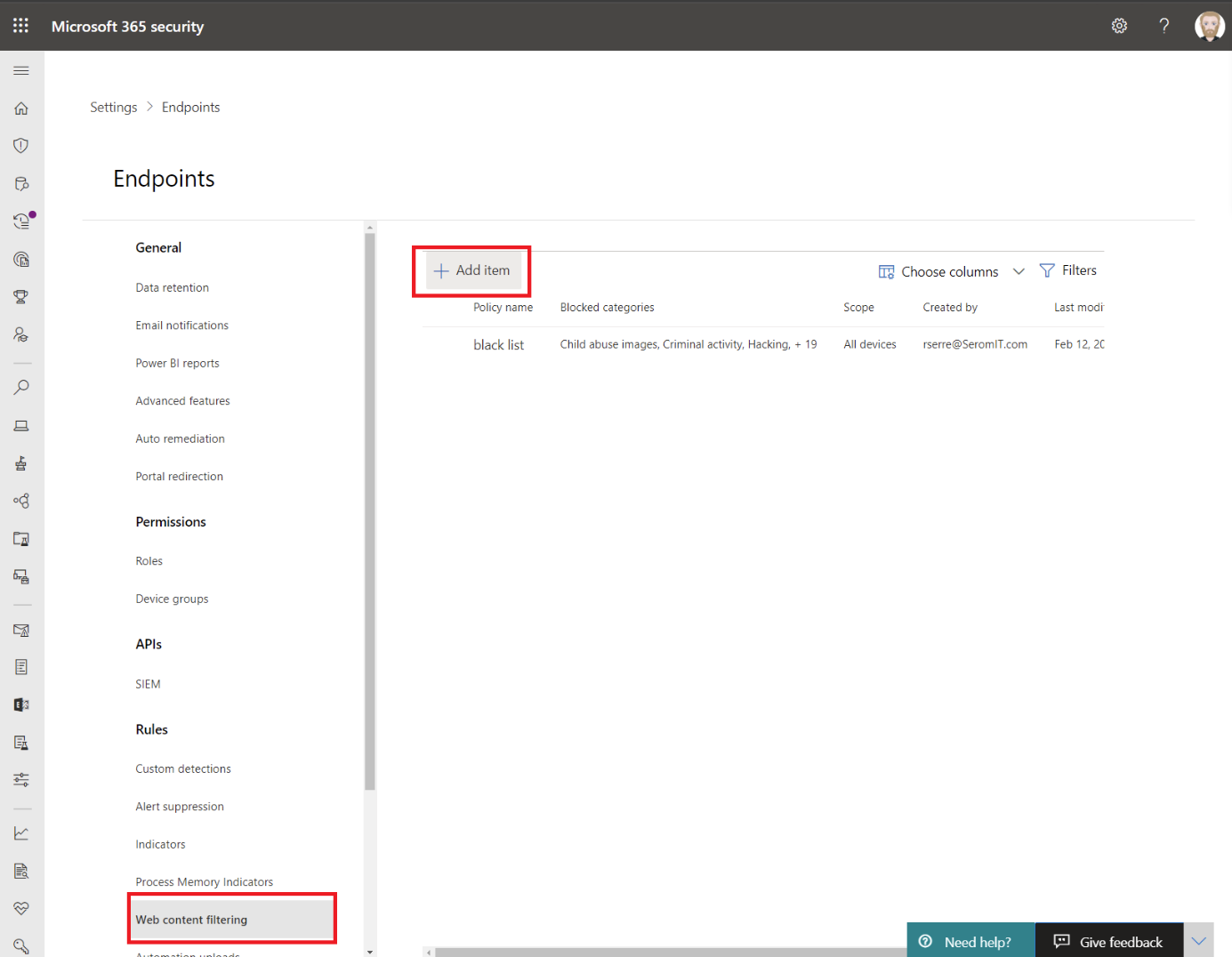
Navigate to Web content filtering and click on Add item.
