The objective of this post is to provide you with some insights of the types of controls necessary to guarantee the confidentiality, integrity and availability with regards to securing data in the cloud.
Introduction
Data security is a core element of cloud security. Service providers often share the responsibility for security with the customer. As with all areas of cloud security, a risk-based approach must be taken since it’s not appropriate to secure everything equally. The last statement being true for data security overall, whether the cloud is involved or not.
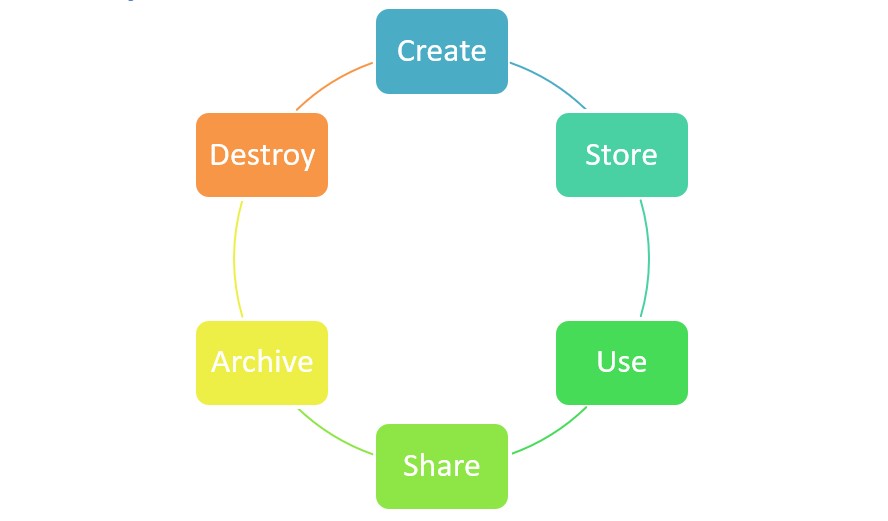
Data Lifecycle
Create: data is either generated or acquired, versioning or the modification of existing data is also considered as creation
Store: initial storage is done right after the creation; when stored, the data must be protected according to the organizational policies regarding the classification level, security controls, access policy, and monitoring requirements.
Use: data is viewed, processed or used. This is the most vulnerable stage because it can be transported to insecure locations. Data Loss Prevention (DLP), data rights management (DRM) and data access monitors must be implemented.
Share: data and information is made available to others, DLP and DRM are used to detect unauthorized sharing and maintain control of the information.
Archive: when data is no longer needed.
Destroy: last phase of the data lifecycle, data is removed from the cloud.
Threats to cloud storage
Without going into the details for each threat hereby is the list of major threats with regards to cloud storage:
- Unauthorized usage
- Unauthorized access
- (Distributed) Denial of Service (DoS & DDoS)
- Data leakage/breaches
- Malware attack
- Improper treatment or sanitization after end of use
Technologies and strategies for securing data
Data Masking/Obfuscation
Data masking or data obfuscation is the method of hiding, replacing, or omitting sensitive information from a specific data set such as PII, commercially sensitive data or to comply with specific regulations such as PCI DSS.
Common approach to data masking are:
- Random substitution
- Algorithmic substitution
- Shuffle
- Masking
- Deletion
Data anonymization
The idea there is make a distinction between the direct identifiers which allows to uniquely identify the subject (such as name, address) and the indirect identifiers (such as events, dates or socioeconomic information) which have the risk of once combined can result in exposing the subject.
Anonymization is the process of removing (by masking or obscuring the information) the indirect identifiers to prevent data analysis or other intelligent mechanisms from collating or pulling data from multiple sources to identify the subject.
Tokenization
Tokenization is the process of replacing sensitive data element with non-sensitive equivalent, referred as a token (e.g. random values). A mapping table must be maintained to link the token with the sensitive data.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP is used to describe the controls in place by an organization to ensure that certain types of data remain under organization controls, in line with policies, standards and procedures. It’s crucial to consider, while defining the DLP strategy for your organization, the data in motion, the data at rest and the data in use.
DLP components:
- Discovery and classification: the discovery process maps data in cloud storage services and databases and enable the classification based on data categories (e.g. regulated data, PCI-DSS data, public data).
- Monitoring: key function of the DLP, it consists of monitoring the usage of data across locations and platforms while enable administrators to define one or more usage policies in order to cover most sharing options available to users (e.g. email applications, portable media) and alert on policy violations.
- Enforcement: if a policy violation is detected, specified relevant enforcement actions can automatically be performed (e.g. alert, block data transfer, trigger a additional validation workflow, encrypt the data).
Import considerations for cloud-based DLP:
- Data in the cloud tends to move and replicate
- DLP technologies can have a significant impact on the performance of your computerized systems.
Encryption
We will not cover in this post the different types of encryption (i.e. symmetric, asymmetric) as the different technologies and strategies available to do so in the cloud since plenty of information is already available on this topic. Nevertheless, this is a must for securing your data both in the cloud and on-premise.
Conclusion
In this post, the objective was clearly to give you a kind of checklist of the aspects that you must consider to store securely your data in the cloud. It’s not an exhaustive list, but gives you a very strong starting point for your journey on moving data to the cloud.
Other considerations not covered in this post is with regards to retention, deletion and archival policies.