Introduction
The new build of StarWind SAN & NAS has just gotten released and it will bring us the long-awaited FC (Fibre Channel) ecosystem support. StarWind SAN & NAS has been designed to give a new life for your existing hardware. Installed either on top of hypervisor of your choice or bare-metal, it turns your server into a fast shared storage pool that can be accessed over iSCSI, SMB or NFS. And in the new build, via FC as well. It uses the same SDS engine as StarWind vSAN which means high performance and also adds new features such as ZFS support to build the utmost resilient storage system using the commodity hardware.
This was a great chance to test how fast StarWind SAN & NAS can go using FC. Folks from StorageReview were kind to provide us with the testing infrastructure where we performed the benchmark. Thanks, StorageReview team once again!
Testing scope
We have tested the performance of shared storage presented from a dedicated storage node full of NVMe drives and StarWind SAN & NAS on top over FC to client nodes. We have decided to include only good old FCP (FCP – Fibre Channel Protocol) benchmark results in this article since the results of NVMe-FC were at the same level (on certain patterns even lower than FCP). To collect NVMe drives into a redundant storage array, we have used MDRAID and GRAID tools and tested them separately. MDRAID is a Linux software RAID that is present as part of StarWind SAN & NAS and serves to collect drives into a redundant array. GRAID is an extremely fast NVMe/NVMeoF RAID card, designed to deliver the full potential of PCIe Gen4 systems.
It is worth mentioning that GRAID SupremeRAID is the only NVMe RAID card as of now capable of delivering the highest SSD performance possible that removes performance bottlenecks altogether. What is the difference, you may wonder? Well, GRAID SupremeRAID SR-1010 is based on an NVIDIA A2000 GPU. In most characteristics, that doesn’t make this solution anything special, but when it comes to the NVMe RAID bottlenecks, the GPU can give a head start to lots of alternatives. In particular, the SupremeRAID is capable of processing all the I/O operations directly, and we don’t need to tell you just how much this frees up the CPU resources. Standard RAID cards are simply no match for the computing potential of the GPU card. Even though the GRAID solution is a software RAID, the NVIDIA GPU card is essential to a lot of benefits that GRAID has to offer. Additionally, thanks to the specifics of GRAID software architecture, data can flow directly from the CPU and straight to the storage, passing by the GRAID card.
Traditionally, NVIDIA cards serve various purposes. They are in demand for use in gaming, video acceleration, cryptocurrency mining, and professional working tools such as VDI. Moreover, NVIDIA also produces GPUs for vehicles. Now? NVIDIA hardware powers storage appliances. This novelty embarks nothing less but a breakthrough in utilizing computing potential of the GPU in a whole new field.
Testing bed
Here is the list of the hardware and software used in our benchmark.
Storage node:
| Hardware | |
| sw-sannas-01 | Dell PowerEdge R750 |
| CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8380 CPU @ 2.30GHz |
| Sockets | 2 |
| Cores/Threads | 80/160 |
| RAM | 1024Gb |
| Storage | 8x (NVMe) – PBlaze6 6926 12.8TB |
| GRAID | SupremeRAID SR-1010 |
| HBAs | 4x Marvell® QLogic® 2772 Series Enhanced 32GFC Fibre Channel Adapters |
| Software | |
StarWind SAN&NAS |
Version 1.0.2 (build 2175 – FC) |
Client nodes:
| Hardware | |
| win-cli-{01..04} | PowerEdge R740xd |
| CPU | Intel® Xeon® Gold 6130 Processor 2.10GHz |
| Sockets | 2 |
| Cores/Threads | 32/64 |
| RAM | 256Gb |
