Introduction
Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct is a new storage feature introduced in Windows Server 2016 Datacenter, which significantly extends the Software-Defined Storage stack in Windows Server product family and allows users building highly available storage systems using directly attached drives.
Storage Spaces Direct, or S2D, simplifies the deployment and management of Software-Defined Storage systems and allows using more disk devices classes like SATA and NVMe drives. Previously, it was not possible to use these types of storage with clustered Storage Spaces with shared disks.
Storage Spaces Direct can use drives that are locally attached to nodes in a cluster or disks that are attached to nodes using enclosure. It aggregates all the disks into a single Storage Pool and enables the creation of virtual disks on top.
Problem
The storage hardware requirements of Microsoft Storage Spaces Direct are very clear:
- Locally attached SATA, SAS, or NVMe drives are supported and every driver must be physically connected to only one single server.
- SSDs should be “enterprise-grade”, meaning they have power-loss protection, and if they are planned to be used for a cache, they should have high write endurance.
- Drives can be 512n, 512e, or 4K native. Microsoft recommends using a separate dedicated drive for boot.
- Multipath IO (MPIO) or physically connected drives via multiple paths is not supported.
The most interesting part of storage requirements is regarding host-bus adapter (HBA). Simple pass-through SAS HBA for both SAS and SATA drives is required and SCSI Enclosure Services (SES) for SAS and SATA drives is necessary. Any directly-attached storage enclosures must present Unique ID.
RAID HBA controllers or SAN (Fibre Channel, iSCSI, FCoE) devices are not supported, which makes it impossible to create a Storage Spaces Direct on top of most RAID controllers even if they have HBA mode or JBOD (Pass-Through) mode switch since some controllers keep reporting drives bus-type as RAID.
Test lab configuration
My test lab consists of 2 x SuperMicro X10DRH Servers powered with 2 x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2630 v4 @ 2.20GHz each. Each server has a decent 128 GB of RAM. Connectivity is provided by Mellanox ConnectX4 100 Gbe dual-port interfaces.
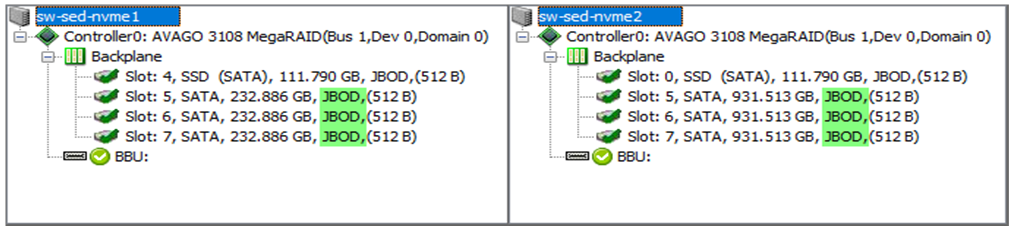
Each server has a single 120 GB Intel(R) SSD for Windows Server 2016 Datacenter operating system, 3 x various spindle HDDs and a single 800 GB Intel(R) P3700 NVMe card. All drives are connected to Avago 3108 MegaRAID controller that is based on LSI SAS 3108. Similar chips are used in DELL Perc and HPE Smart Array controllers and most of them support JBOD (pass-through) mode.
Creating the S2D cluster
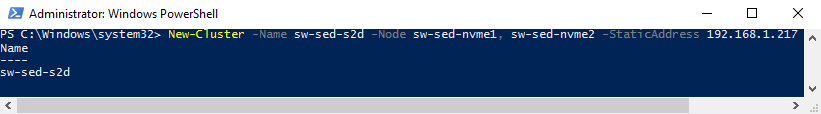
Let us start with creating a new Microsoft Failover Cluster.
New-Cluster -Name sw-sed-s2d -Node sw-sed-nvme1, sw-sed-nvme2 -StaticAddress 192.168.1.217Before creating the storage cluster, we must check whether our storage configuration fits the Storage Spaces Direct requirements on both hosts. We have to check if the drives we are going to use for S2D can be added to the storage pool (CanPool value is set to True) and if the BusType is correct. Here’s the PowerShell command I ran on each host:
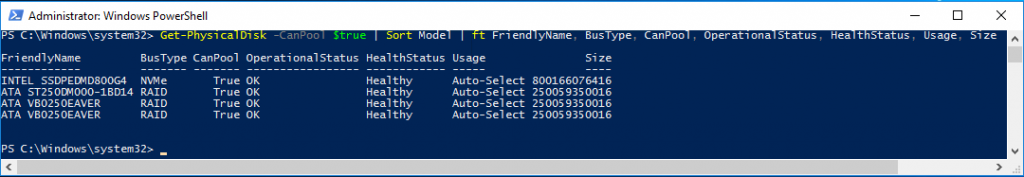
Get-PhysicalDisk -CanPool $true | Sort Model | ft FriednlyName, BusType, CanPool, OperationalStatus, HealthStatus, Usage, SizeHost 1 output:
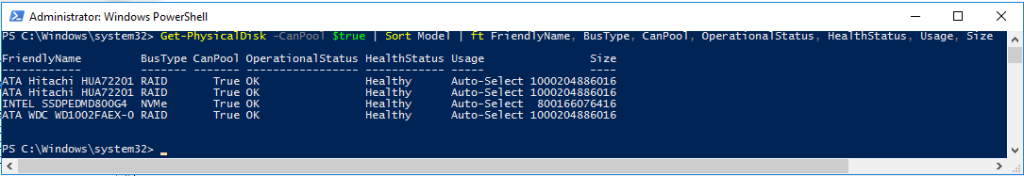
Host 2 output:
We can already see that the reported bus types are ‘RAID’ instead of ‘SAS’, which is not what we usually expect from a storage controller in ‘HBA’ mode. Now, let’s see how Storage Spaces Direct reacts to our disk configuration. I enable S2D using the following command:
Enable-ClusterS2DOutput:
The result speaks for itself: S2D cannot be enabled due to the unsupported disk bus type.
Solution
So, what can we do overcome this problem? Well, quite a few things.
Go for S2D-compatible storage controller
The first and most obvious solution would be to replace your existing storage controller with a Storage Spaces Direct compatible one. This should be a simple pass-through SAS HBA for both SAS and SATA drives.
Update the firmware and drivers
If your drives keep reporting the BusType as RAID despite being configured as JBOD (pass-through), like in the situation described here, you might try updating storage controller’s firmware and drivers. This solution is known to be helpful on some HPE SmartArray controllers.
Use IT firmware for LSI controllers
For many LSI controllers, there are two types of firmware that can be used. IT firmware keeps the controller working as a simple HBA while IR firmware upgrades the controller to a RAID controller. In order to be used with Storage Spaces Direct, these controllers must be flashed with IT firmware.
Previously, we have covered one more way to make S2D work with unsupported bus types. While it was useful in some cases, now, it brings more issues than benefits as the number of users reporting that it works unstable and causes problems has grown significantly. That’s why we have removed the description of this hack. We don’t know if it works in GA builds, so we encourage using proper hardware in accordance with HCL and MSFT requirements. And don’t Google or Bing for options – you’ll just be asking for trouble.
Conclusion
Some RAID controllers support “JBOD mode” or “HBA mode”, so this may be the first and the most simple way to go. Also, do not forget to keep the RAID controller drivers up to date. Additionally, you can try reflashing the RAID controller firmware from IR to IT mode. Since most of HBA and RAID controllers share the same hardware components, this could be a simple and effective way of turning your RAID controller to HBA and using it to deploy S2D. You may have probably thought about this yourself, but the last resort is to simply replace your RAID controller for S2D-compatible HBA.