If you’re maintaining VMware vSphere infrastructure, one of the tasks you have, is certainly patching. In this post we’ll show you how to manually patch VMware vCenter Server Appliance. One of the best practices by VMware is to keep your environment up-to date.
Installing security patches in any environment is crucial. The days when you could leave your environment unpatched for months/years, are gone.
The risk of security breach explored by hackers are more and more important, that’s why keeping your environment up to date is one of the key factors today.
If you’re running part of your infrastructure disconnected from the Internet, you’ll most likely need to install patches offline. It means that you must download the patches to some workstation/laptop and put them into a portable USB drive/key, and then carry them onto the offline system.
Usually, the patching process is simple if you have internet access, however when you don’t, you must do that manually.
Another reasons might also be that VMware online repo is broken or, as it has already happened, the path to the online repo is simply wrong. (Note that this can be corrected manually by entering the correct path when you’re in the WAMI management).
We’ll show two ways of manual patching VMware VCSA. One easy from the UI and one from the command line.
We’ll be using the appliance patch ISO as I’m assuming that you’re running VMware vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) and not the vCenter on Windows.
The Steps:
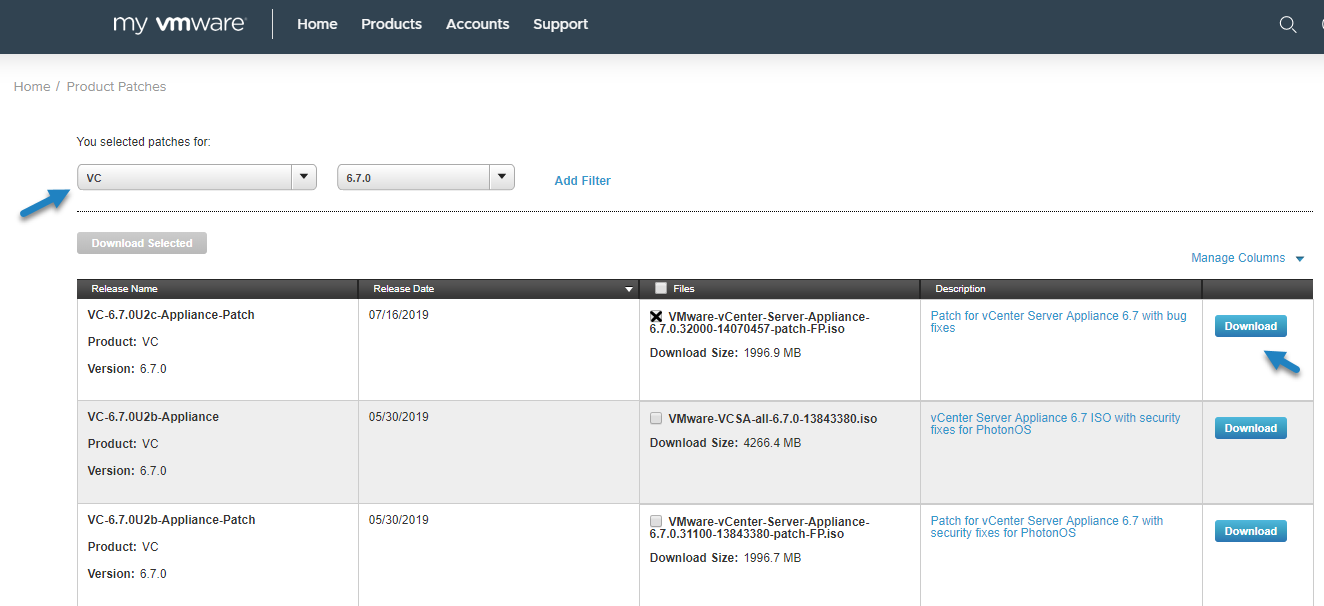
First, download the ISO patch from VMware Patch Download center. You’ll find it at this address: https://my.vmware.com/group/vmware/patch
Note: login using your “My VMware” credentials.
You’ll need to select “VC” and then hit the Search Button. You’ll get a list of patches where the latest one is the top one. Download only this as it’s always cumulative. It means that previous patches are included.
Download the latest VCSA ISO Patch
Once done, put it on a removable media if your system is completely disconnected from other networks in your environment, or if you can access the remote system via LAN, store it at
In our case, the name of the file is VC-6.7.0U2c-Appliance-Patch.iso and it is usually saying “appliance patch” in the wording, but you might be already on another version while reading this article.