| HBAs | 1x Marvell® QLogic® 2772 Series Enhanced 32GFC Fibre Channel Adapters |
| Software | |
| OS | Windows Server 2019 Standard Edition |
Testbed architecture overview:
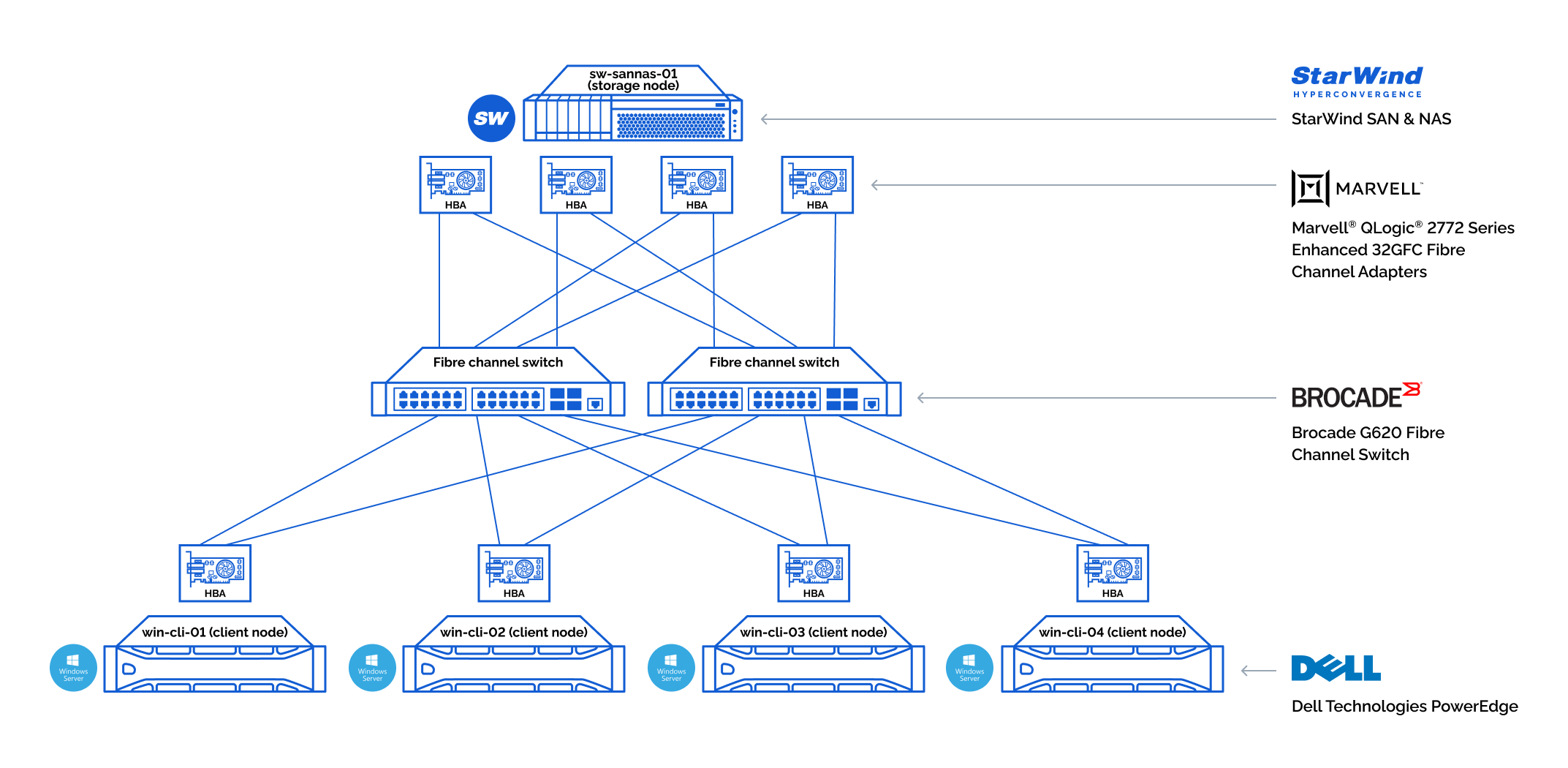
The communication between storage node and client nodes has been carried out over 32GFC Fibre Channel fabric. The storage node had 4x Marvell® QLogic® 2772 Series Enhanced 32GFC Fibre Channel Adapters while each client node had one. The storage and client nodes were connected using two Brocade G620 Fibre Channel Switches to ensure resilience.
The interesting thing behind Marvell Qlogic 2772 Fibre Channel adapters is that the ports on it are independently resourced which gives an additional layer of resilience. The complete port-level isolation across the FC controller architecture prevents errors and firmware crashes from propagating across all ports. If you want to find out more about Marvell Qlogic 2772 Fibre Channel adapters in terms of high availability and reliability, you can look it up here.
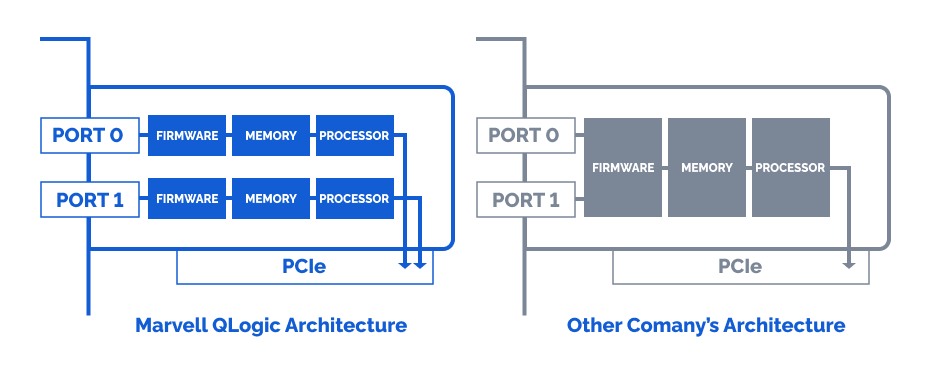
Marvell QLogic ports act independently from each other giving more flexibility in terms of resilience. More details are here
Storage connection diagram:
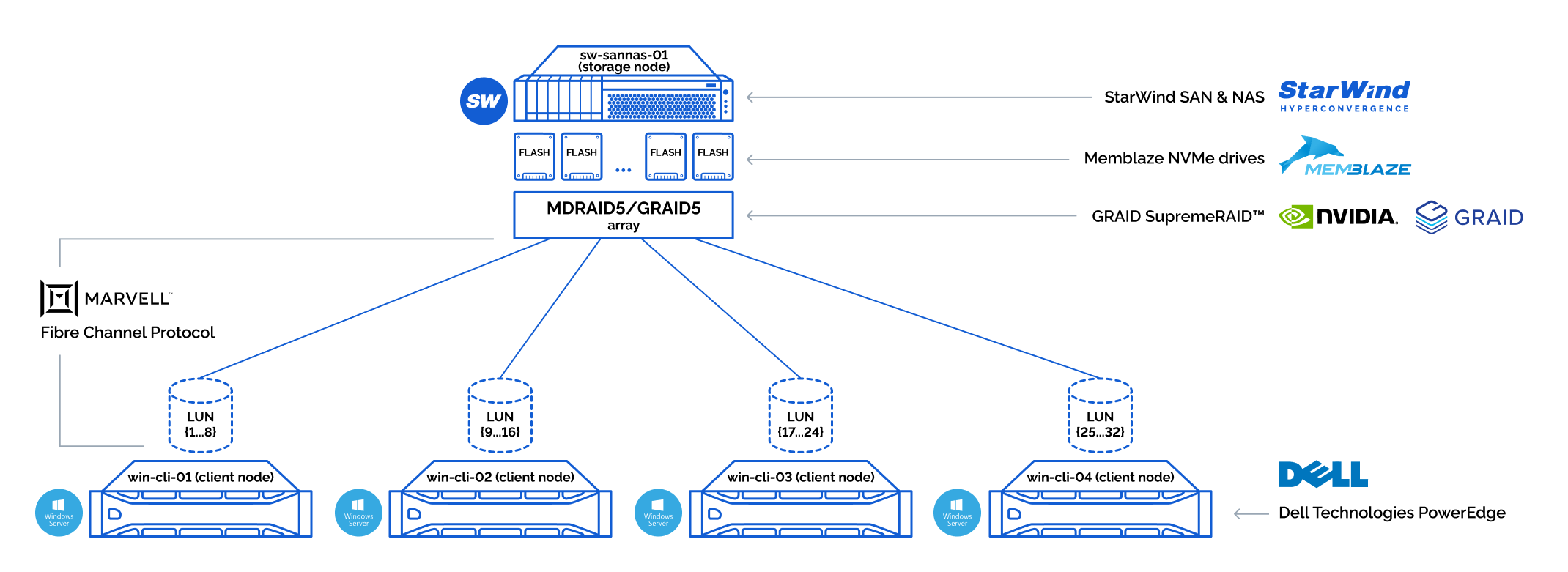
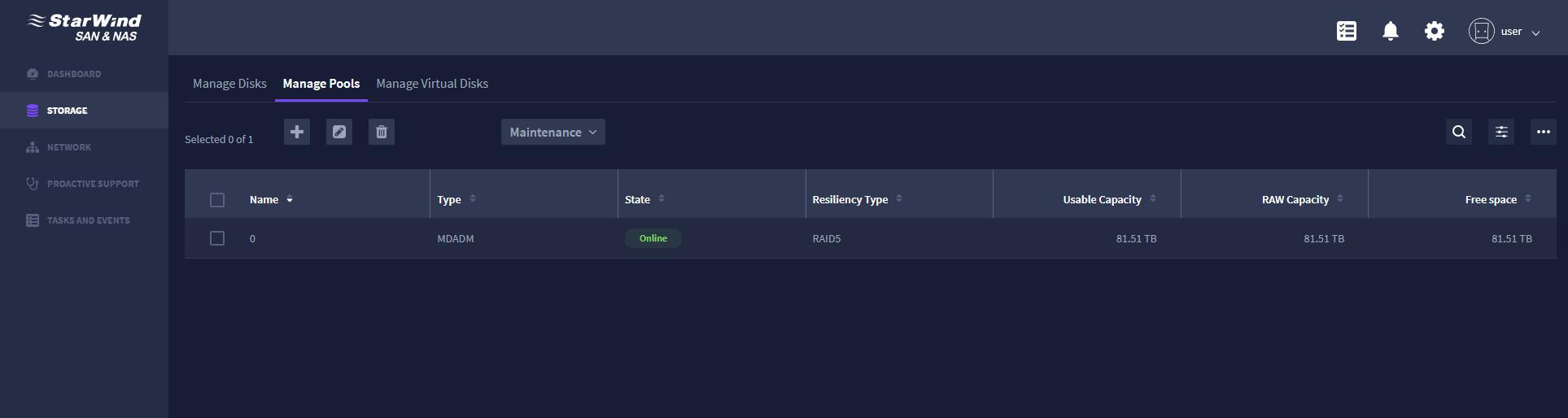
We have collected 8 NVMe drives on the storage node in RAID5 array:
First, using MDRAID:
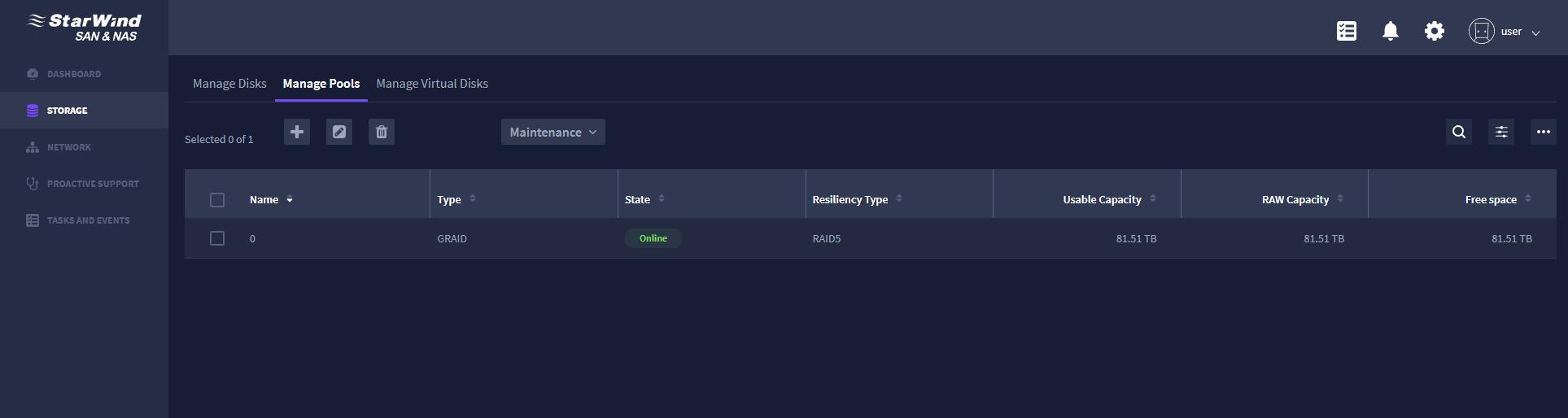
And then, with GRAID correspondingly:
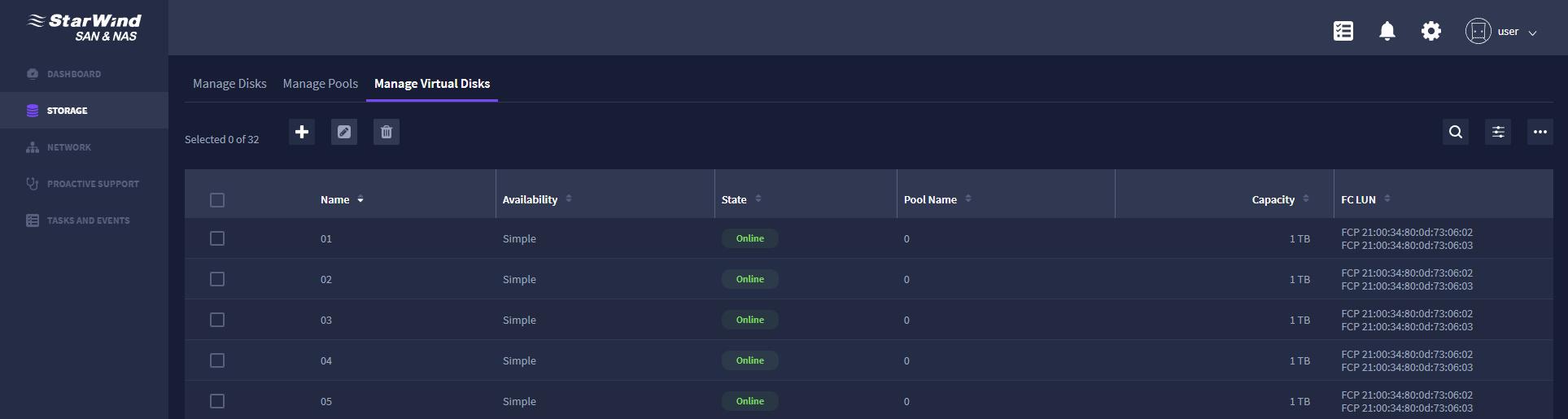
Once the RAID arrays were ready, we have sliced them into 32 LUNs, 1TB each. These were distributed by 8 LUNs per client node. This was done since 1 LUN has a performance limitation and we wanted to squeeze max out of our storage.
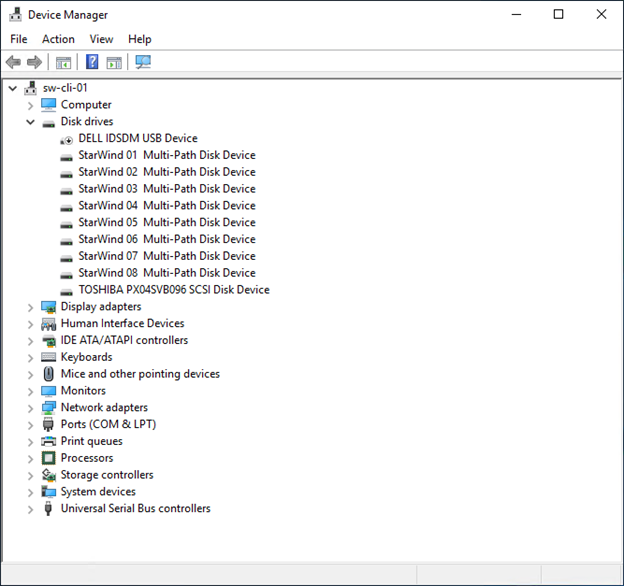
This is the example of 8 LUNs connected on one client node:
Testing Methodology
The benchmark was held using the fio utility. fio is a cross-platform, industry-standard benchmark tool used to test local storage as well as shared.
Testing patterns:
- 4k random read;
- 4k random write;
- 4k random read/write 70/30;
- 64K random read;
- 64K random write;
- 1M sequential read;
- 1M sequential write.
Test duration:
- Single test duration = 600 seconds;
- Before starting the write benchmark, storage has been first warmed ups for 2 hours;
Testing stages
- Testing single NVMe drive performance to get reference numbers;
- Testing MDRAID and GRAID RAID5 arrays performance locally;
- Running benchmark remotely from client nodes.
1. Testing single NVMe drive performance:
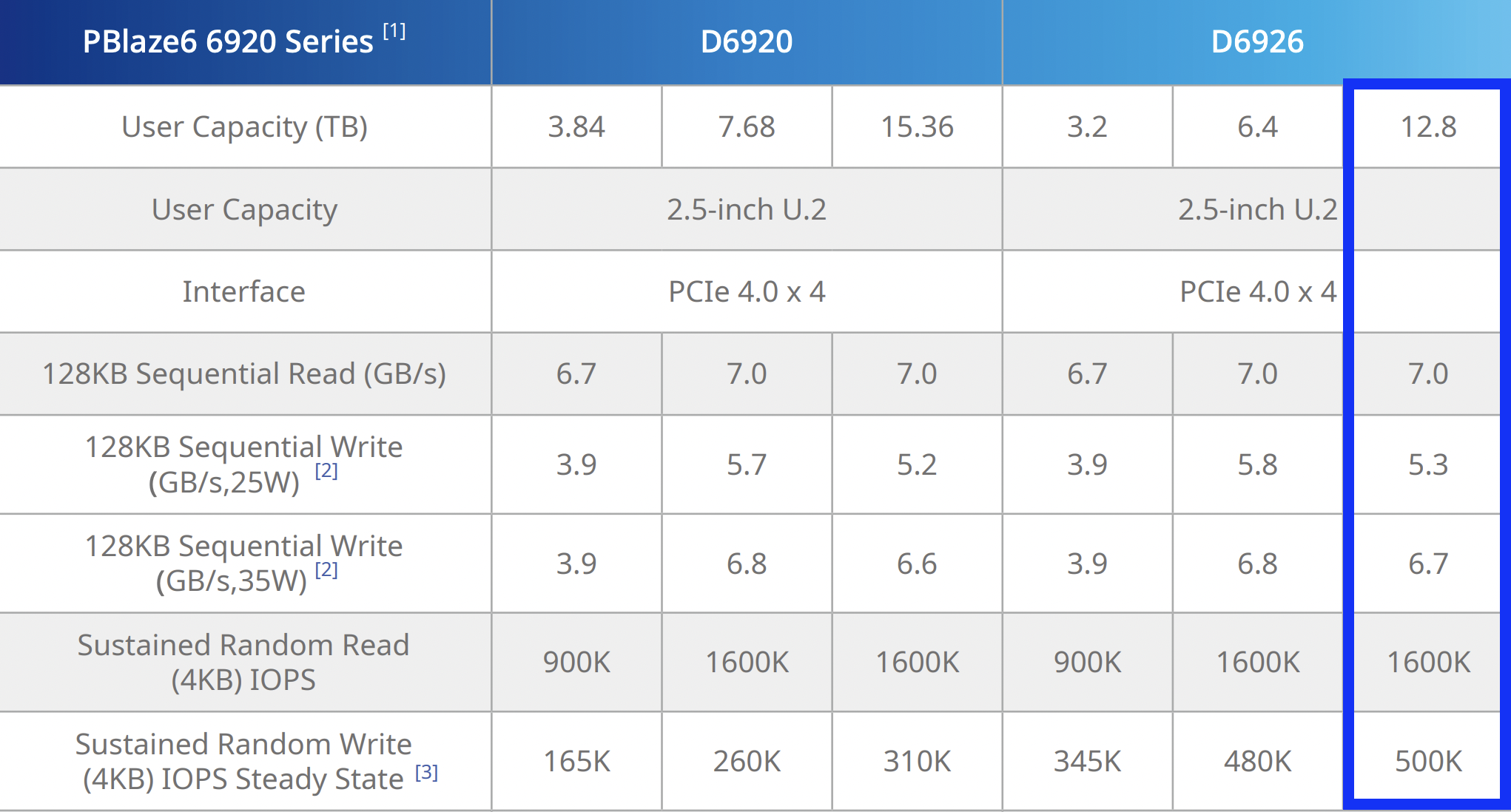
The values for NVMe drive speed according to the vendor
Talking about these NVMe SSDs, an interesting thing is that they support 10W~35W flexible power management and 25W power mode by default. Basically, Memblaze’s NVMe drives increase performance on sequential writes by consuming more power, which gives a flexible way to tune drive performance as per specific workload.
We have received the optimal (speed/latency) performance patterns of a single NVMe drive under the following number of jobs and IO depth values:
| 1 NVMe PBlaze6 D6926 Series 12.8TB | |||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
| 4k random read | 16 | 32 | 1514000 | 5914 | 0,337 |
| 4k random write | 4 | 4 | 537000 | 2096 | 0,029 |
| 64k random read | 4 | 8 | 103000 | 6467 | 0,308 |
| 64k random write | 2 | 2 | 42000 | 2626 | 0,094 |
| 1M read | 1 | 4 | 6576 | 6576 | 0,607 |
| 1M write | 1 | 2 | 5393 | 5393 | 0,370 |
Before running the actual tests, we have determined the time needed to warm up these NVMe drives to Steady State:
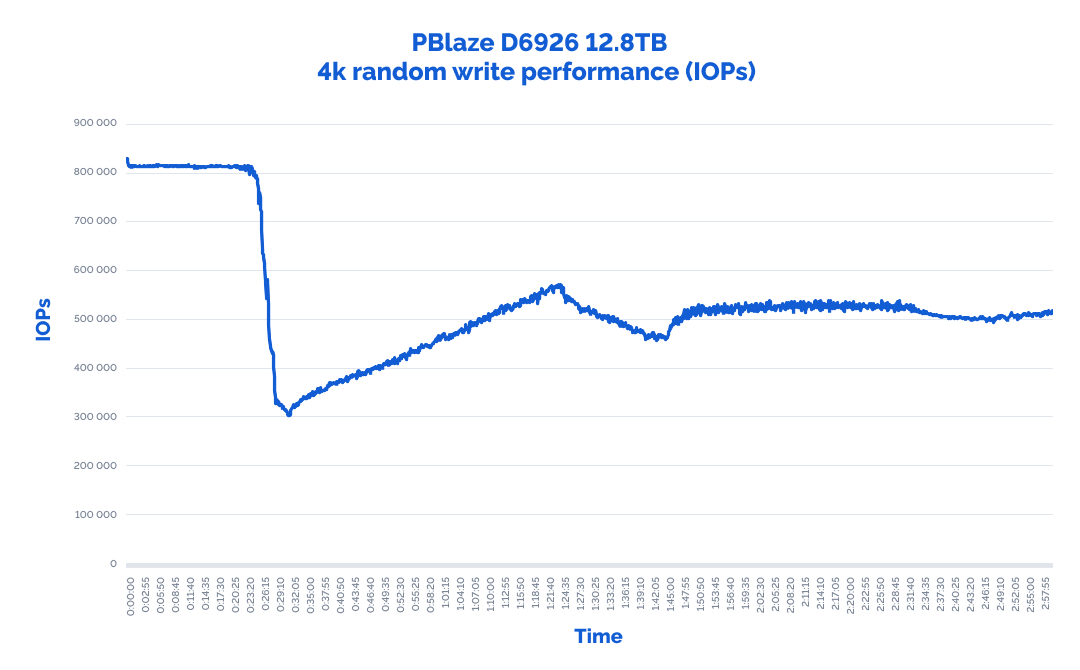
P.S. You can find more information about Performance States here.