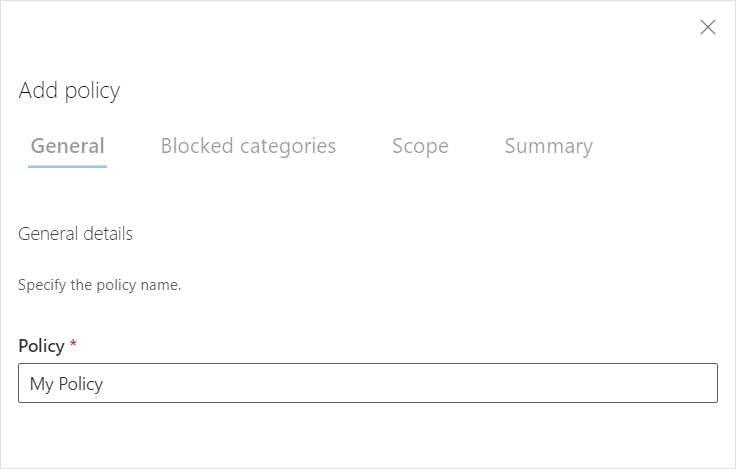
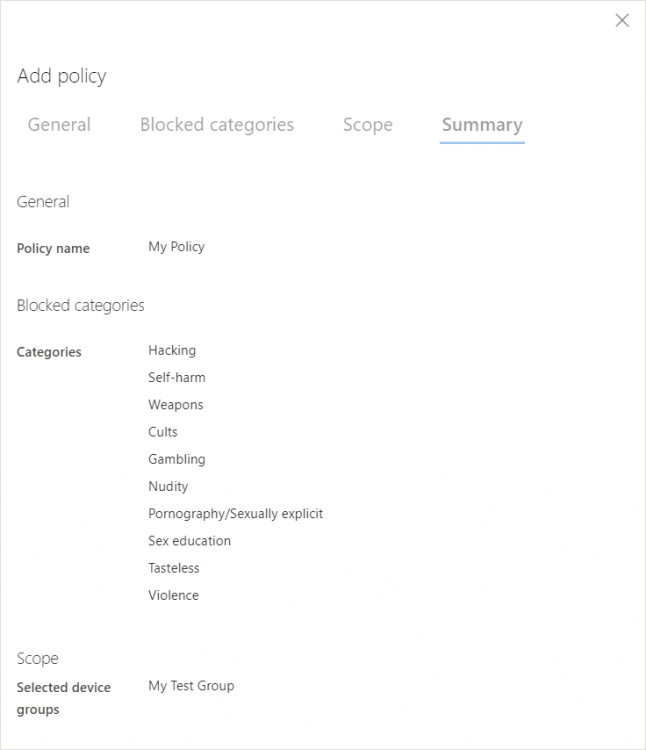
Provide a name for the policy:
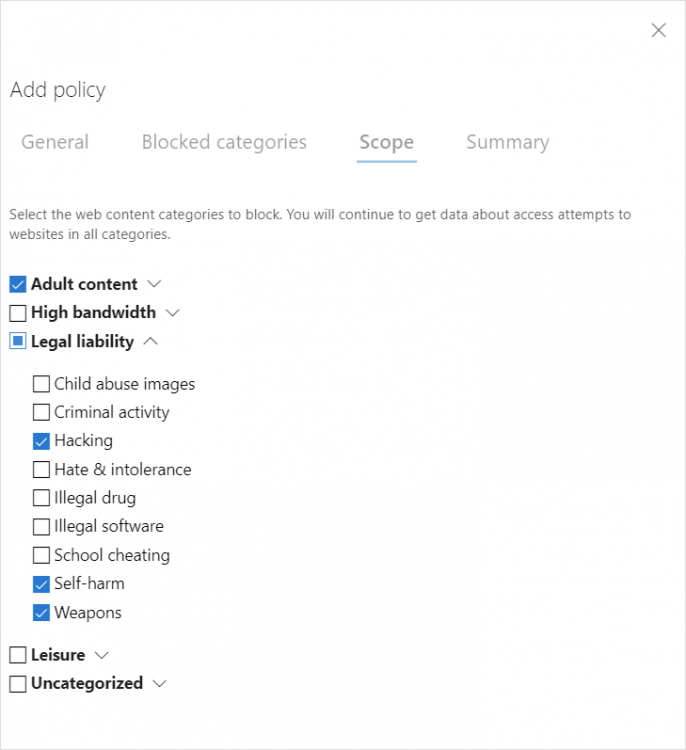
Next, select the categories of the website you want to block. You can block a whole category or subcategories.