Once you have that file, upload it to a local or shared datastore.
Manual Patching of VCSA via User interface (UI)
This guide is simple, and I believe most admins know their way around, but new people might not.
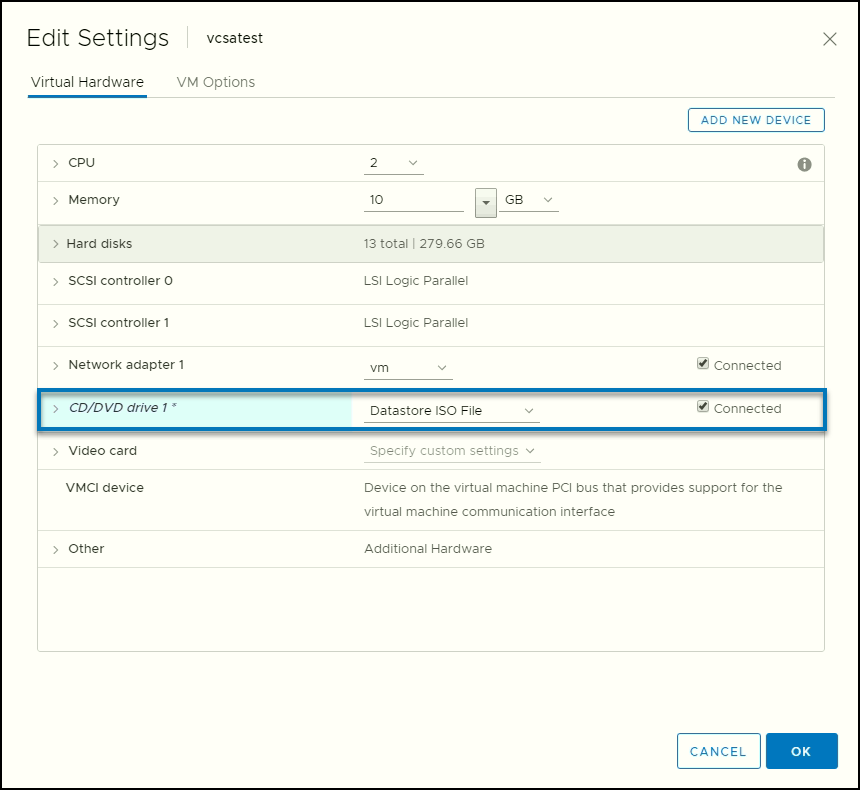
First, connect to your vCenter server or ESXi and select your VCSA Virtual Machine (VM) and go and edit its settings.
On the CD-ROM settings, attach the ISO file you just uploaded to the datastore.
Attach the ISO to the Appliance
Connect to the VCSA via IP or Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) followed by a port number 5480 which is a special management port for VCSA.
https://IP_of_VCSA:5480
Backup your VCSA by your usual backup software and create also a file-level backup from within a VAMI. VMware Appliance Management Interface (VAMI) which is accessed through Port 5480.
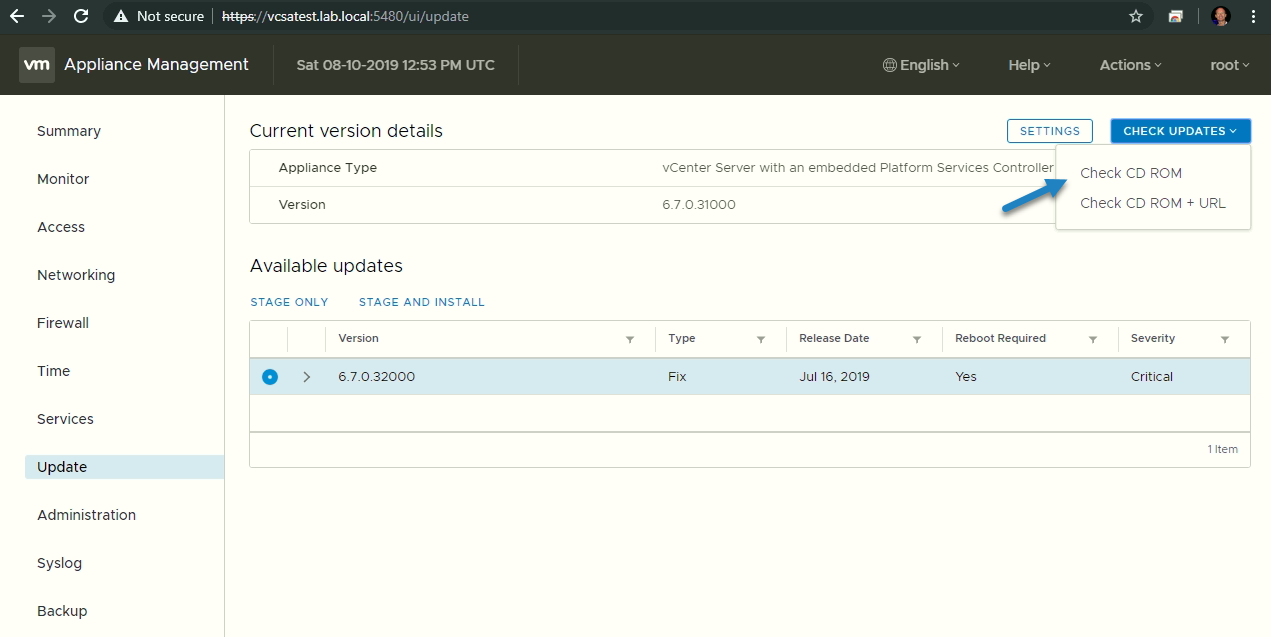
After this step, go to the Update menu and make sure to select the Check CD ROM from the button drop-down.