From the graph, it was visible that the NVMe drives should be warmed up for around 2 hours.
2. Testing MD and GRAID RAID arrays performance locally:
Less words, more numbers. Heading to MDRAID and GRAID local performance tests.
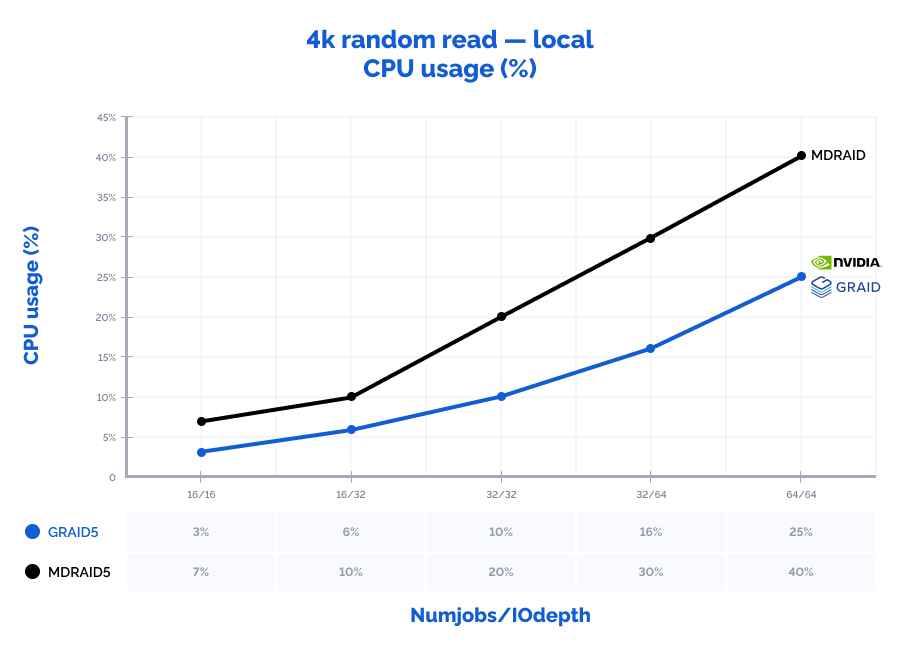
4k random read:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | ||||||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage |
| 4k random read | 16 | 16 | 2670000 | 10430 | 0,095 | 7% | 1281000 | 5004 | 0,198 | 3% | 48% | 48% | 208% | 46% |
| 4k random read | 16 | 32 | 3591000 | 14027 | 0,141 | 10% | 2451000 | 9574 | 0,207 | 6% | 68% | 68% | 147% | 60% |
| 4k random read | 32 | 32 | 4049000 | 15816 | 0,250 | 20% | 4474000 | 17477 | 0,227 | 10% | 110% | 110% | 91% | 50% |
| 4k random read | 32 | 64 | 4032000 | 15750 | 0,504 | 30% | 7393000 | 28879 | 0,275 | 16% | 183% | 183% | 55% | 53% |
| 4k random read | 64 | 64 | 4061000 | 15863 | 0,998 | 40% | 10800000 | 42188 | 0,377 | 25% | 266% | 266% | 38% | 63% |
Graphs:
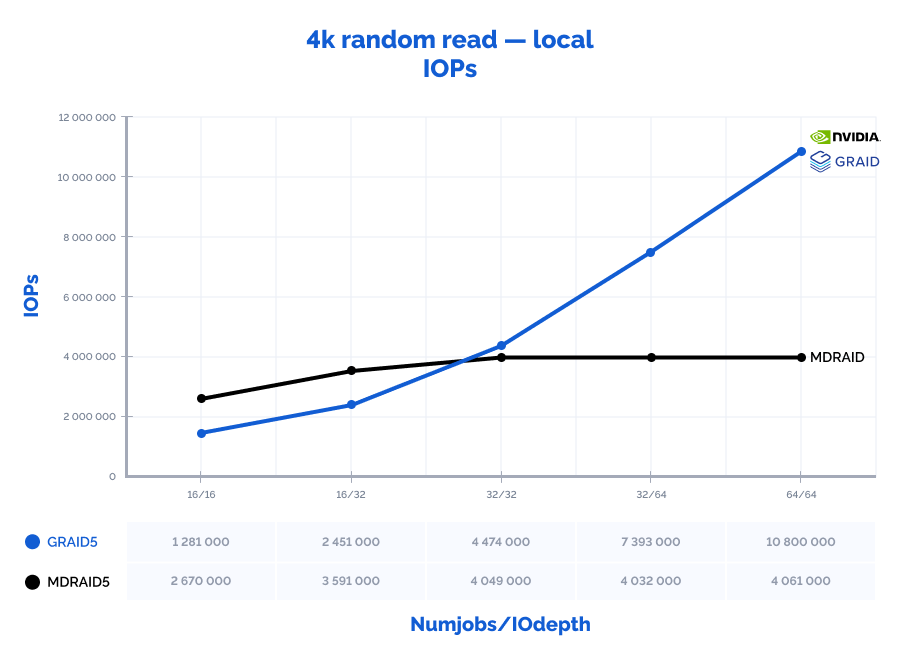
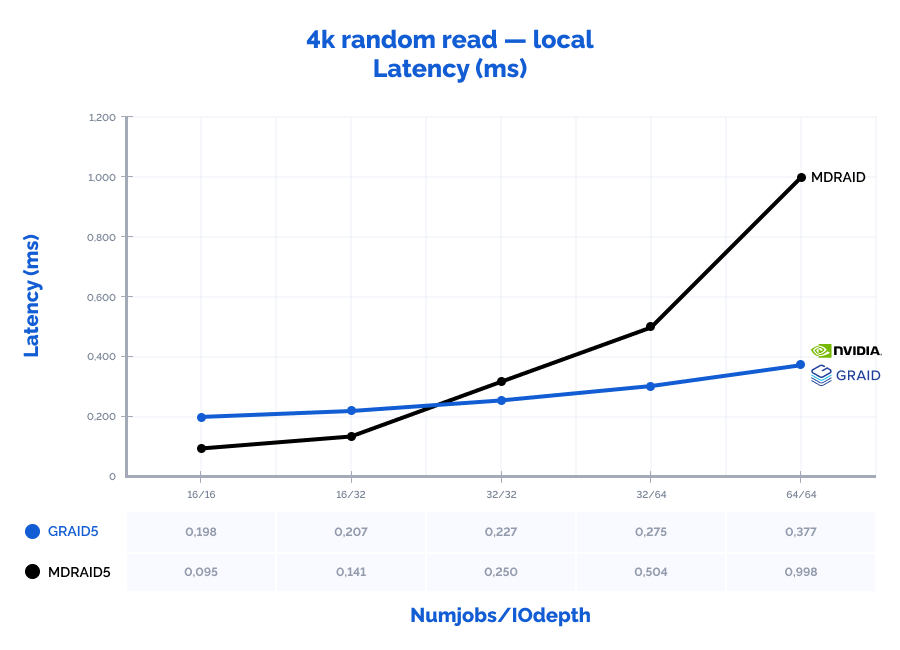
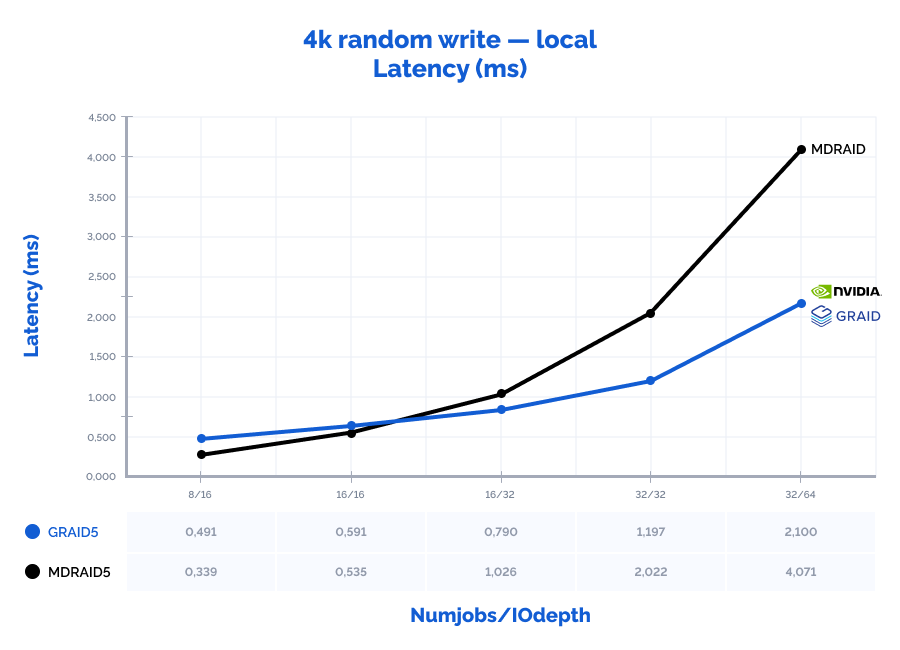
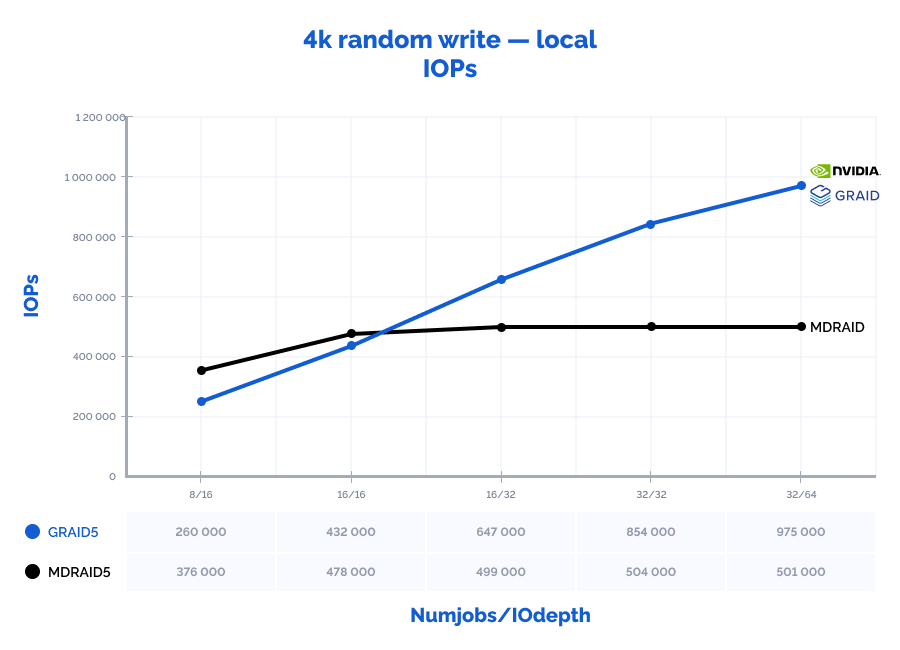
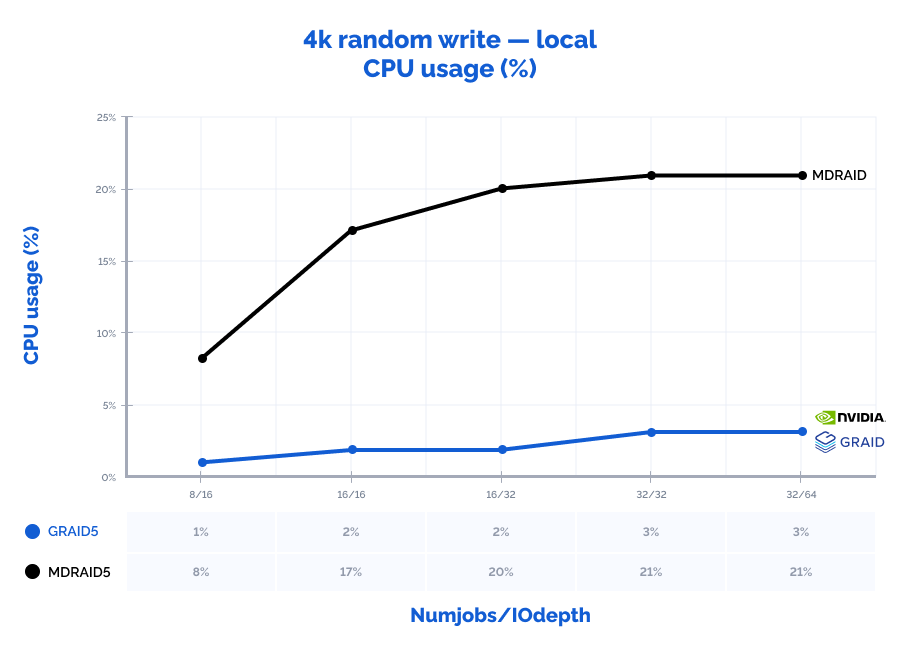
4k random write:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5* | Comparison | ||||||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage |
| 4k random write | 8 | 16 | 376000 | 1469 | 0,339 | 8% | 260000 | 1016 | 0,491 | 1% | 69% | 69% | 145% | 13% |
| 4k random write | 16 | 16 | 478000 | 1867 | 0,535 | 17% | 432000 | 1688 | 0,591 | 2% | 90% | 90% | 110% | 9% |
| 4k random write | 16 | 32 | 499000 | 1949 | 1,026 | 20% | 647000 | 2527 | 0,790 | 2% | 130% | 130% | 77% | 10% |
| 4k random write | 32 | 32 | 504000 | 1969 | 2,022 | 21% | 854000 | 3336 | 1,197 | 3% | 169% | 169% | 59% | 12% |
| 4k random write | 32 | 64 | 501000 | 1957 | 4,071 | 21% | 975000 | 3809 | 2,100 | 3% | 195% | 195% | 52% | 12% |
* – in order to get maximum performance of 1.5M IOPs with GRAID SR-1010, you need PCIe Gen4x16. Our server however had only Gen4x8 PCIe slots.