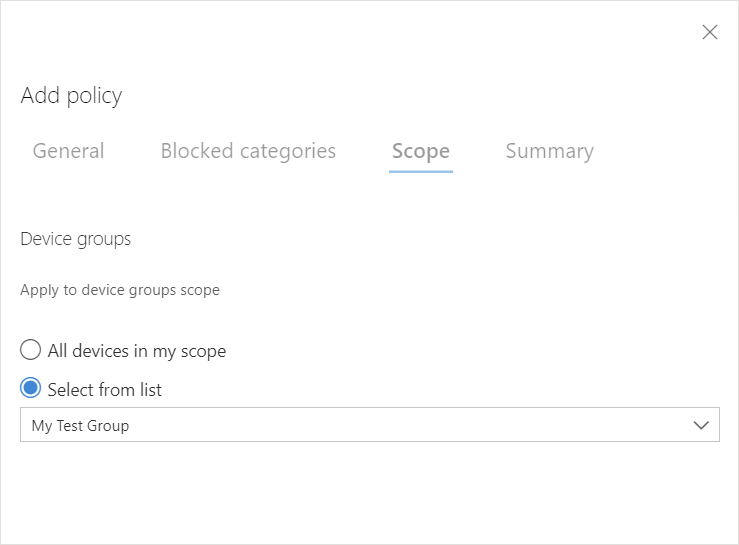
Next, choose the device group you have created previously.
Finally, click on Save to create the policy.
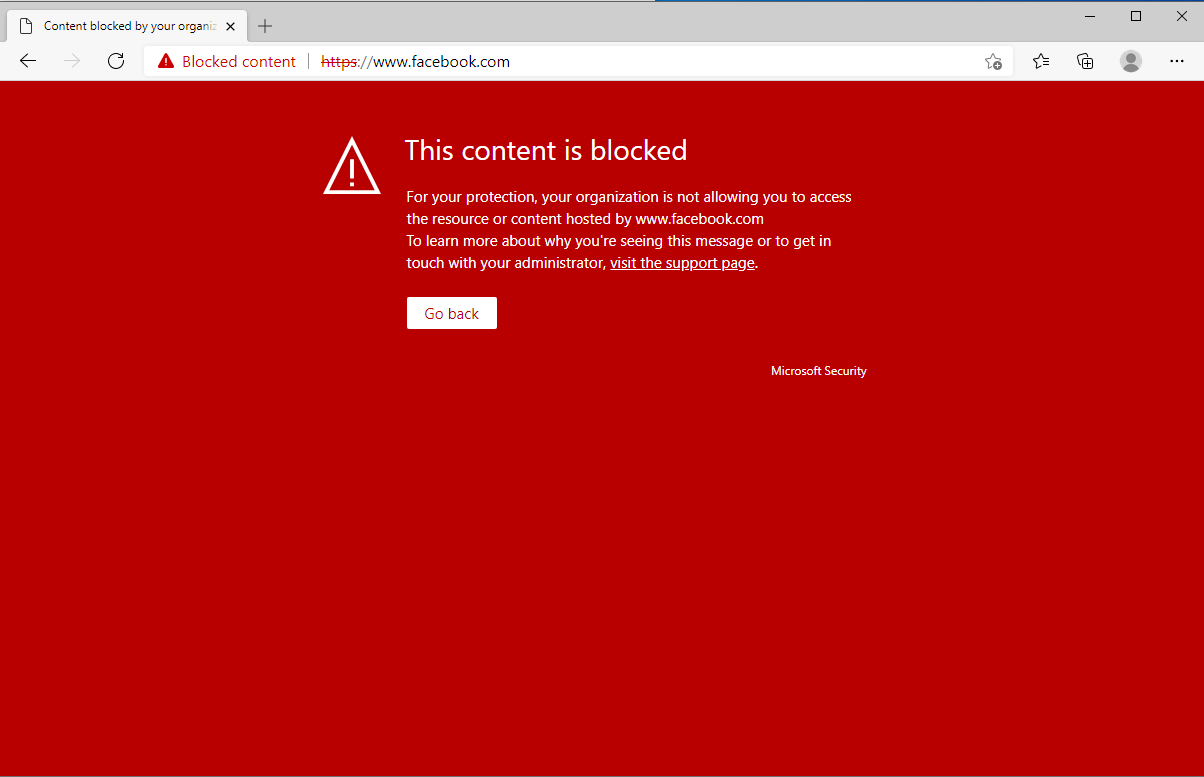
Now I open a web browser from a Windows 10 device, and