There was a race to bring NVMe-oF to Windows some time ago. Many tried, but I know that only StarWind and Chelsio succeeded so far. Now, it’s time to see who won this race! It is the fourth part of my NVMe-oF Initiators’ performance study. Before, I tested NVMe-oF initiators developed by Linux, Chelsio and StarWind. Here, the battle ends: which NVMe-oF initiator delivers the highest performance and which one Windows admins should use
INTRODUCTION
There was a race to bring NVMe-oF to Windows some time ago. Many tried, but I know that only StarWind and Chelsio succeeded so far. Now, it’s time to see who won this race!

It is the fourth part of my NVMe-oF Initiators’ performance study. Before, I tested NVMe-oF initiators developed by Linux, Chelsio and StarWind. Here, the battle ends: which NVMe-oF initiator delivers the highest performance and which one Windows admins should use?
RESULTS
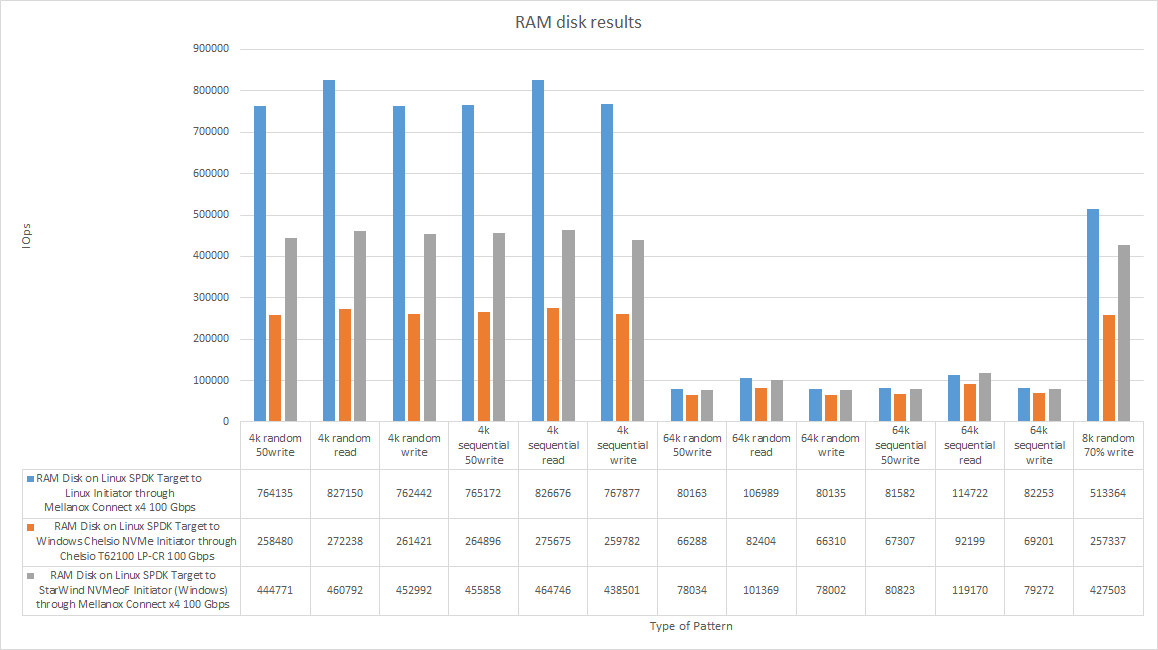
RAM disk performance (all results)
I guess that it is good to have a table with RAM disk performance measured over loopback and locally. Just to see the maximum performance.