Graphs:
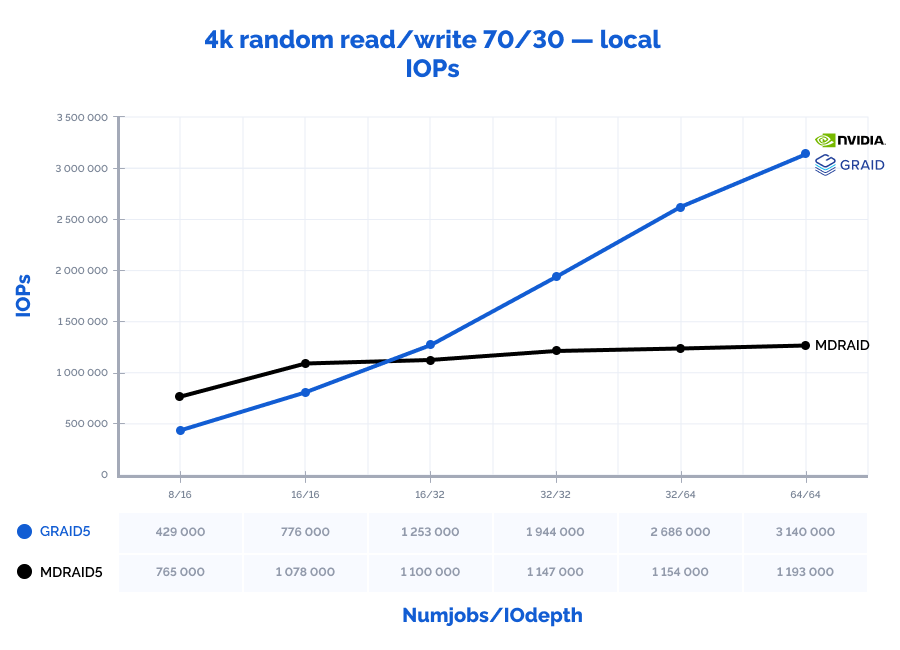
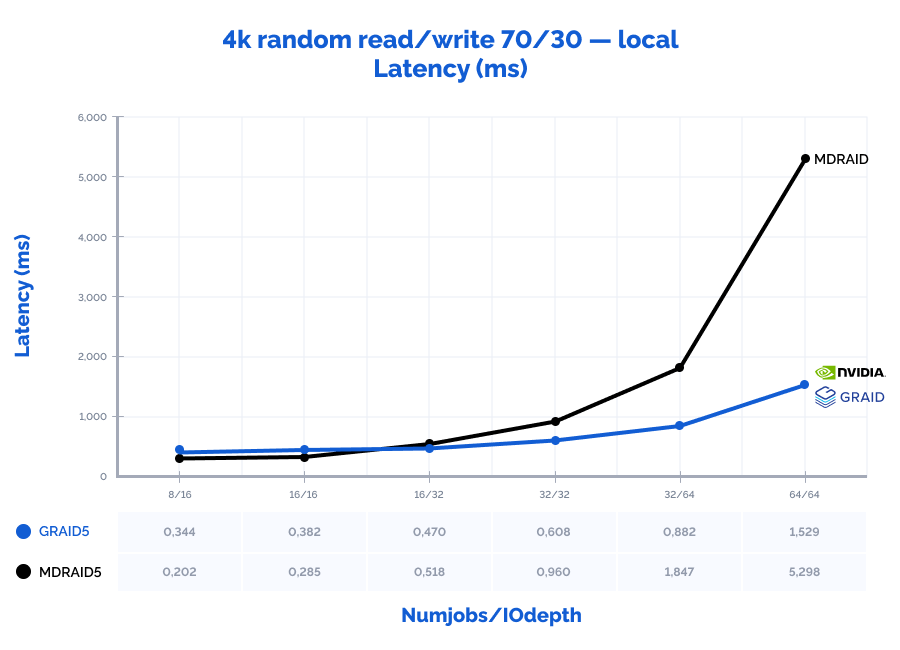
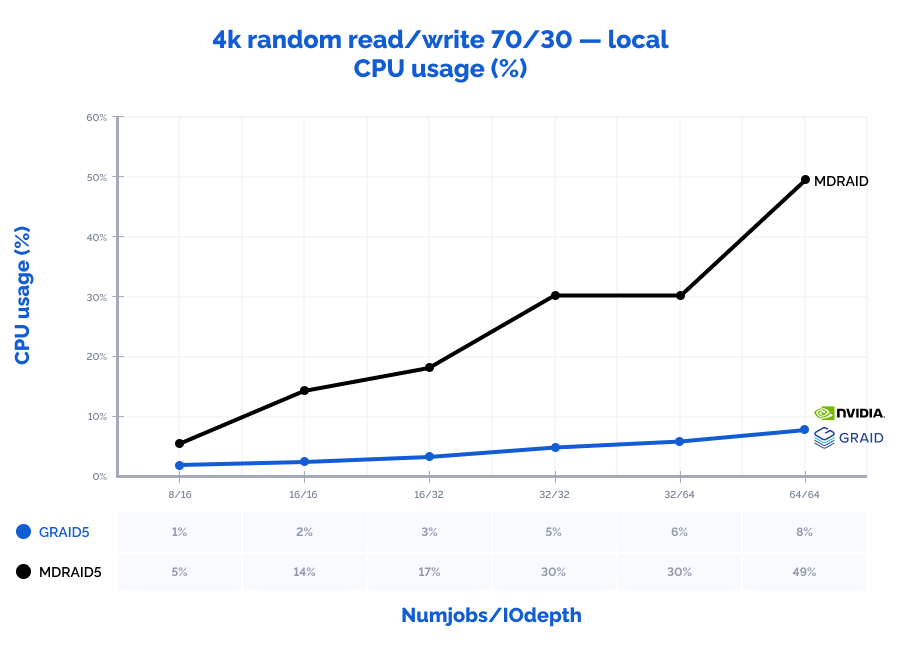
4k random read/write 70/30:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | ||||||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 8 | 16 | 765000 | 2988 | 0,202 | 5% | 429000 | 1676 | 0,344 | 1% | 56% | 56% | 170% | 31% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 16 | 16 | 1078000 | 4211 | 0,285 | 14% | 776000 | 3031 | 0,382 | 2% | 72% | 72% | 134% | 14% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 16 | 32 | 1100000 | 4297 | 0,518 | 17% | 1253000 | 4895 | 0,470 | 3% | 114% | 114% | 91% | 18% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 32 | 32 | 1147000 | 4480 | 0,960 | 30% | 1944000 | 7594 | 0,608 | 5% | 169% | 169% | 63% | 15% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 32 | 64 | 1154000 | 4508 | 1,847 | 30% | 2686000 | 10492 | 0,882 | 6% | 233% | 233% | 48% | 20% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 64 | 64 | 1193000 | 4660 | 5,298 | 49% | 3140000 | 12266 | 1,529 | 8% | 263% | 263% | 29% | 15% |
Graphs:
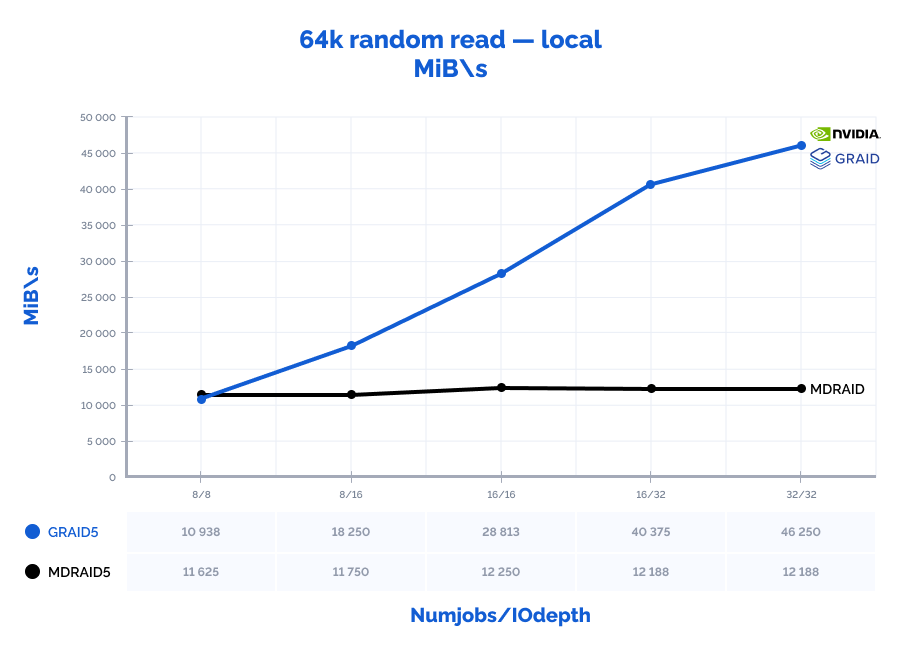
64k random read:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | ||||||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage |
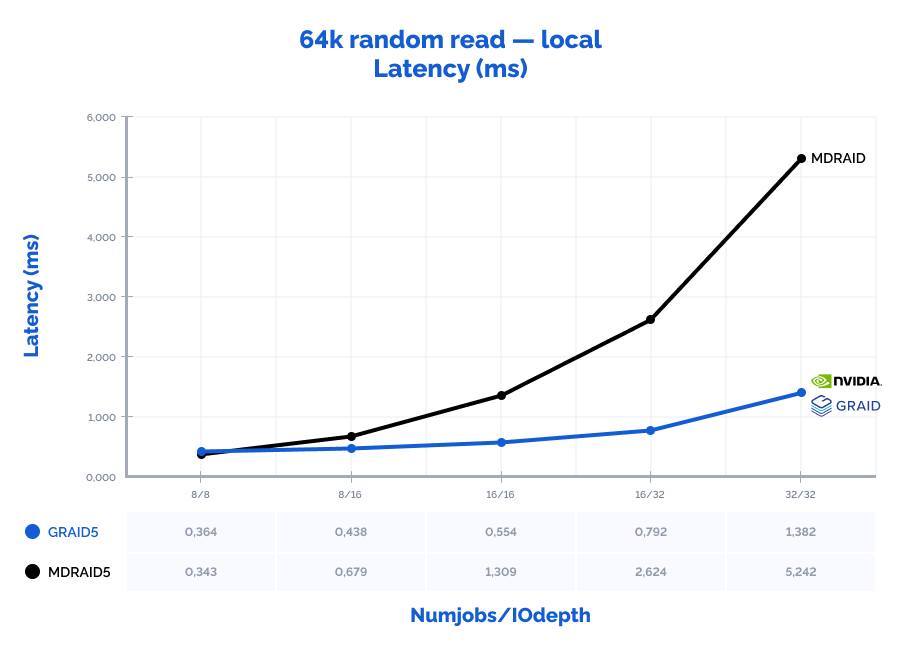
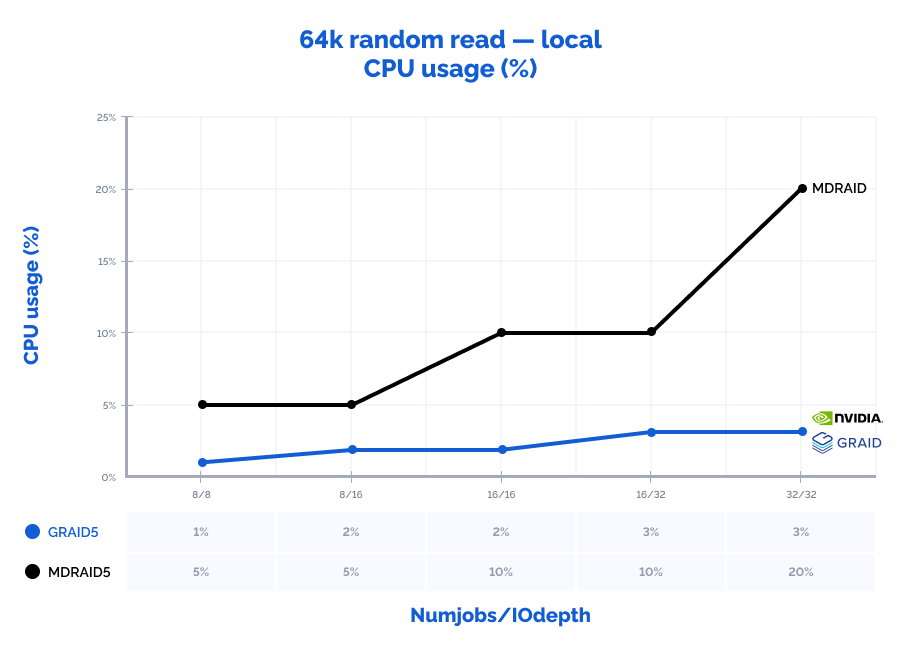
| 64k random read | 8 | 8 | 186000 | 11625 | 0,343 | 5% | 175000 | 10938 | 0,364 | 1% | 94% | 94% | 106% | 16% |
| 64k random read | 8 | 16 | 188000 | 11750 | 0,679 | 5% | 292000 | 18250 | 0,438 | 2% | 155% | 155% | 65% | 30% |
| 64k random read | 16 | 16 | 196000 | 12250 | 1,309 | 10% | 461000 | 28813 | 0,554 | 2% | 235% | 235% | 42% | 20% |
| 64k random read | 16 | 32 | 195000 | 12188 | 2,624 | 10% | 646000 | 40375 | 0,792 | 3% | 331% | 331% | 30% | 30% |
| 64k random read | 32 | 32 | 195000 | 12188 | 5,242 | 20% | 740000 | 46250 | 1,382 | 3% | 379% | 379% | 26% | 15% |
Graphs:
64k random write:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | ||||||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage |
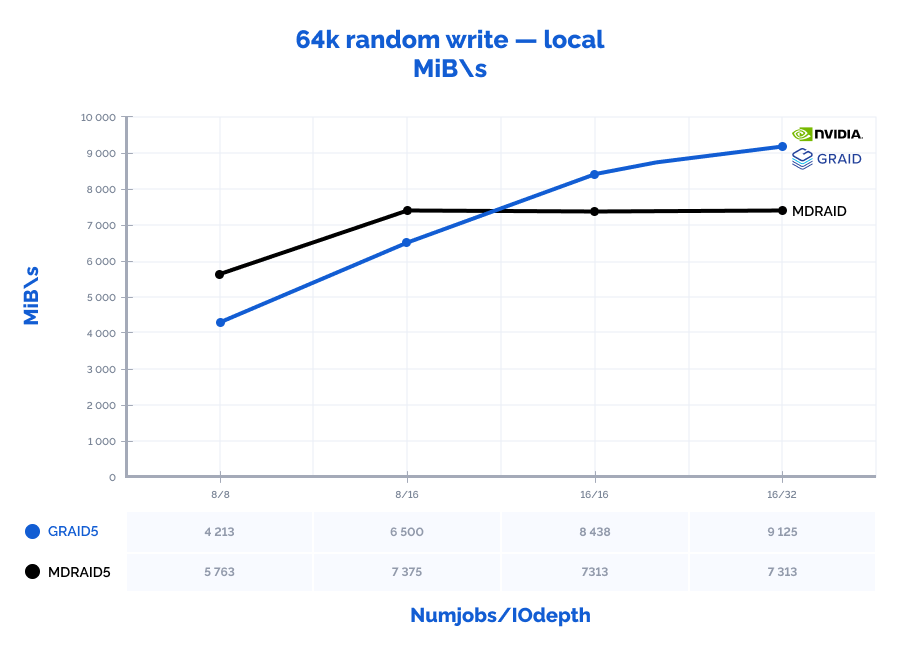
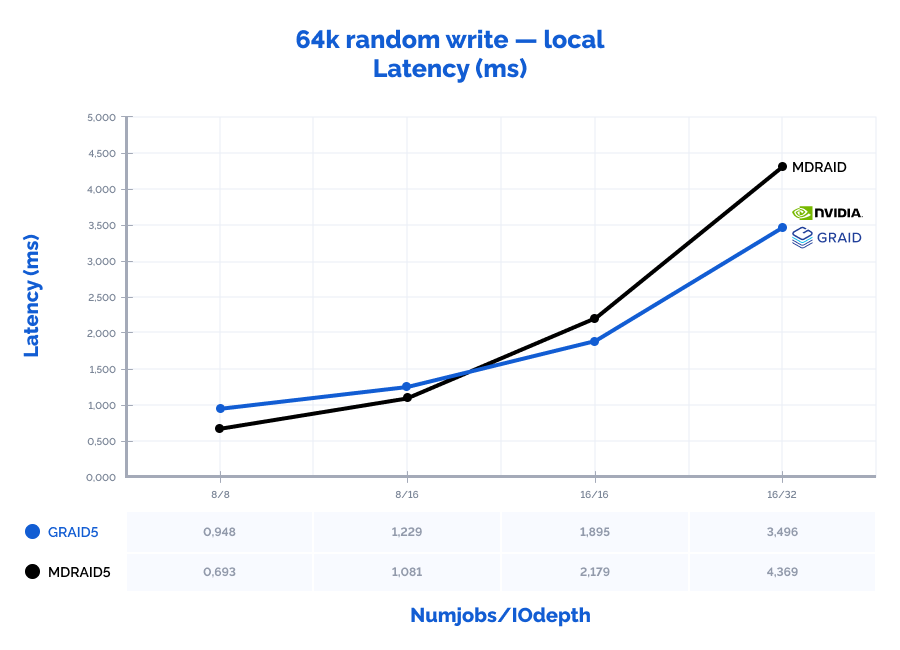
| 64k random write | 8 | 8 | 92200 | 5763 | 0,693 | 7% | 67400 | 4213 | 0,948 | 1% | 73% | 73% | 137% | 10% |