Check CD-ROM for updates
As the VCSA does not have a way to connect to the Internet (isolated system), the only way is to “feed” the patch is via CD-ROM.
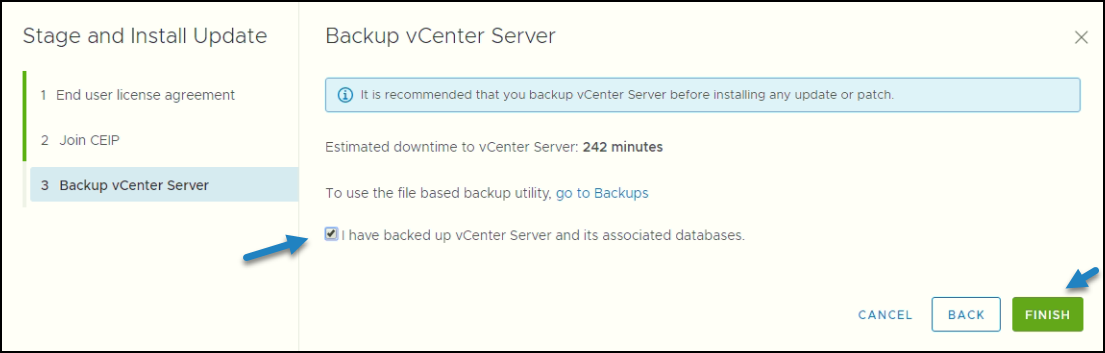
From there simply follow the assistant after clicking the Stage and Install button. A new wizard will appear asking first to accept EULA and making sure that you have made a backup of your VCSA.
Proceed with the patching of VCSA
Manual Patching of VCSA via Command Line Interface (CLI)
In case the UI has problems (one never knows) there is also a CLI way to patch VMware VCSA. To proceed, follow those steps.
Once again, you’ll need to attach the ISO file you have downloaded, to the VCSA VM, the same as in the first procedure.
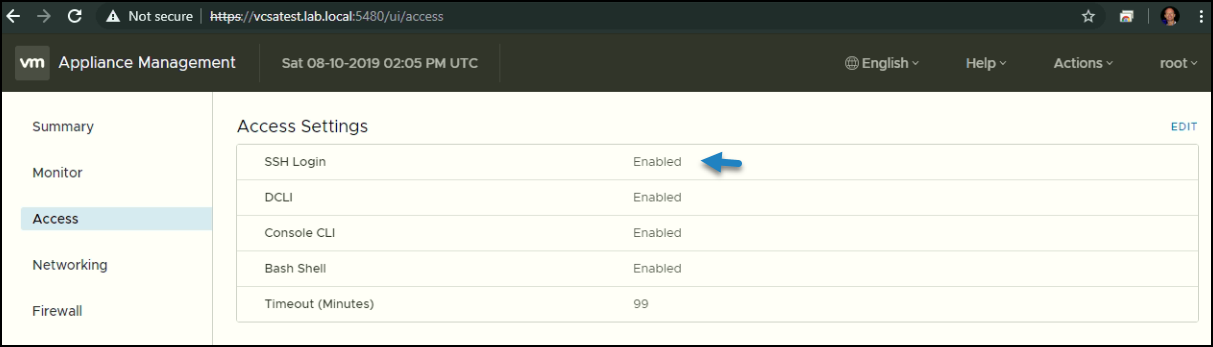
Then connect to the appliance via SSH (Make sure to enable SSH access). To enable SSH, just connect to the administration UI and go to Access.