| Local device | Loopback | RAM Disk on Linux SPDK NVMe-oF Target to Linux NVMe-oF Initiator through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
RAM Disk on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Windows Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator through Chelsio T62100 LP-CR 100 Gbps |
RAM Disk on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator (Windows) through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAM Disk Linux Local | RAM Disk loopback (127.0.0.1) Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target | ||||||||||||||
| Job name | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) |
| 4k random 50write | 458958 | 1792.81 | 0.07 | 709451 | 2771.30 | 0.04 | 764135 | 2984.91 | 0.04 | 258480 | 1009.70 | 0.08 | 444771 | 1737.40 | 0.05 |
| 4k random read | 558450 | 2181.45 | 0.05 | 709439 | 2771.26 | 0.04 | 827150 | 3231.06 | 0.05 | 272238 | 1063.44 | 0.07 | 460792 | 1799.98 | 0.05 |
| 4k random write | 460132 | 1797.40 | 0.07 | 703042 | 2746.27 | 0.04 | 762442 | 2978.30 | 0.04 | 261421 | 1021.18 | 0.08 | 452992 | 1769.51 | 0.05 |
| 4k sequential 50write | 525996 | 2054.68 | 0.06 | 715444 | 2794.71 | 0.04 | 765172 | 2988.97 | 0.04 | 264896 | 1034.76 | 0.08 | 455858 | 1780.71 | 0.05 |
| 4k sequential read | 656666 | 2565.11 | 0.05 | 753439 | 2943.14 | 0.04 | 826676 | 3229.22 | 0.03 | 275675 | 1076.87 | 0.07 | 464746 | 1815.43 | 0.05 |
| 4k sequential write | 520115 | 2031.71 | 0.06 | 713012 | 2785.22 | 0.05 | 767877 | 2999.54 | 0.04 | 259782 | 1014.79 | 0.08 | 438501 | 1712.90 | 0.05 |
| 64k random 50write | 50641 | 3165.26 | 0.62 | 79322 | 4957.85 | 0.39 | 80163 | 5010.47 | 0.39 | 66288 | 4143.17 | 0.45 | 78034 | 4877.35 | 0.39 |
| 64k random read | 69812 | 4363.57 | 0.45 | 103076 | 6442.53 | 0.30 | 106989 | 6687.09 | 0.29 | 82404 | 5150.49 | 0.36 | 101369 | 6335.77 | 0.30 |
| 64k random write | 50525 | 3158.06 | 0.62 | 78188 | 4887.01 | 0.40 | 80135 | 5008.57 | 0.39 | 66310 | 4144.67 | 0.45 | 78002 | 4875.36 | 0.39 |
| 64k sequential 50write | 58900 | 3681.56 | 0.53 | 81830 | 5114.63 | 0.38 | 81582 | 5099.17 | 0.38 | 67307 | 4207.04 | 0.45 | 80823 | 5051.73 | 0.38 |
| 64k sequential read | 73434 | 4589.86 | 0.42 | 131613 | 8226.06 | 0.23 | 114722 | 7170.29 | 0.27 | 92199 | 5762.73 | 0.32 | 119170 | 7448.45 | 0.25 |
| 64k sequential write | 57200 | 3575.31 | 0.54 | 79085 | 4943.10 | 0.39 | 82253 | 5141.09 | 0.38 | 69201 | 4325.34 | 0.43 | 79272 | 4954.69 | 0.38 |
| 8k random 70% write | 337332 | 2635.47 | 0.09 | 465745 | 3638.69 | 0.07 | 513364 | 4010.70 | 0.06 | 257337 | 2010.51 | 0.08 | 427503 | 3339.91 | 0.05 |
RAM disk performance (initiators only)
Here is the table to compare Initiators’ performance.