| 64k random write | 8 | 16 | 118000 | 7375 | 1,081 | 14% | 104000 | 6500 | 1,229 | 1% | 88% | 88% | 114% | 10% |
| 64k random write | 16 | 16 | 117000 | 7313 | 2,179 | 16% | 135000 | 8438 | 1,895 | 2% | 115% | 115% | 87% | 11% |
| 64k random write | 16 | 32 | 117000 | 7313 | 4,369 | 16% | 146000 | 9125 | 3,496 | 2% | 125% | 125% | 80% | 13% |
Graphs:
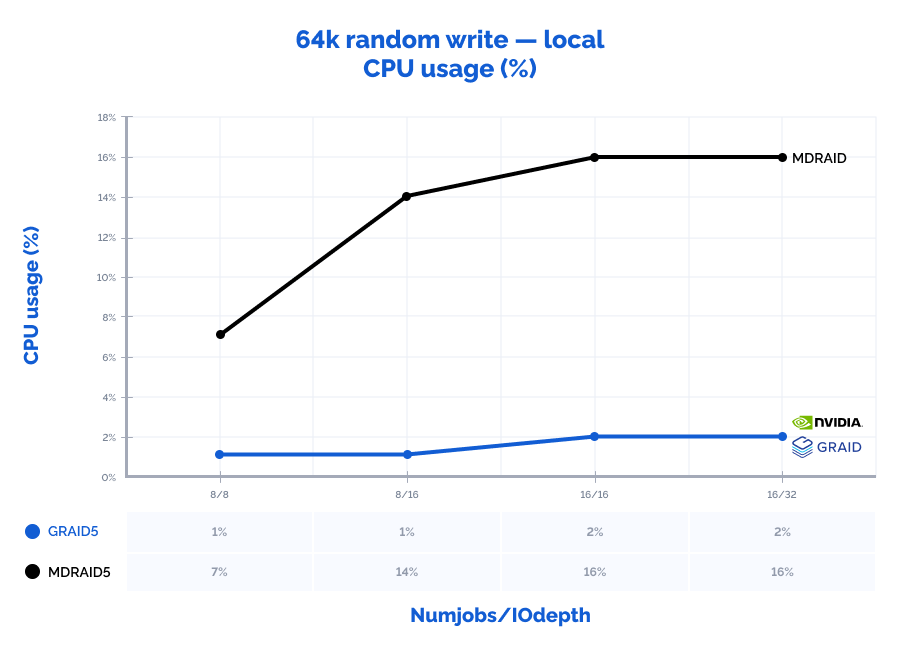
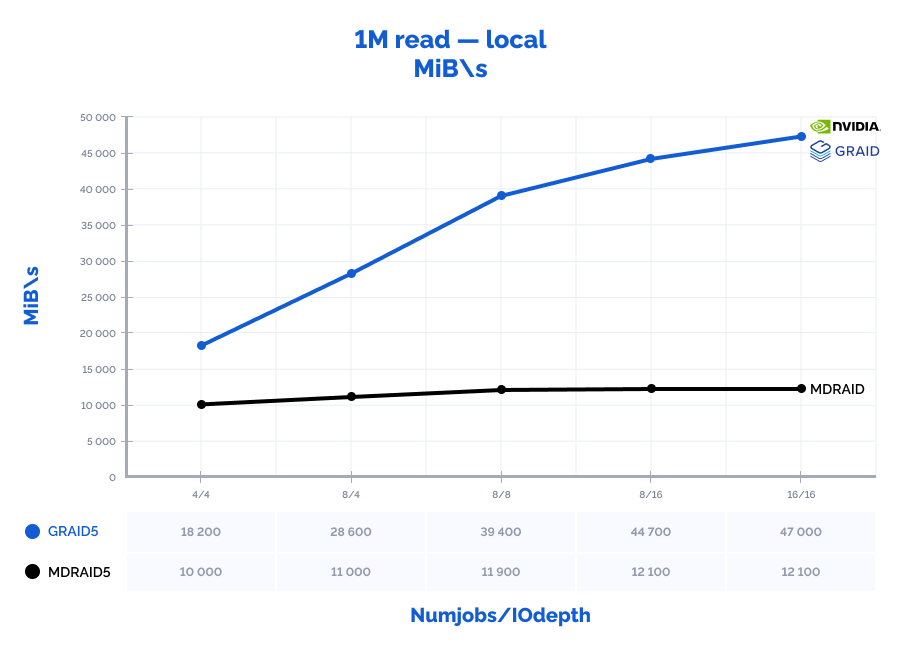
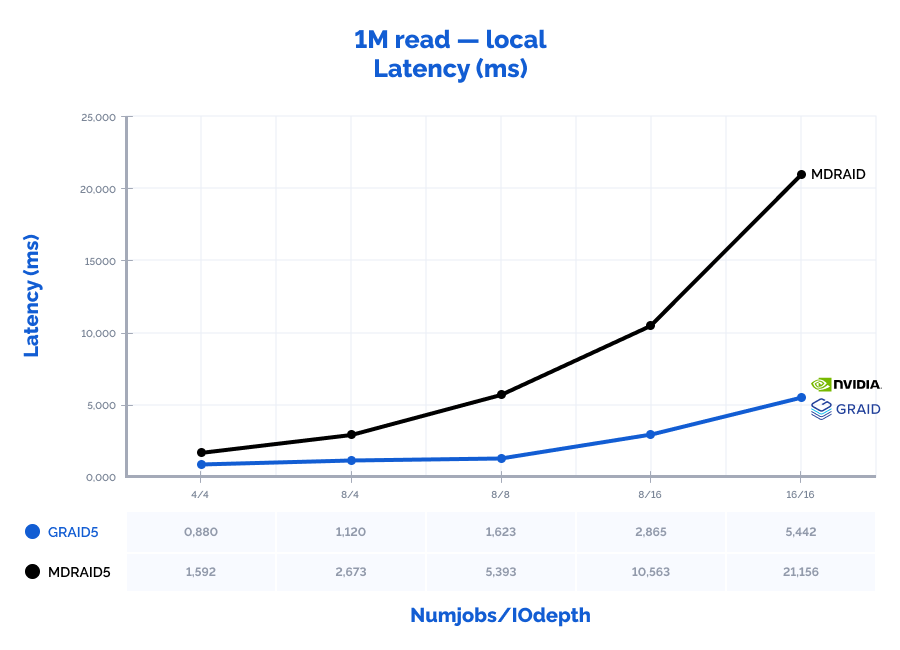
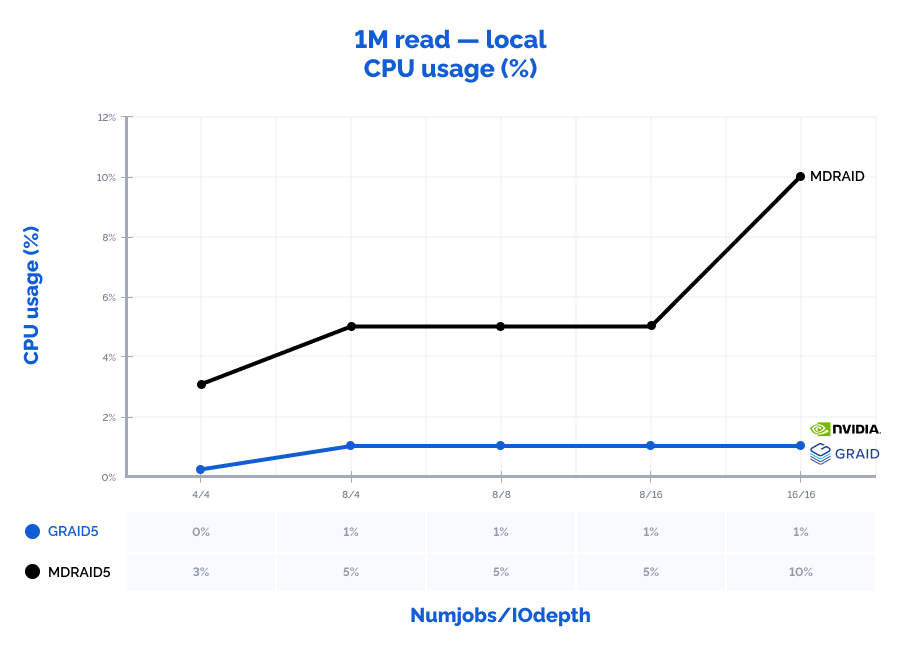
1M read:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | ||||||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage |
| 1M read | 4 | 4 | 10000 | 10000 | 1,592 | 3% | 18200 | 18200 | 0,880 | 0% | 182% | 182% | 55% | 12% |
| 1M read | 8 | 4 | 11000 | 11000 | 2,673 | 5% | 28600 | 28600 | 1,120 | 1% | 260% | 260% | 42% | 10% |
| 1M read | 8 | 8 | 11900 | 11900 | 5,393 | 5% | 39400 | 39400 | 1,623 | 1% | 331% | 331% | 30% | 10% |
| 1M read | 8 | 16 | 12100 | 12100 | 10,563 | 5% | 44700 | 44700 | 2,865 | 1% | 369% | 369% | 27% | 12% |
| 1M read | 16 | 16 | 12100 | 12100 | 21,156 | 10% | 47000 | 47000 | 5,442 | 1% | 388% | 388% | 26% | 6% |
Graphs:
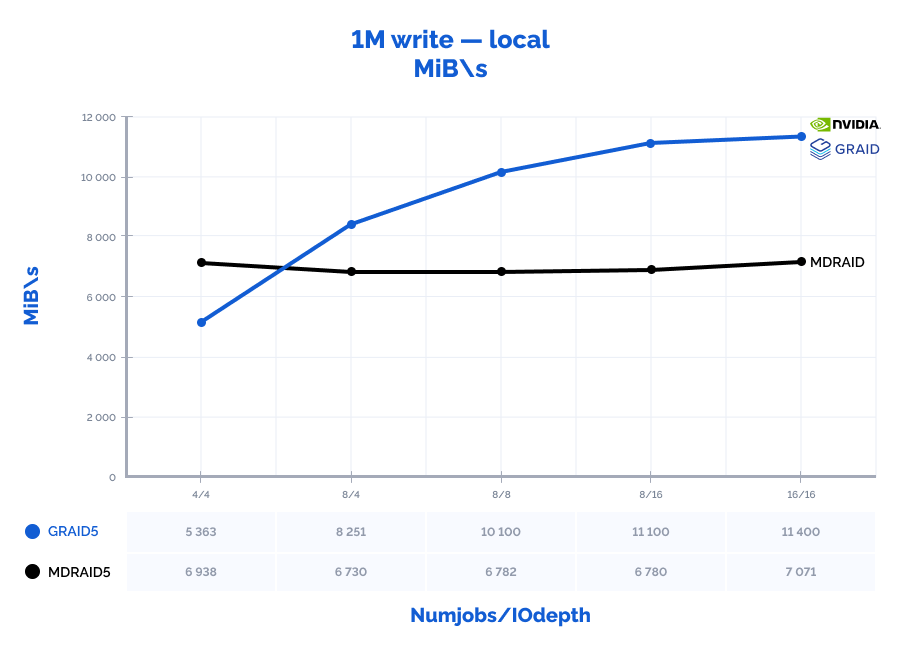
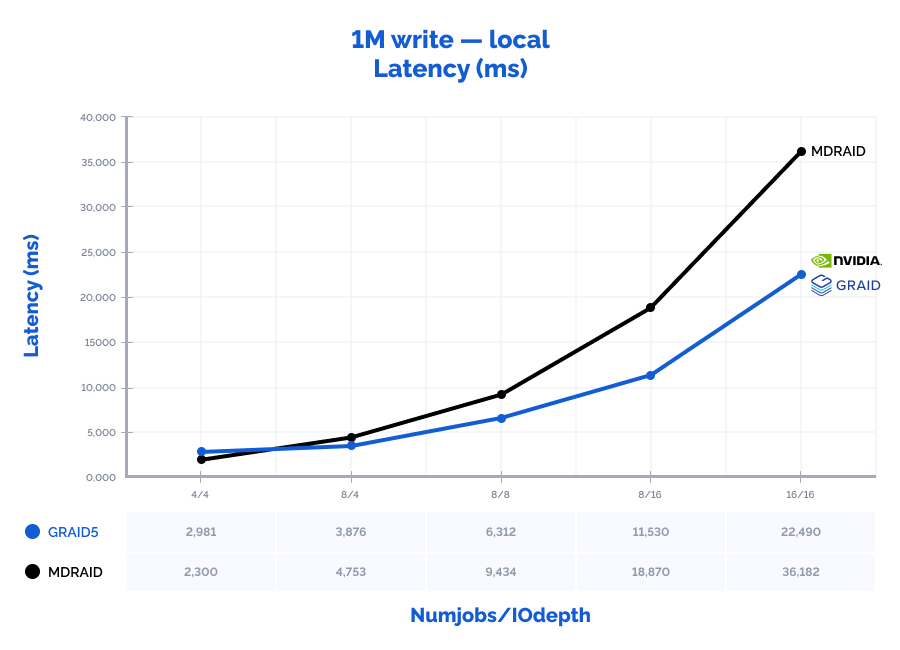
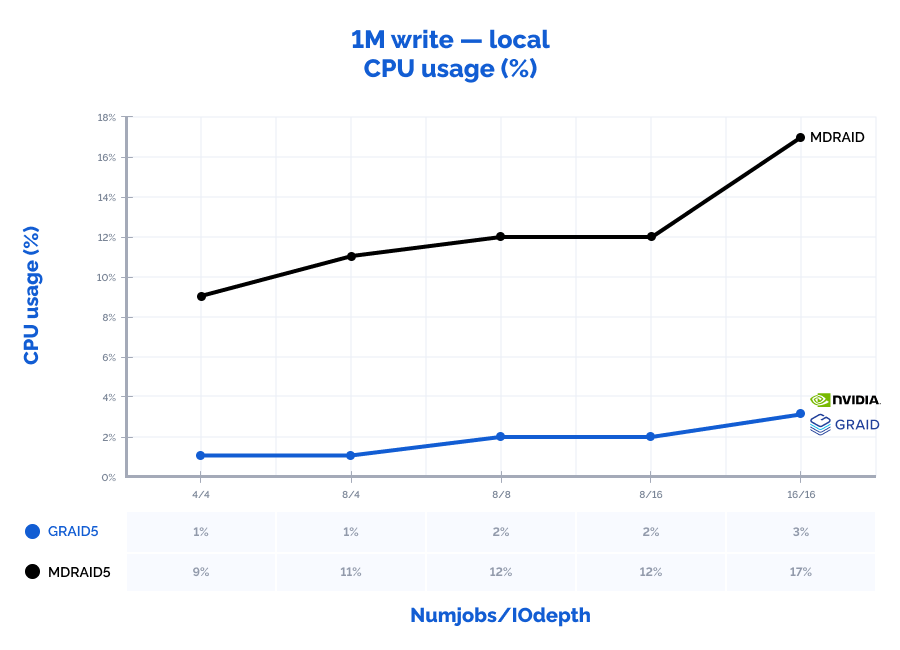
1M write:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | ||||||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | CPU usage |
| 1M write | 4 | 4 | 6938 | 6938 | 2,300 | 9% | 5363 | 5363 | 2,981 | 1% | 77% | 77% | 130% | 9% |
| 1M write | 8 | 4 | 6730 | 6730 | 4,753 | 11% | 8251 | 8251 | 3,876 | 1% | 123% | 123% | 82% | 12% |
| 1M write | 8 | 8 | 6782 | 6782 | 9,434 | 12% | 10100 | 10100 | 6,312 | 2% | 149% | 149% | 67% | 17% |
| 1M write | 8 | 16 | 6780 | 6780 | 18,870 | 12% | 11100 | 11100 | 11,530 | 2% | 164% | 164% | 61% | 17% |
| 1M write | 16 | 16 | 7071 | 7071 | 36,182 | 17% | 11400 | 11400 | 22,490 | 3% | 161% | 161% | 62% | 15% |
Graphs:
Results:
MDRAID shows decent performance on low Numjobs and IOdepth values but as the workload increases, so does the latency and performance stops growing. On the other hand, GRAID gives better results with high Numjobs and IOdepth values: on a 4k random read pattern, we have received the incredible 10,8M IOPs with the latency of just 0,377 ms. That is basically the speed of 7 NVMe drives out of 8. On large block reads 64k/1M, GRAID reaches the throughput of 40/47GiB/s., while MDRAID reached the ceiling with 12GiB/s.
3. Running benchmark remotely from client nodes:
Once we have received such an impressive local storage results, we were fully ready to give FCP a try and see if it can deliver comparable performance on the client nodes.
In the results below, Numjobs parameter is stated for all 32 LUNs.
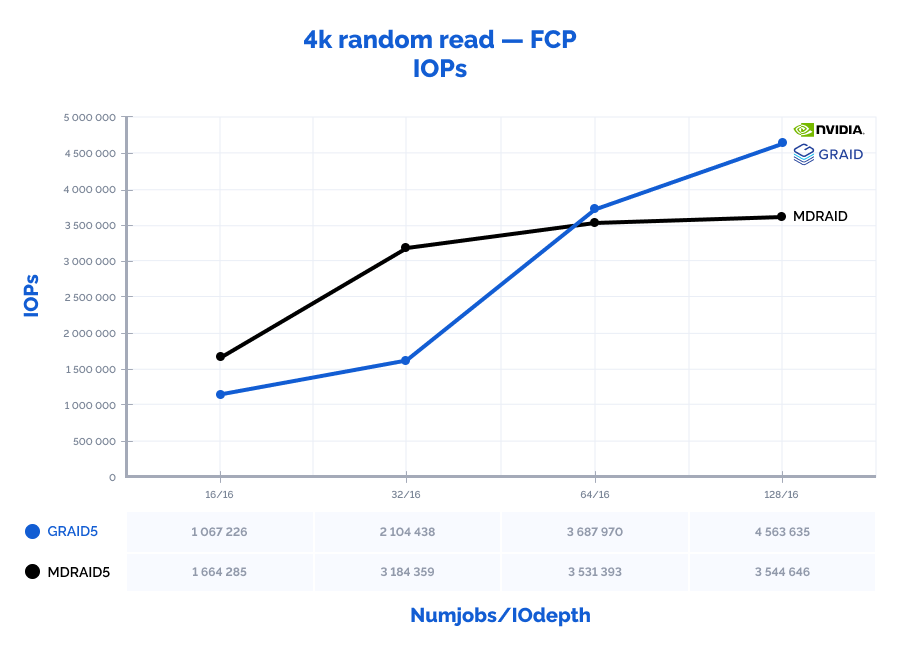
4k random read:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | |||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
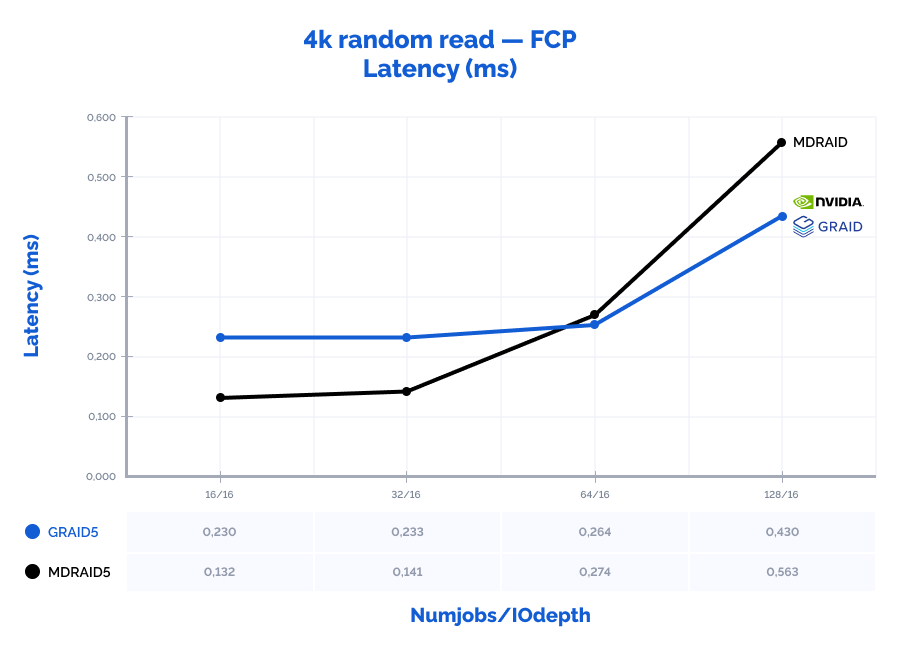
| 4k random read | 16 | 16 | 1664285 | 6501 | 0,132 | 1067226 | 4169 | 0,230 | 64% | 64% | 174% |
| 4k random read | 32 | 16 | 3184359 | 12439 | 0,141 | 2104438 | 8221 | 0,233 | 66% | 66% | 165% |
| 4k random read | 64 | 16 | 3531393 | 13795 | 0,274 | 3687970 | 14406 | 0,264 | 104% | 104% | 96% |
| 4k random read | 128 | 16 | 3544646 | 13847 | 0,563 | 4563635 | 17827 | 0,430 | 129% | 129% | 76% |
| 4k random read | 16 | 32 | 1783060 | 6965 | 0,199 | 1772981 | 6926 | 0,261 | 99% | 99% | 131% |
| 4k random read | 32 | 32 | 3500411 | 13674 | 0,253 | 3475477 | 13576 | 0,268 | 99% | 99% | 106% |
| 4k random read | 64 | 32 | 3532084 | 13797 | 0,563 | 4459783 | 17421 | 0,436 | 126% | 126% | 77% |
| 4k random read | 128 | 32 | 3549901 | 13867 | 1,139 | 4578663 | 17886 | 0,873 | 129% | 129% | 77% |
Graphs:
4k random write:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | |||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
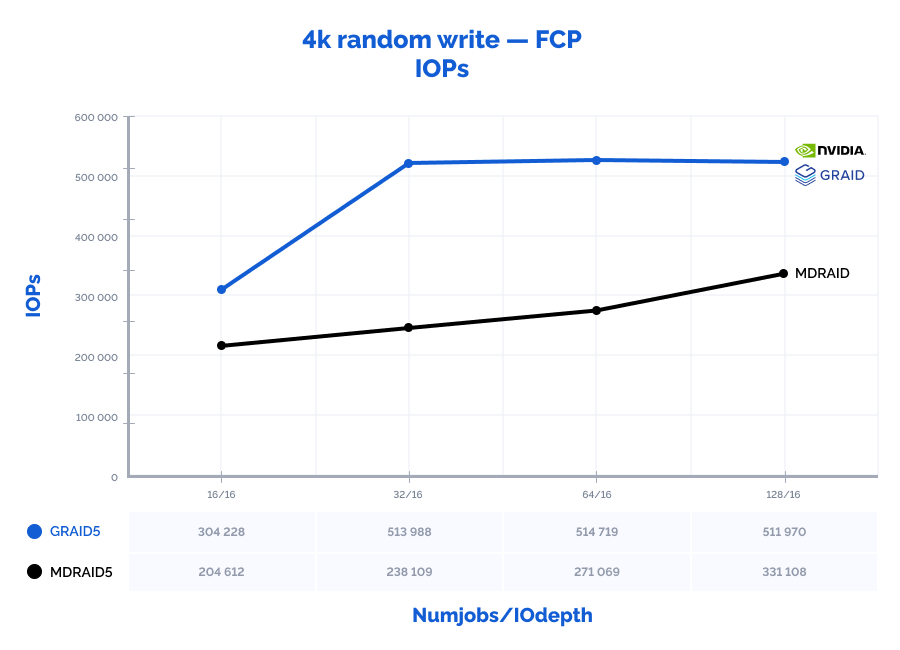
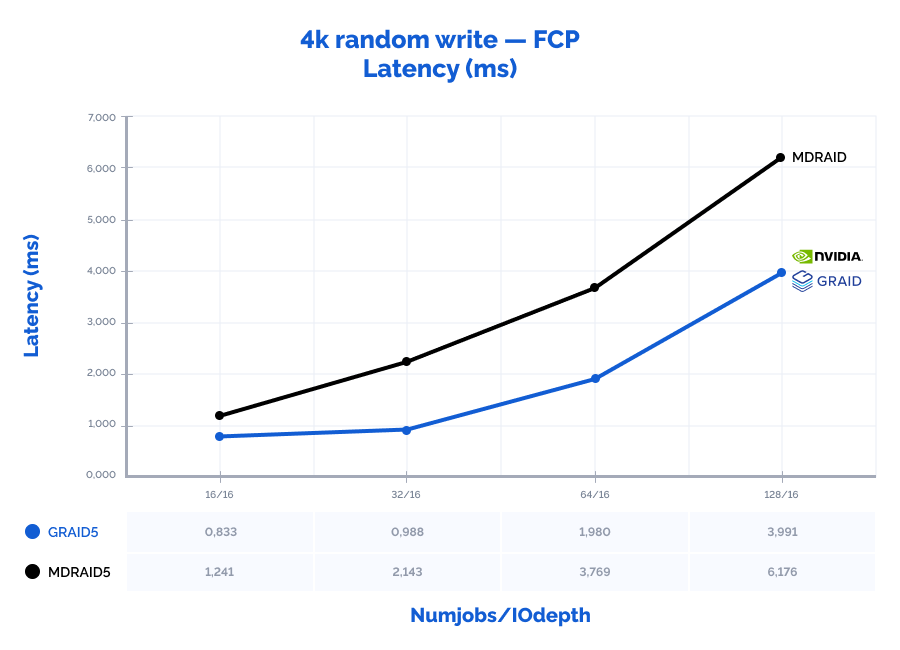
| 4k random write | 16 | 16 | 204612 | 799 | 1,241 | 304228 | 1188 | 0,833 | 149% | 149% | 67% |
| 4k random write | 32 | 16 | 238109 | 930 | 2,143 | 513988 | 2008 | 0,988 | 216% | 216% | 46% |
| 4k random write | 64 | 16 | 271069 | 1059 | 3,769 | 514719 | 2011 | 1,980 | 190% | 190% | 53% |
| 4k random write | 128 | 16 | 331108 | 1294 | 6,176 | 511970 | 2000 | 3,991 | 155% | 155% | 65% |