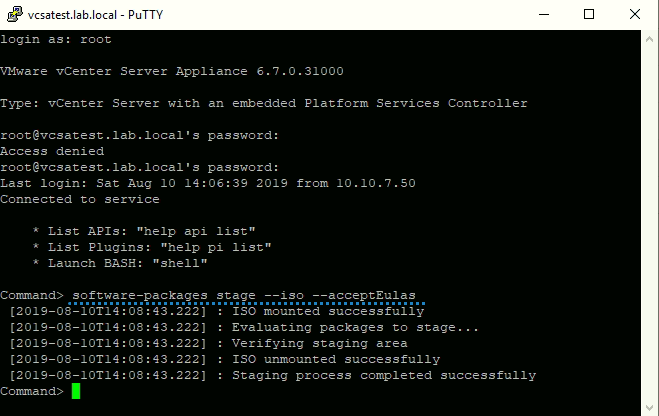
To stage the update packages, enter this command:
software-packages stage –iso –acceptEulasHere is the lab example of Putty (free SSH client) window where we are entering this command:
Enter this command to stage the packages
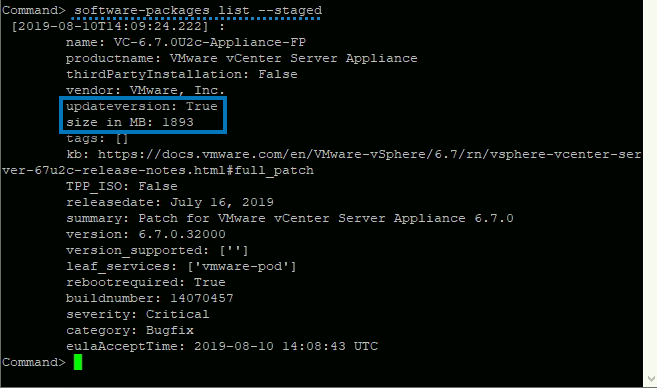
And then we can easily list the staged packages we have with the ISO including the version.
List staged packages
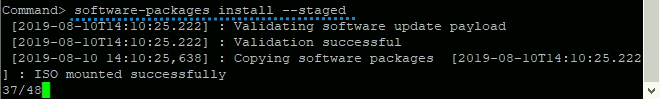
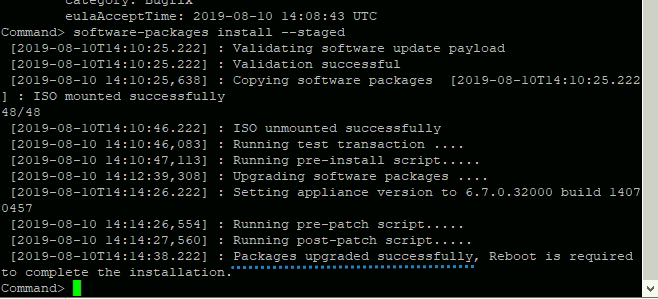
To start the installation of the staged packages, we will need another command. We will use this command for installing the packages:
software-packages install –stagedHere is the view
Install staged packages
It will take some time to install. Once done, we have a message saying that we’ve been successful. Great.
Now we just need to reboot the appliance to finish the process. Just type “exit” into the SSH window and then reboot the appliance via your vSphere web client.
Note: you can also reboot VCSA via command line
Packages Installed successfully
Final Words
Offline patching can be useful for high secure environments without internet access or during times when your internet access isn’t fast enough or unreliable.
VMware Makes the administration of the VCSA easy. It’s been several years since the movement has started but at first, the VCSA wasn’t as scalable than vCenter running on Windows. Also, the VCSA has had some serious bugs which did not really triggered mass adoption.
However now, since 6.7 the VCSA has more features and functions than vCenter on Windows and VMware clearly pushes people to switch from Windows to VCSA. The product has new “VCSA to Windows” utility allowing you to seamlessly migrate from Windows based vCenter server into VCSA and keep all history and settings (including network settings, certificates etc).
You don’t need to re-configure any third-party software you’re using in your company as the vCenter ID is kept during migration.
https://www.virtualizationhowto.com/2019/07/manually-patch-vmware-vcenter-server-vcsa-with-iso/