| RAM Disk on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Linux NVMe-oF Initiator through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
RAM Disk on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Windows Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator through Chelsio T62100 LP-CR 100 Gbps |
RAM Disk on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator (Windows) through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Job name | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) |
| 4k random 50write | 764135 | 2984.91 | 0.04 | 258480 | 1009.70 | 0.08 | 444771 | 1737.40 | 0.05 |
| 4k random read | 827150 | 3231.06 | 0.05 | 272238 | 1063.44 | 0.07 | 460792 | 1799.98 | 0.05 |
| 4k random write | 762442 | 2978.30 | 0.04 | 261421 | 1021.18 | 0.08 | 452992 | 1769.51 | 0.05 |
| 4k sequential 50write | 765172 | 2988.97 | 0.04 | 264896 | 1034.76 | 0.08 | 455858 | 1780.71 | 0.05 |
| 4k sequential read | 826676 | 3229.22 | 0.03 | 275675 | 1076.87 | 0.07 | 464746 | 1815.43 | 0.05 |
| 4k sequential write | 767877 | 2999.54 | 0.04 | 259782 | 1014.79 | 0.08 | 438501 | 1712.90 | 0.05 |
| 64k random 50write | 80163 | 5010.47 | 0.39 | 66288 | 4143.17 | 0.45 | 78034 | 4877.35 | 0.39 |
| 64k random read | 106989 | 6687.09 | 0.29 | 82404 | 5150.49 | 0.36 | 101369 | 6335.77 | 0.30 |
| 64k random write | 80135 | 5008.57 | 0.39 | 66310 | 4144.67 | 0.45 | 78002 | 4875.36 | 0.39 |
| 64k sequential 50write | 81582 | 5099.17 | 0.38 | 67307 | 4207.04 | 0.45 | 80823 | 5051.73 | 0.38 |
| 64k sequential read | 114722 | 7170.29 | 0.27 | 92199 | 5762.73 | 0.32 | 119170 | 7448.45 | 0.25 |
| 64k sequential write | 82253 | 5141.09 | 0.38 | 69201 | 4325.34 | 0.43 | 79272 | 4954.69 | 0.38 |
| 8k random 70% write | 513364 | 4010.70 | 0.06 | 257337 | 2010.51 | 0.08 | 427503 | 3339.91 | 0.05 |
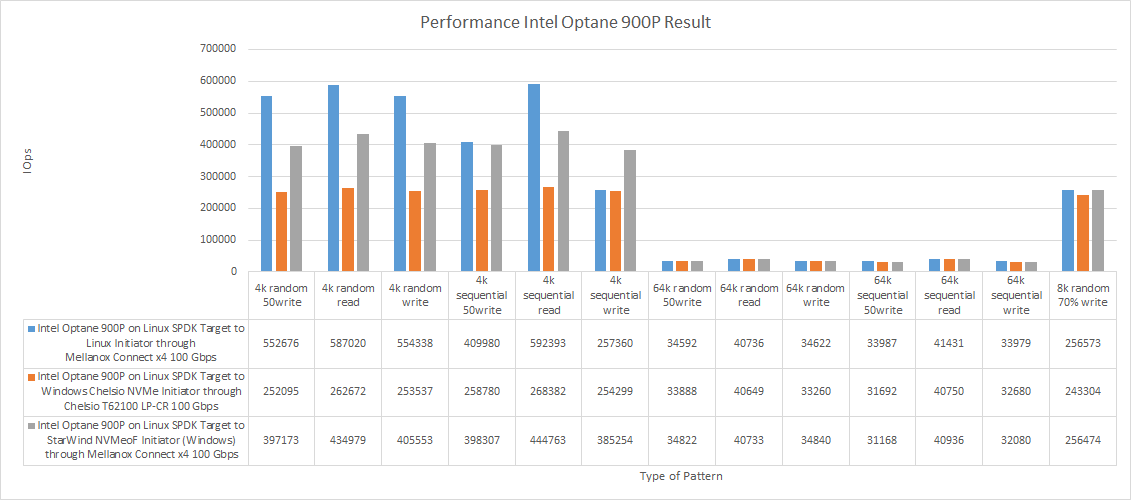
Intel Optane 900P performance (all results)
Now, let’s take a closer look at the efficacy of studied NVMe-oF Initiators for presenting flash over RDMA.