| 4k random write | 16 | 32 | 247398 | 966 | 2,059 | 307504 | 1201 | 1,657 | 124% | 124% | 80% |
| 4k random write | 32 | 32 | 285527 | 1115 | 3,578 | 512118 | 2001 | 1,992 | 179% | 179% | 56% |
| 4k random write | 64 | 32 | 341017 | 1332 | 5,996 | 491534 | 1920 | 4,157 | 144% | 144% | 69% |
| 4k random write | 128 | 32 | 385361 | 1506 | 10,617 | 498065 | 1946 | 8,212 | 129% | 129% | 77% |
Graphs:
4k random read/write 70/30:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | |||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
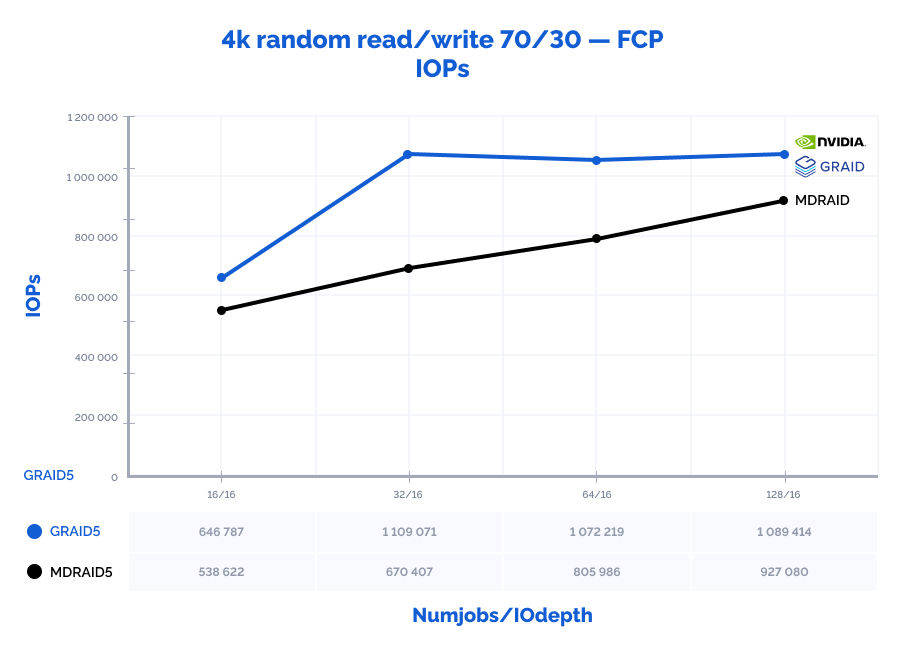
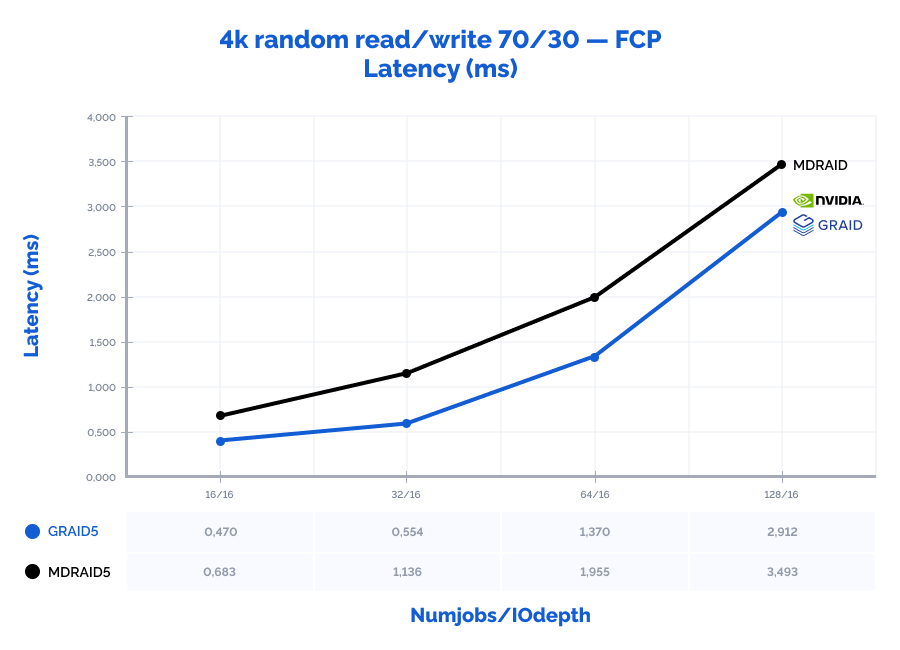
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 16 | 16 | 538622 | 2104 | 0,683 | 646787 | 2 527 | 0,470 | 120% | 120% | 69% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 32 | 16 | 670407 | 2619 | 1,136 | 1109071 | 4 332 | 0,554 | 165% | 165% | 49% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 64 | 16 | 805986 | 3149 | 1,955 | 1072219 | 4 188 | 1,370 | 133% | 133% | 70% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 128 | 16 | 927080 | 3622 | 3,493 | 1089414 | 4 256 | 2,912 | 118% | 118% | 83% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 16 | 32 | 700225 | 2735 | 1,065 | 644987 | 2 520 | 1,133 | 92% | 92% | 106% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 32 | 32 | 817516 | 3194 | 1,928 | 1103024 | 4 309 | 1,329 | 135% | 135% | 69% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 64 | 32 | 933090 | 3645 | 3,471 | 1098277 | 4 290 | 2,888 | 118% | 118% | 83% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 128 | 32 | 997943 | 3899 | 6,616 | 1061938 | 4 149 | 6,202 | 106% | 106% | 94% |
Graphs:
64k random read:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | |||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
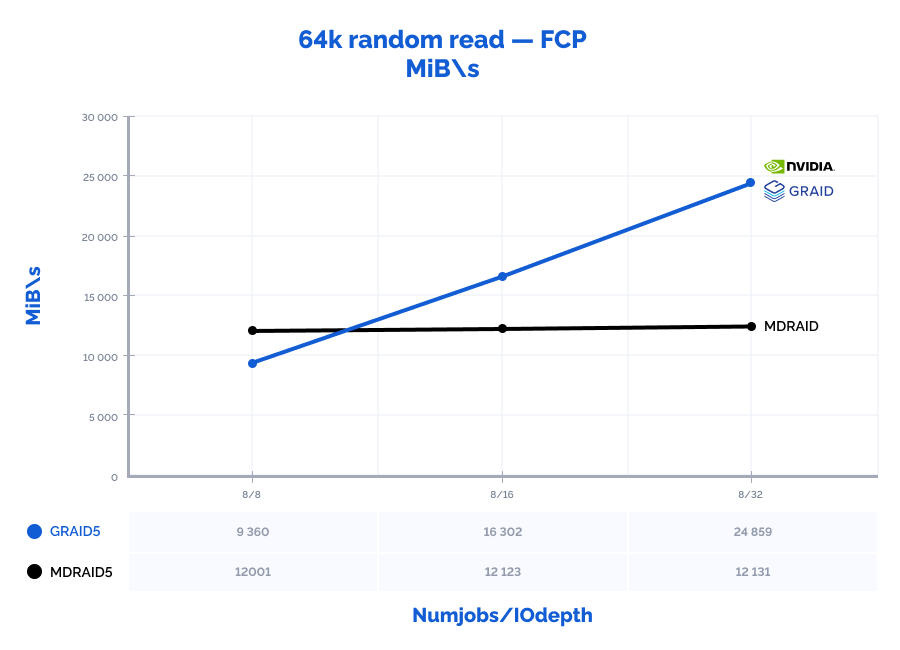
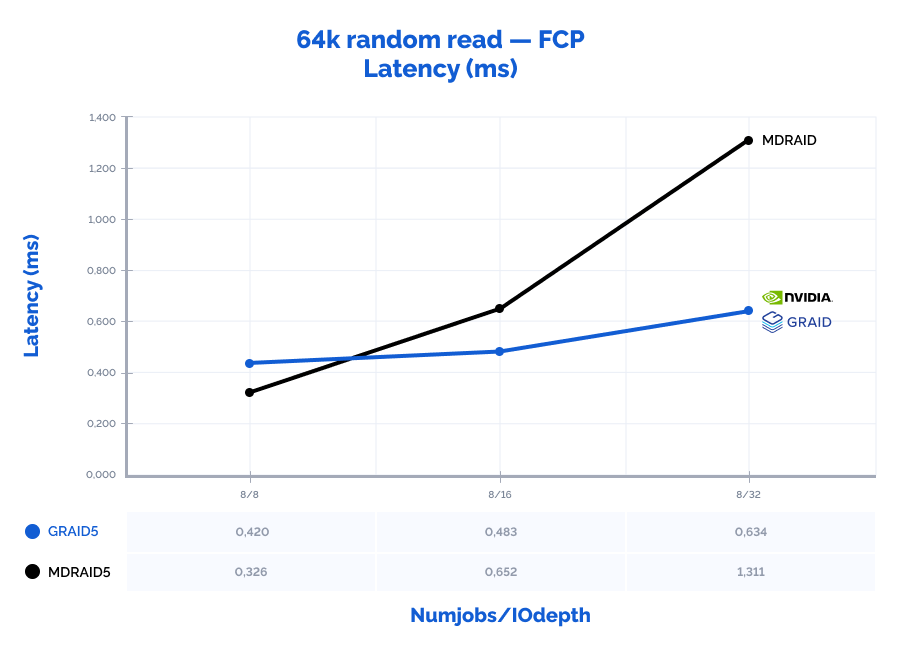
| random read 64K | 8 | 8 | 192015 | 12001 | 0,326 | 149755 | 9360 | 0,420 | 78% | 78% | 129% |
| random read 64K | 8 | 16 | 193967 | 12123 | 0,652 | 260821 | 16302 | 0,483 | 134% | 134% | 74% |
| random read 64K | 8 | 32 | 194089 | 12131 | 1,311 | 397736 | 24859* | 0,634 | 205% | 205% | 48% |
* – throughput limitation of our FC adapters (3200MB\s * 8 ports = 25600MB\s).