I try to navigate to Facebook. As you can see, the content is blocked:
How to block a custom URL
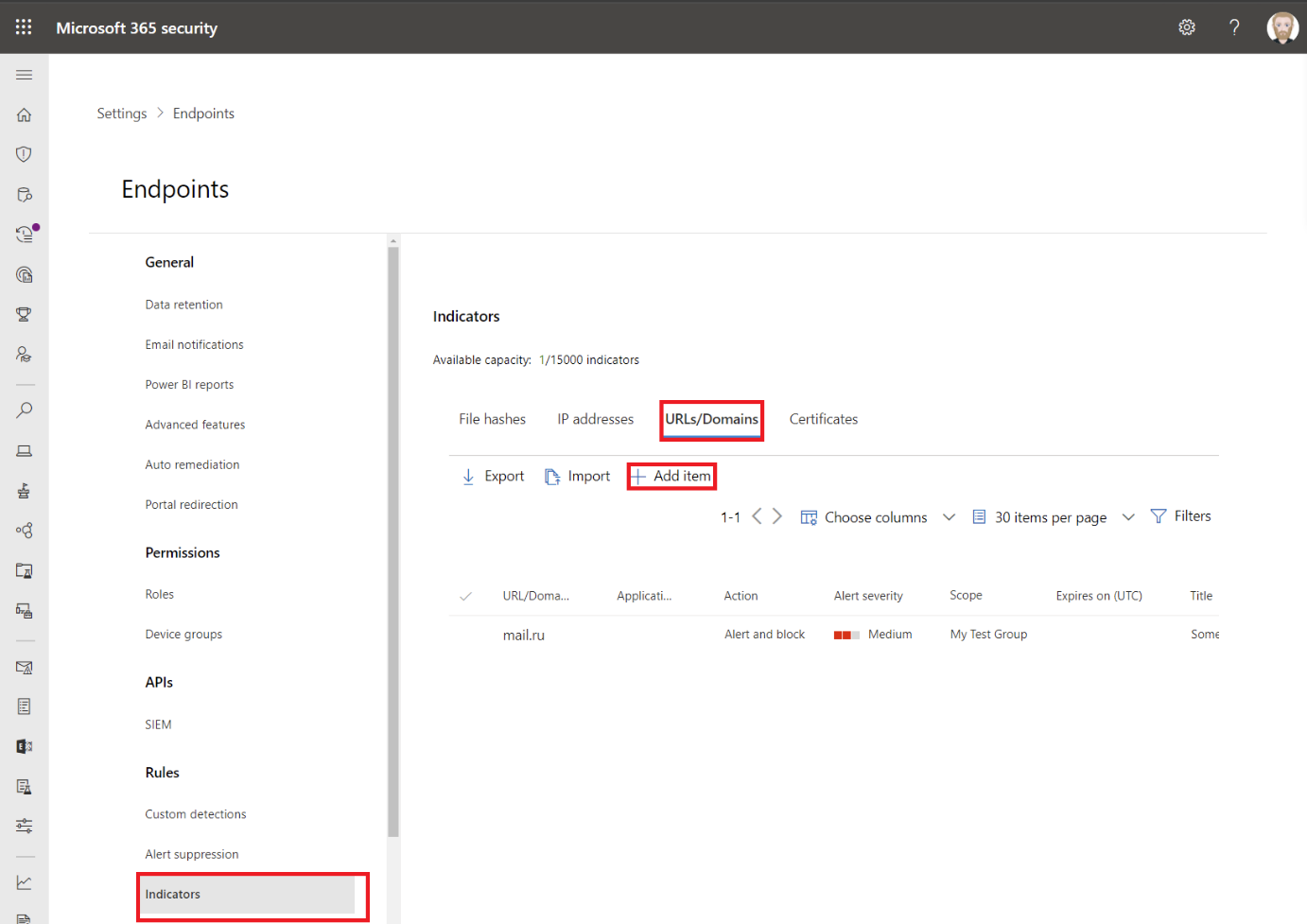
Go back to MDE and this time navigate to Indicators and URLs / Domains. Then click on Add Item.