| Local device | Loopback | Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Linux NVMe-oF Initiator through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Windows Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator through Chelsio T62100 LP-CR 100 Gbps |
Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator (Windows) through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Optane 900P Linux local | Intel Optane 900P loopback (127.0.0.1) Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target | ||||||||||||||
| Job name | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) |
| 4k random 50write | 542776 | 2120.23 | 0.05 | 550744 | 2151.35 | 0.05 | 552676 | 2158.90 | 0.05 | 252095 | 984.76 | 0.08 | 397173 | 1551.47 | 0.06 |
| 4k random read | 586811 | 2292.24 | 0.05 | 586964 | 2292.84 | 0.05 | 587020 | 2293.06 | 0.05 | 262672 | 1026.07 | 0.08 | 434979 | 1699.15 | 0.05 |
| 4k random write | 526649 | 2057.23 | 0.06 | 550865 | 2151.82 | 0.05 | 554338 | 2165.39 | 0.05 | 253537 | 990.39 | 0.08 | 405553 | 1584.20 | 0.06 |
| 4k sequential 50write | 323441 | 1263.45 | 0.09 | 509616 | 1990.70 | 0.06 | 409980 | 1601.49 | 0.07 | 258780 | 1010.87 | 0.08 | 398307 | 1555.89 | 0.06 |
| 4k sequential read | 595622 | 2326.66 | 0.05 | 590101 | 2305.09 | 0.05 | 592393 | 2314.05 | 0.05 | 268382 | 1048.38 | 0.08 | 444763 | 1737.37 | 0.05 |
| 4k sequential write | 416667 | 1627.61 | 0.07 | 537876 | 2101.09 | 0.06 | 257360 | 1005.33 | 0.12 | 254299 | 993.37 | 0.08 | 385254 | 1504.91 | 0.06 |
| 64k random 50write | 34224 | 2139.32 | 0.92 | 34566 | 2160.66 | 0.91 | 34592 | 2162.21 | 0.91 | 33888 | 2118.26 | 0.92 | 34822 | 2176.51 | 0.91 |
| 64k random read | 40697 | 2543.86 | 0.77 | 40733 | 2546.02 | 0.77 | 40736 | 2546.28 | 0.77 | 40649 | 2540.81 | 0.76 | 40733 | 2546.04 | 0.77 |
| 64k random write | 33575 | 2098.76 | 0.94 | 34590 | 2162.01 | 0.91 | 34622 | 2164.18 | 0.91 | 33260 | 2079.03 | 0.94 | 34840 | 2177.88 | 0.91 |
| 64k sequential 50write | 34462 | 2154.10 | 0.91 | 34201 | 2137.77 | 0.92 | 33987 | 2124.37 | 0.92 | 31692 | 1981.07 | 0.99 | 31168 | 1948.23 | 1.01 |
| 64k sequential read | 41369 | 2585.79 | 0.76 | 41418 | 2588.87 | 0.76 | 41431 | 2589.68 | 0.76 | 40750 | 2547.18 | 0.76 | 40936 | 2558.75 | 0.77 |
| 64k sequential write | 34435 | 2152.52 | 0.91 | 34499 | 2156.53 | 0.91 | 33979 | 2123.92 | 0.92 | 32680 | 2042.69 | 0.96 | 32080 | 2005.06 | 0.99 |
| 8k random 70% write | 256307 | 2002.46 | 0.12 | 256435 | 2003.45 | 0.12 | 256573 | 2004.52 | 0.12 | 243304 | 1900.87 | 0.09 | 256474 | 2003.76 | 0.11 |
Intel Optane 900P performance (all results)
| Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Linux NVMe-oF Initiator through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Windows Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator through Chelsio T62100 LP-CR 100 Gbps |
Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator (Windows) through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Job name | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) |
| 4k random 50write | 552676 | 2158.90 | 0.05 | 252095 | 984.76 | 0.08 | 397173 | 1551.47 | 0.06 |
| 4k random read | 587020 | 2293.06 | 0.05 | 262672 | 1026.07 | 0.08 | 434979 | 1699.15 | 0.05 |
| 4k random write | 554338 | 2165.39 | 0.05 | 253537 | 990.39 | 0.08 | 405553 | 1584.20 | 0.06 |
| 4k sequential 50write | 409980 | 1601.49 | 0.07 | 258780 | 1010.87 | 0.08 | 398307 | 1555.89 | 0.06 |
| 4k sequential read | 592393 | 2314.05 | 0.05 | 268382 | 1048.38 | 0.08 | 444763 | 1737.37 | 0.05 |
| 4k sequential write | 257360 | 1005.33 | 0.12 | 254299 | 993.37 | 0.08 | 385254 | 1504.91 | 0.06 |
| 64k random 50write | 34592 | 2162.21 | 0.91 | 33888 | 2118.26 | 0.92 | 34822 | 2176.51 | 0.91 |
| 64k random read | 40736 | 2546.28 | 0.77 | 40649 | 2540.81 | 0.76 | 40733 | 2546.04 | 0.77 |
| 64k random write | 34622 | 2164.18 | 0.91 | 33260 | 2079.03 | 0.94 | 34840 | 2177.88 | 0.91 |
| 64k sequential 50write | 33987 | 2124.37 | 0.92 | 31692 | 1981.07 | 0.99 | 31168 | 1948.23 | 1.01 |
| 64k sequential read | 41431 | 2589.68 | 0.76 | 40750 | 2547.18 | 0.76 | 40936 | 2558.75 | 0.77 |
| 64k sequential write | 33979 | 2123.92 | 0.92 | 32680 | 2042.69 | 0.96 | 32080 | 2005.06 | 0.99 |
| 8k random 70% write | 256573 | 2004.52 | 0.12 | 243304 | 1900.87 | 0.09 | 256474 | 2003.76 | 0.11 |
WHAT ABOUT THE LATENCY?
