In this article we are going to install and setup a Database management tool which is DBeaver. DBeaver is available for the cross platforms to support multiple databases including MySQL, Postgresql and GreenPlum. DBeaver can be used as an alternative of MySQL-Workbench and PGAdmin. It has a user-friendly interface that makes it more useful for its new users. Using DBeaver, you can create local databases and also configure the maximum result size to avoid session hanging issues in case the query results take time to process big queries.
DBeaver comes with a community edition which is free to use as well as with an enterprise edition that supports NoSQL Databases. We will be using its latest available community edition on a Linux CentOS 7 Desktop and LinuxMint Desktop.
Prerequisites:
The prerequisite for this article is to have a Linux System running with Linux based GUI system with user having sudo rights.
Login to your system and update with the latest available security updates using yum command as below.
For RHEL/CentOS:
$ sudo yum update -yFor Ubuntu/LinuxMint:
$ sudo apt-get update -yDownloading DBeaver Community:
You can get the DBeaver Community edition download installer from their official web link https://dbeaver.io/download/ where you can choose the installer for your system.
Let’s get the RPM package for your RHEL/CentOS based system and DEBIAN in case you are using Ubuntu or LinuxMint.
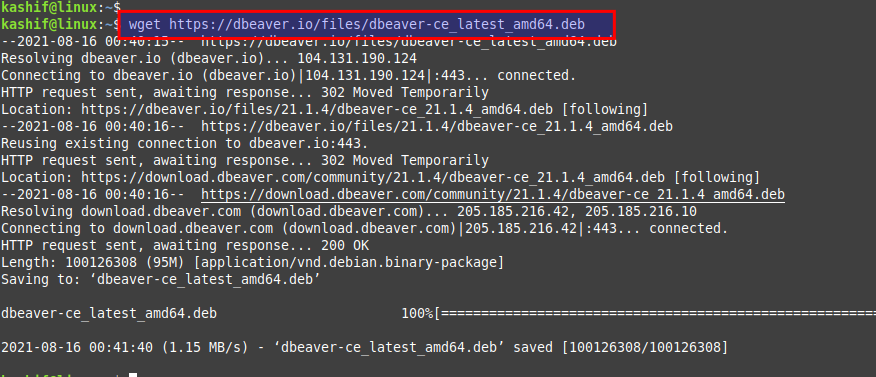
Get it downloaded on your system and then upload on the server you have to make its setup or simply use the ‘wget’ command as below on your system.
$ wget https://dbeaver.io/files/dbeaver-ce-latest-stable.x86_64.rpmOn Ubuntu/LinuxMint:
$ wget https://dbeaver.io/files/dbeaver-ce_latest_amd64.debInstalling DBeaver in Linux:
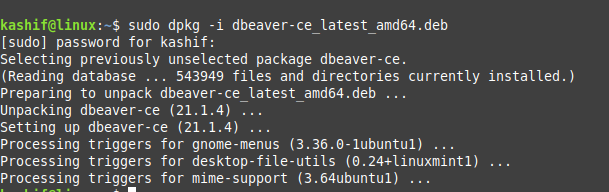
Once you have got your Dbeaver package uploaded, let install it using the command below.
On RHEL/CentOS:
$ sudo rpm -ivh dbeaver-ce-21.1.4-stable.x86_64.rpmOn Debian/LinuxMint:
$ sudo dpkg -i dbeaver-ce_latest_amd64.debUsing DBeaver in Linux:
Now, as we have installed DBeaver, let’s open it from the menu or search it in the application finder.
You will be prompted with an option to create the sample database or start with a new connection.
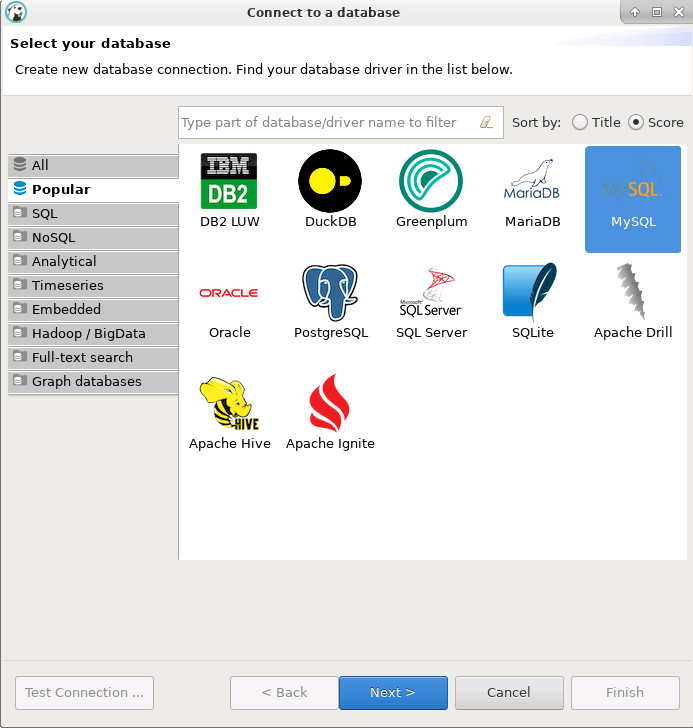
Point to the Database tab and select to create a new connection by choosing your desired Database as shown below.