N.B: You can import a list from a CSV file.
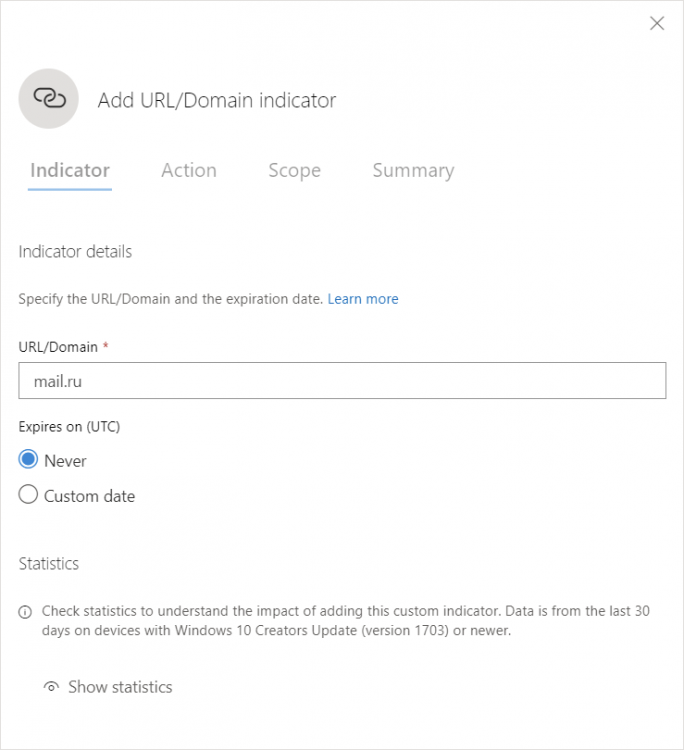
Next, specify the URL you want to block and the expiration date if you want one:
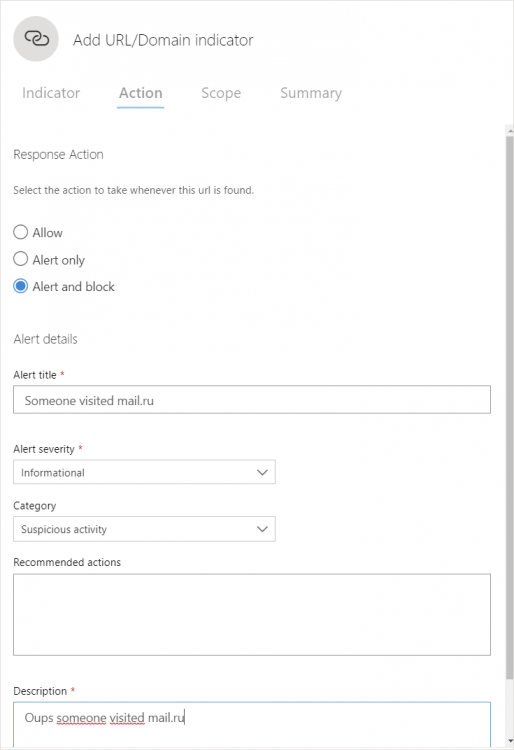
Then choose a response action. To block the URL, I chose Alert and Block. Specify an alert title, severity, and a description.