Performance is not only about IOPS. Here is the table demonstrating what the latency was like in all experiments.
| Local device | RAM Disk on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Linux NVMe-oF Initiator through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
RAM Disk on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Windows Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator through Chelsio T62100 LP-CR 100 Gbps |
RAM Disk on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator (Windows) through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAM Disk Linux Local | ||||||||||||
| Job name | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) |
| 4k random 50write | 97108 | 379.33 | 0.0069433 | 85115 | 332.48 | 0.0089677 | 17269 | 67.46 | 0.0404688 | 22671 | 88.56 | 0.0344373 |
| 4k random read | 114417 | 446.94 | 0.0056437 | 82328 | 321.60 | 0.0092321 | 17356 | 67.80 | 0.0402686 | 22841 | 89.23 | 0.0345294 |
| 4k random write | 95863 | 374.46 | 0.0070643 | 81544 | 318.53 | 0.0093238 | 14821 | 57.90 | 0.0432964 | 23049 | 90.04 | 0.0341427 |
| 4k sequential 50write | 107010 | 418.01 | 0.0061421 | 87099 | 340.23 | 0.0088669 | 18134 | 70.84 | 0.0390418 | 23020 | 89.92 | 0.0341291 |
| 4k sequential read | 117168 | 457.69 | 0.0054994 | 83217 | 325.07 | 0.0092358 | 17452 | 68.17 | 0.0404430 | 22910 | 89.49 | 0.0344851 |
| 4k sequential write | 98065 | 383.07 | 0.0068343 | 84504 | 330.10 | 0.0090527 | 17437 | 68.12 | 0.0398902 | 22906 | 89.48 | 0.0342793 |
| 64k random 50write | 27901 | 1743.87 | 0.0266555 | 23219 | 1451.25 | 0.0346774 | 13558 | 847.38 | 0.0459828 | 13665 | 854.07 | 0.0609151 |
| 64k random read | 36098 | 2256.14 | 0.0203593 | 35823 | 2238.99 | 0.0235566 | 14099 | 881.25 | 0.0449975 | 15826 | 989.18 | 0.0520607 |
| 64k random write | 28455 | 1778.48 | 0.0260830 | 21049 | 1315.59 | 0.0367933 | 13607 | 850.50 | 0.0476149 | 14614 | 913.38 | 0.0546317 |
| 64k sequential 50write | 28534 | 1783.42 | 0.0262397 | 23753 | 1484.61 | 0.0342470 | 11151 | 697.00 | 0.0700821 | 12820 | 801.27 | 0.0634169 |
| 64k sequential read | 36727 | 2295.44 | 0.0200747 | 35762 | 2235.17 | 0.0236739 | 14616 | 913.50 | 0.0450857 | 15918 | 994.93 | 0.0518925 |
| 64k sequential write | 28988 | 1811.78 | 0.0256918 | 24059 | 1503.74 | 0.0341105 | 13605 | 850.34 | 0.0506481 | 13737 | 858.61 | 0.0605783 |
| 8k random 70% write | 85051 | 664.47 | 0.0083130 | 68362 | 534.09 | 0.0118387 | 17630 | 137.74 | 0.0398817 | 21648 | 169.13 | 0.0381733 |
| Intel Optane 900P Linux local | Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Linux NVMe-oF Initiator through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to Windows Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator through Chelsio T62100 LP-CR 100 Gbps |
Intel Optane 900P on Linux NVMe-oF SPDK Target to StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator (Windows) through Mellanox Connect x4 100 Gbps |
|||||||||
| Job name | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) | Total IOPS | Total bandwidth (MB/s) | Average latency (ms) |
| 4k random 50write | 73097 | 285.54 | 0.0108380 | 53664 | 209.63 | 0.0154448 | 14735 | 57.56 | 0.0437604 | 17563 | 68.61 | 0.0455358 |
| 4k random read | 82615 | 322.72 | 0.0093949 | 54558 | 213.12 | 0.0150121 | 17751 | 69.34 | 0.0408734 | 18097 | 70.69 | 0.0442594 |
| 4k random write | 73953 | 288.88 | 0.0108047 | 55483 | 216.73 | 0.0151169 | 11703 | 45.71 | 0.0690179 | 17217 | 67.26 | 0.0463379 |