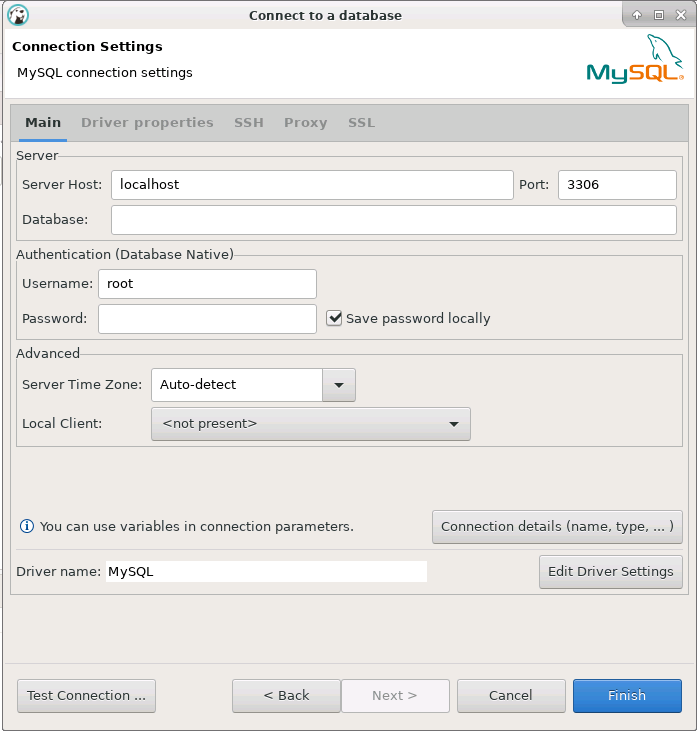
Moving next to the database connection settings, give the details of your database server you want to connect with and click to finish.
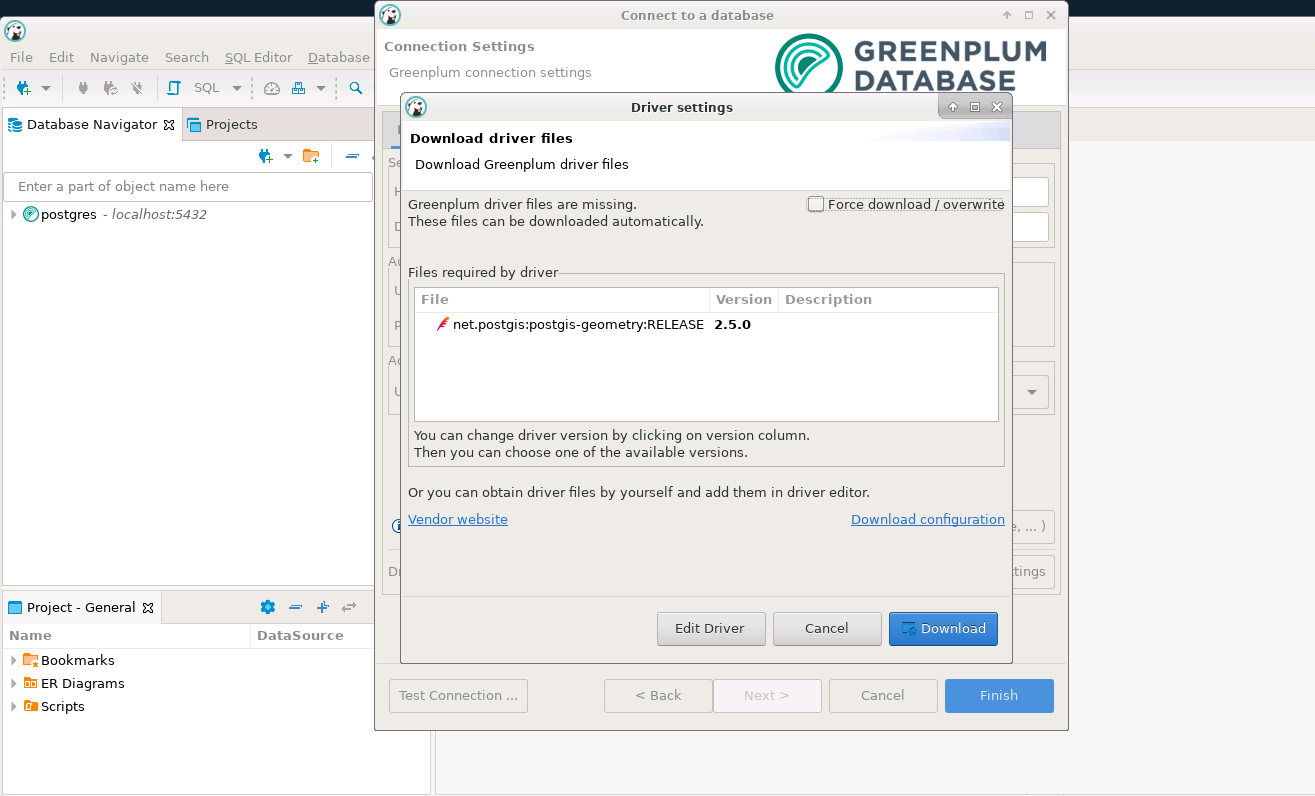
As we have mentioned earlier, DBeaver supports multiple ranges of database engines, so in some cases, you may need to upload its jar files.
Just like in the image below, you can see that while loading the Greenplum DB it asks to load the required drivers that you can directly download.
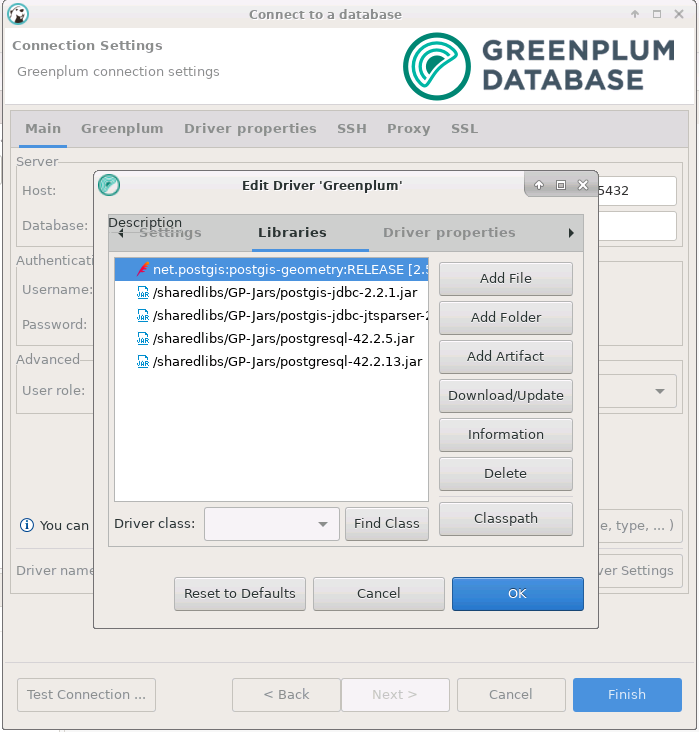
In case if you don’t have internet access available on your system, you can take the offline jars required for your database and upload using the DBeaver Driver Manager.
Here, when you have successfully uploaded the jars, you can delete the old one which is not required for your db connection.
Setting JVM Parameters for DBeaver:
In case you have multiple databases and high workloads that may impact the performance of dbeaver. In that case you can also tweak its JVM parameters by editing the file below with its XMS and XMX values.
$ sudo vim /usr/share/dbeaver/dbeaver.ini -startup plugins/org.eclipse.equinox.launcher_1.6.100.v20201223-0822.jar --launcher.library plugins/org.eclipse.equinox.launcher.gtk.linux.x86_64_1.2.100.v20210209-1541 -vmargs -XX:+IgnoreUnrecognizedVMOptions --add-modules=ALL-SYSTEM -Dosgi.requiredJavaVersion=11-Xms512m -Xmx4096mConclusion:
At the end of this article, you should be familiar with the DBeaver, its installation setup on Linux and use of making DB Connections of your choice. It has many features that many other database managers don’t have like its support for multiple databases, OpenSource edition, SQL query execution and SSH tunneling etc. Hope you have found this article much helpful while working on DBeaver or while searching for a best Database manager solution.