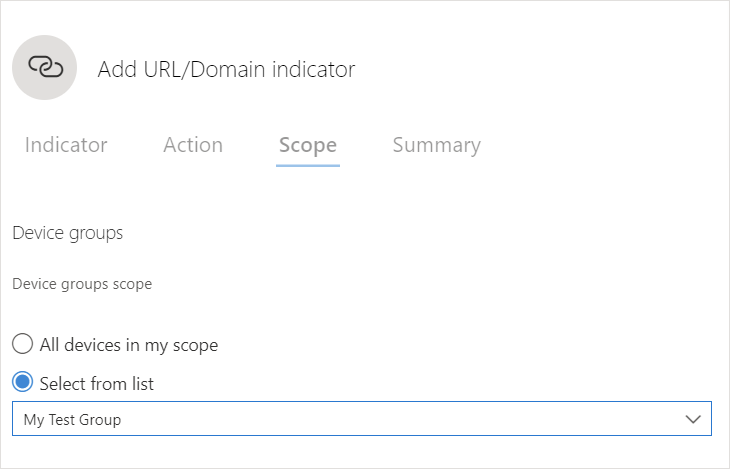
Choose the device group you have created:
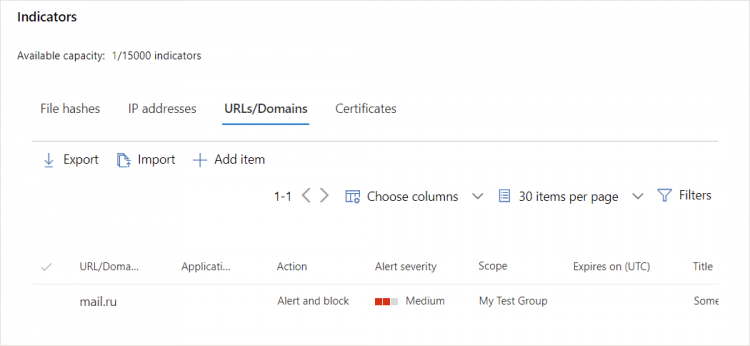
Add the end of the process, click on create. Now you have filtered an URL:
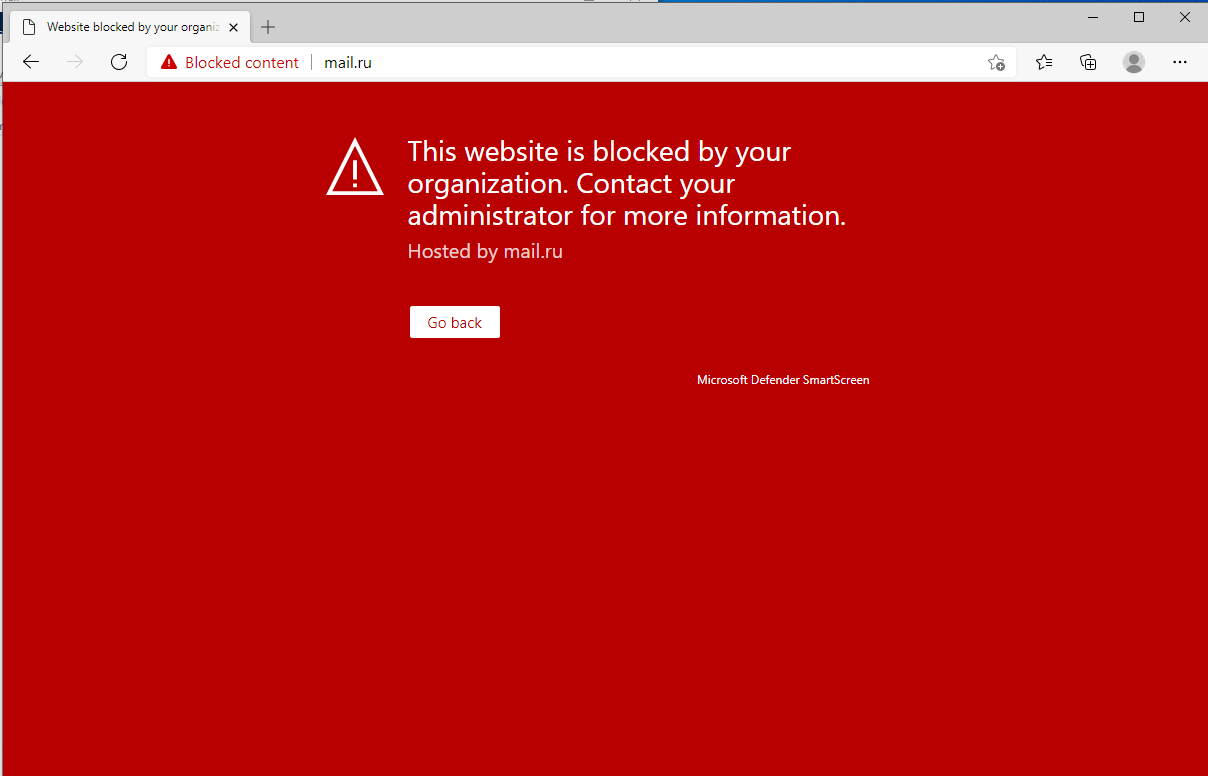
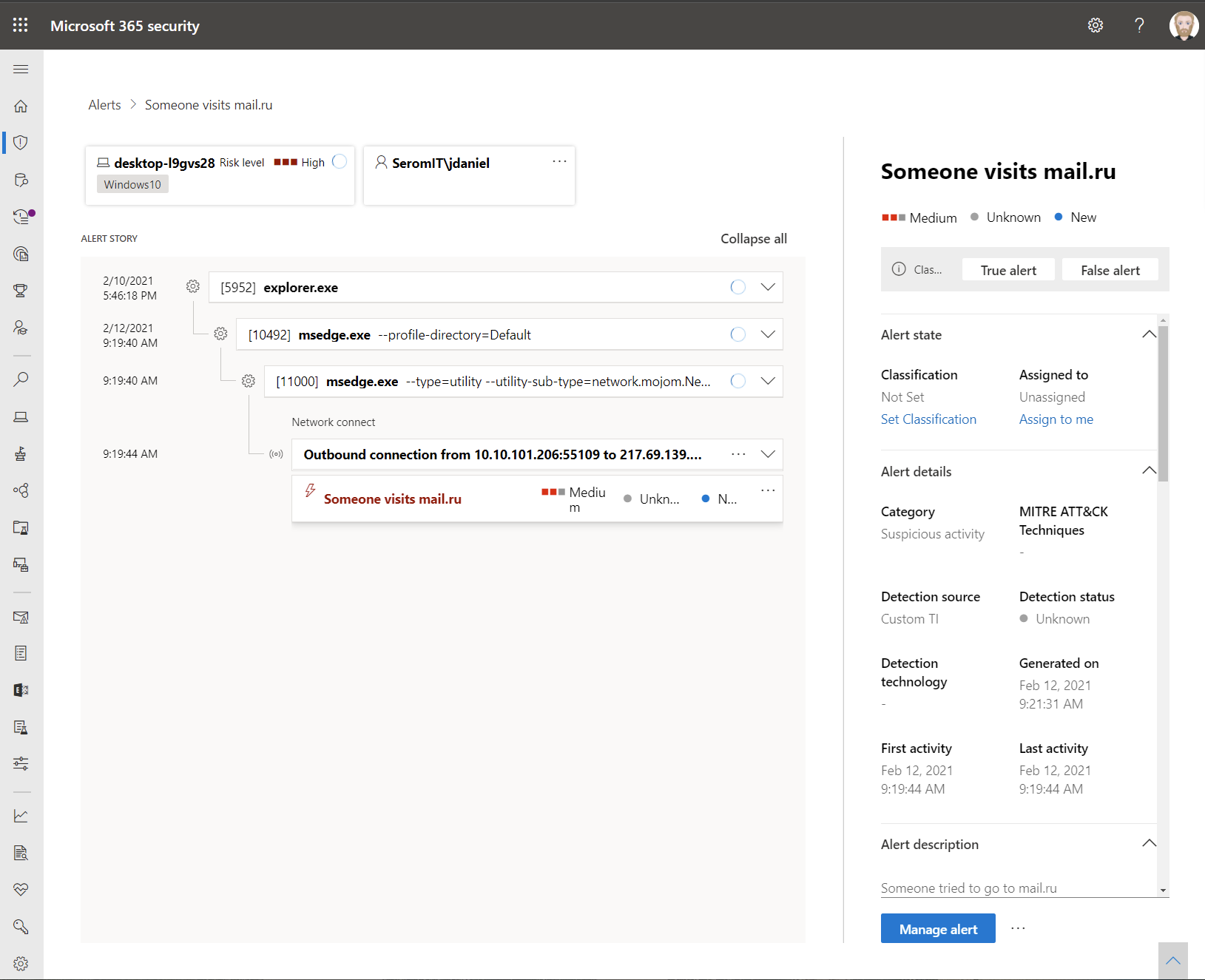
Open again the web browser on the Windows 10 device and navigate to your URL:
If you look at MDE, an alert is raised:
Conclusion
As you have seen in this topic, you can do web content filtering without configuring proxy settings in a web browser. You don’t need to configure GPO or scripts to manage these settings anymore. It’s a perfect solution to filter web content even if your user is at home and not connected to the company.