| 4k sequential 50write | 74555 | 291.23 | 0.0108105 | 52762 | 206.10 | 0.0157316 | 11734 | 45.84 | 0.0676898 | 17463 | 68.22 | 0.0458633 |
| 4k sequential read | 85858 | 335.39 | 0.0092789 | 53125 | 207.52 | 0.0154067 | 17243 | 67.36 | 0.0418020 | 18850 | 73.63 | 0.0432678 |
| 4k sequential write | 74998 | 292.96 | 0.0107804 | 56571 | 220.98 | 0.0150328 | 11743 | 45.87 | 0.0675165 | 19135 | 74.75 | 0.0401418 |
| 64k random 50write | 19119 | 1194.99 | 0.0423029 | 13914 | 869.68 | 0.0602535 | 10654 | 665.90 | 0.0667292 | 9580 | 598.80 | 0.0899450 |
| 64k random read | 22589 | 1411.87 | 0.0356328 | 17077 | 1067.35 | 0.0482814 | 10593 | 662.11 | 0.0766167 | 11481 | 717.62 | 0.0745408 |
| 64k random write | 18762 | 1172.63 | 0.0427555 | 13900 | 868.78 | 0.0602887 | 9629 | 601.81 | 0.0847440 | 9653 | 603.36 | 0.0892458 |
| 64k sequential 50write | 19320 | 1207.54 | 0.0423435 | 13896 | 868.50 | 0.0602752 | 10656 | 666.06 | 0.0655762 | 9629 | 601.84 | 0.0900962 |
| 64k sequential read | 22927 | 1432.96 | 0.0353837 | 17628 | 1101.79 | 0.0475938 | 11724 | 732.77 | 0.0642400 | 10757 | 672.33 | 0.0801468 |
| 64k sequential write | 18663 | 1166.44 | 0.0429796 | 13822 | 863.88 | 0.0604900 | 10536 | 658.52 | 0.0724088 | 9588 | 599.30 | 0.0901930 |
| 8k random 70% write | 72212 | 564.16 | 0.0114044 | 47450 | 370.71 | 0.0184596 | 14761 | 115.33 | 0.0555947 | 17258 | 134.84 | 0.0469456 |
DISCUSSION
I believe that we’ve seen enough to judge on NVMe-oF initiators’ performance. Linux NVMe-oF Initiator beats all other initiators under any workload. StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator took the second place. Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator took the third place.
Let’s discuss how efficient can be presenting a RAM disk over RDMA in detail. In 64k blocks, StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator exhibited the same performance as Linux NVMe-oF Initiator. Interestingly, the former did slightly better in 64k sequential reading than Linux NVMe-oF Initiator. Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator, in turn, showed only ¼ of Linux NVMe-oF Initiator performance in most of the tests.
Now, let’s see how the discussed NVMe-oF Initiators work with an NVMe drive (Intel Optane 900P). In 4k blocks, Linux NVMe-oF Initiator was doing better than any other Initiator. But, under some patterns, StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator was doing better than the solution developed by Linux. Under mixed loads in small blocks (4k sequential 50%read50%write), StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator performance was close to Linux NVMe-oF Initiator. For 4k sequential writing, StarWind NVMe-oF exhibited better performance than Linux NVMe-oF Initiator (385 254 and 257 360 IOPS respectively). Under that testing pattern, Chelsio NVMe-oF Initiator performance was close to what we saw for Linux NVMe-oF Initiator (254 299 and 257 360 IOPS respectively). All initiators exhibited similar performance in 64k blocks.
CONCLUSION
Linux NVMe-oF Initiator is the best solution to present an NVMe drive over the network so far. There was some serious work done to bring NVMe-oF to Windows; and StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator is the best solution for Windows so far. It just works great for any type of virtualized workload.