Graphs:
64k random write:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | |||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
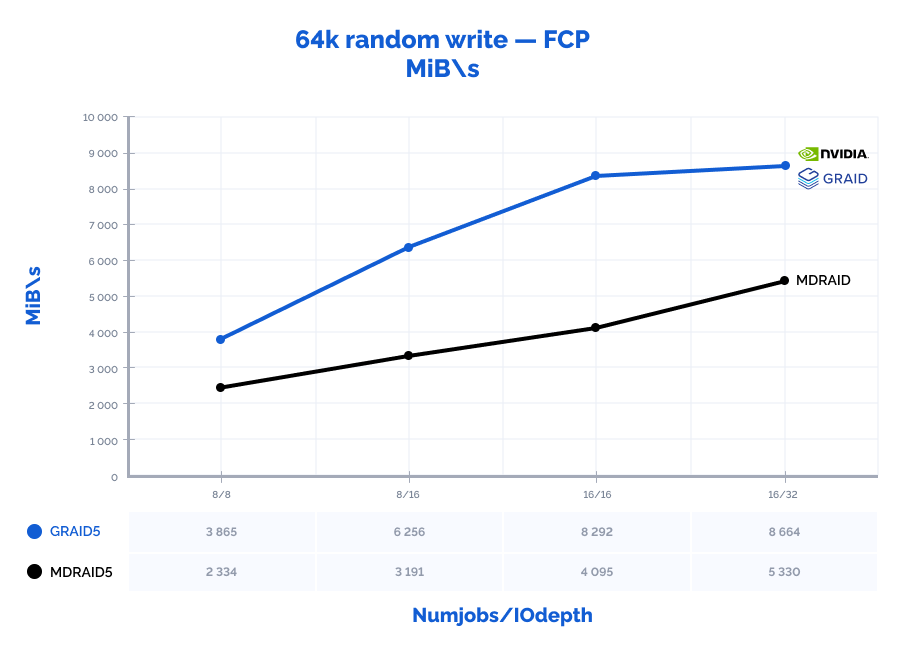
| random write 64K | 8 | 8 | 37343 | 2334 | 1,705 | 61839 | 3865 | 1,027 | 166% | 166% | 60% |
| random write 64K | 8 | 16 | 51048 | 3191 | 2,497 | 100093 | 6256 | 1,269 | 196% | 196% | 51% |
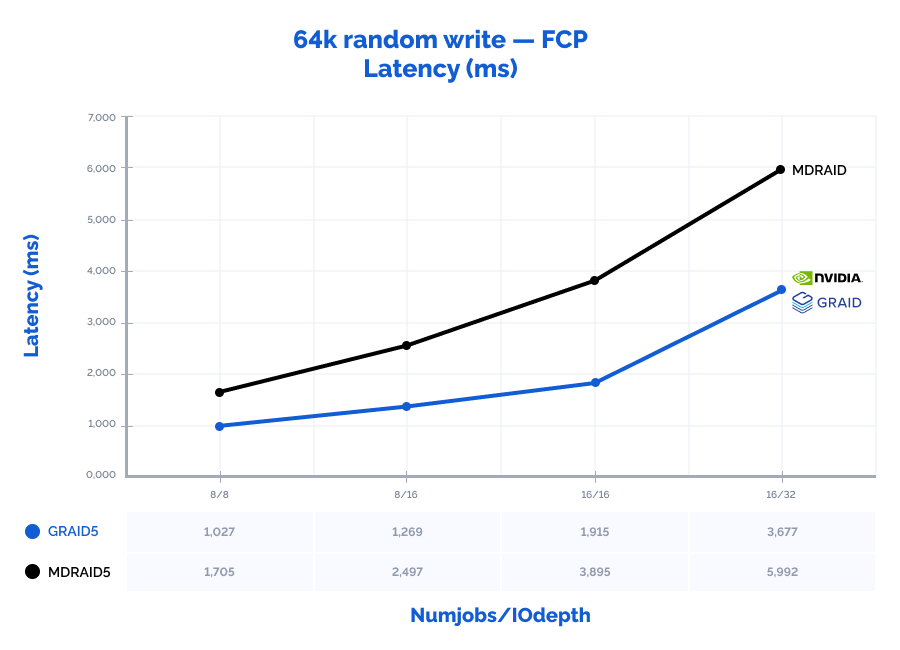
| random write 64K | 16 | 16 | 65517 | 4095 | 3,895 | 132669 | 8292 | 1,915 | 202% | 202% | 49% |
| random write 64K | 16 | 32 | 85255 | 5330 | 5,992 | 138609 | 8664 | 3,677 | 163% | 163% | 61% |
Graphs:
1M read:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | |||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
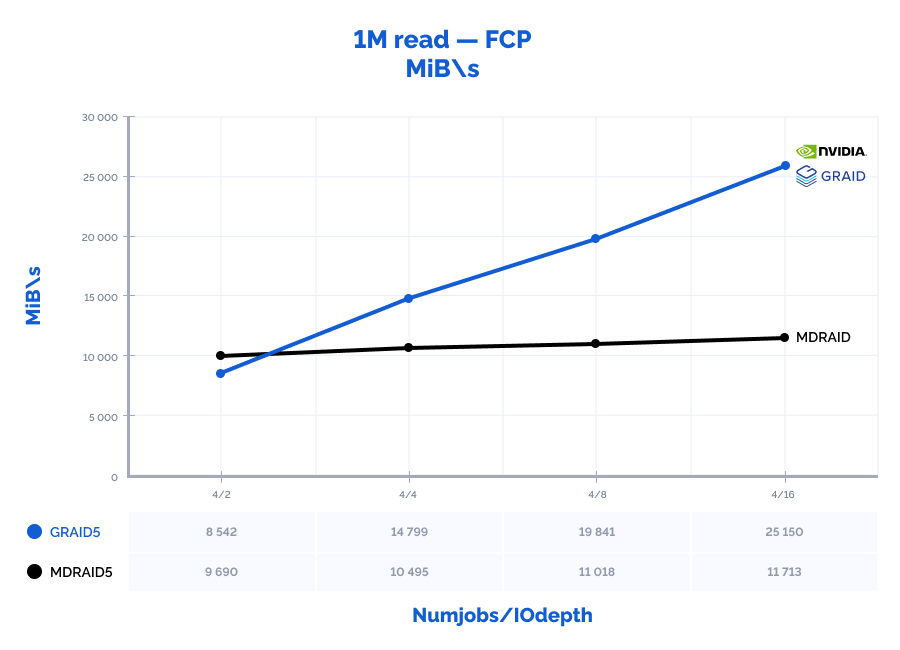
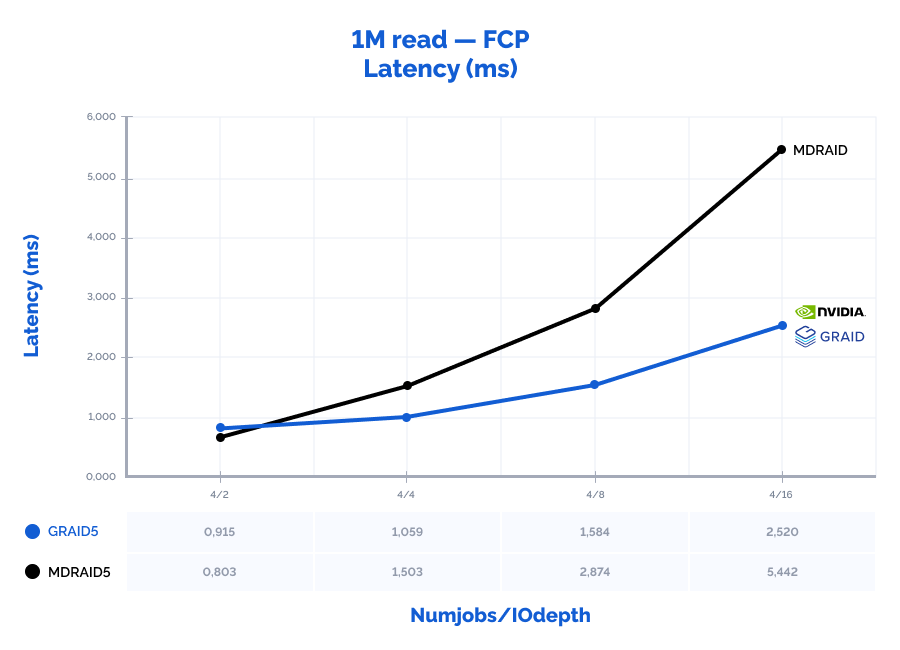
| 1M read | 4 | 2 | 9690 | 9690 | 0,803 | 8542 | 8542 | 0,915 | 88% | 88% | 114% |
| 1M read | 4 | 4 | 10495 | 10495 | 1,503 | 14799 | 14799 | 1,059 | 141% | 141% | 70% |
| 1M read | 4 | 8 | 11018 | 11018 | 2,874 | 19841 | 19841 | 1,584 | 180% | 180% | 55% |
| 1M read | 4 | 16 | 11713 | 11713 | 5,442 | 25150 | 25150* | 2,520 | 215% | 215% | 46% |
* – throughput limitation of our FC adapters (3200MB\s * 8 ports = 25600MB\s).
Graphs:
1M write:
Table result:
| MDRAID5 | GRAID5 | Comparison | |||||||||
| Pattern | Numjobs | IOdepth | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
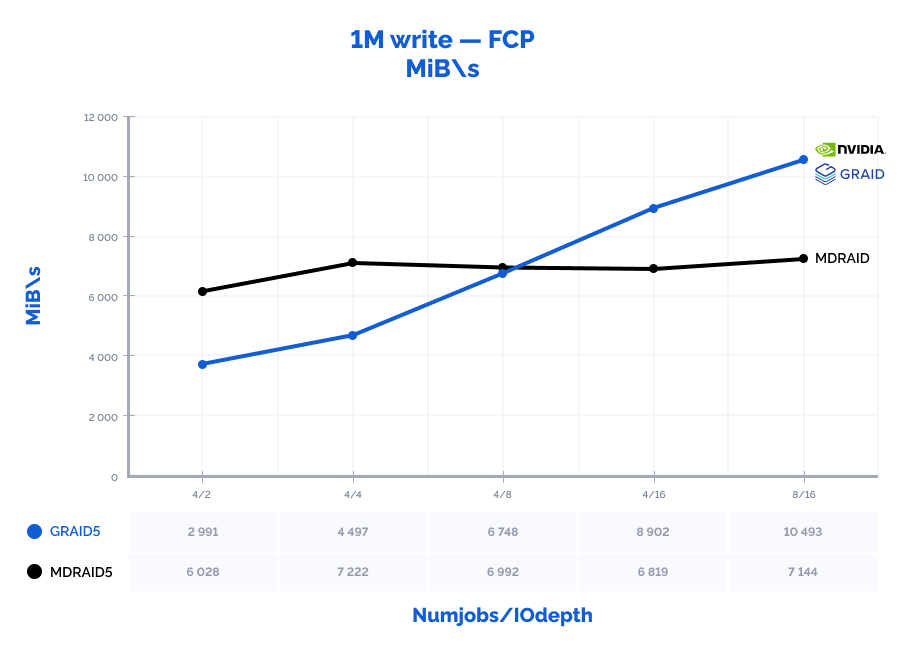
| 1M write | 4 | 2 | 6028 | 6028 | 1,284 | 2991 | 2991 | 2,633 | 50% | 50% | 205% |
| 1M write | 4 | 4 | 7222 | 7222 | 2,167 | 4497 | 4497 | 3,509 | 62% | 62% | 162% |
| 1M write | 4 | 8 | 6992 | 6992 | 4,521 | 6748 | 6748 | 4,684 | 96% | 97% | 104% |
| 1M write | 4 | 16 | 6819 | 6819 | 9,310 | 8902 | 8902 | 7,125 | 131% | 131% | 77% |
| 1M write | 8 | 16 | 7144 | 7144 | 17,832 | 10493 | 10493 | 12,117 | 147% | 147% | 68% |
Graphs:
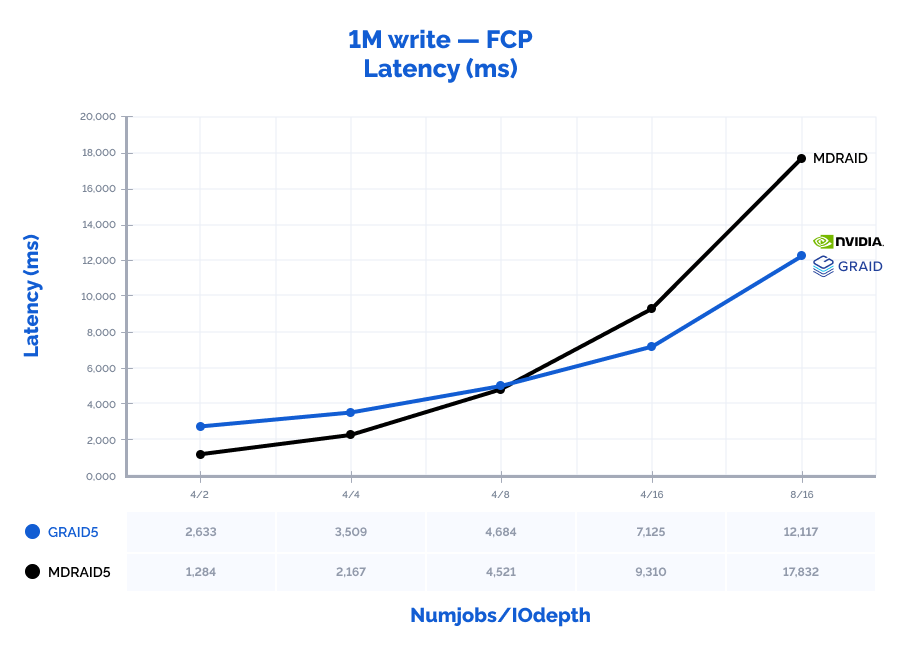
Comparing local and remote performance results:
In the tables below, we have provided best results achieved from each test as to performance/latency ratio. The full performance benchmark results are provided above.
MDRAID:
| MDRAID5 – local | MDRAID5 – FCP | Comparison | |||||||
| Pattern | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
| 4k random read | 4049000 | 15816 | 0,250 | 3531393 | 13795 | 0,274 | 87% | 87% | 110% |
| 4k random write | 478000 | 1867 | 0,535 | 341017 | 1332 | 5,996 | 71% | 71% | 1121% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 1078000 | 4211 | 0,285 | 927080 | 3622 | 3,493 | 86% | 86% | 1226% |
| 64k random read | 186000 | 11625 | 0,343 | 192015 | 12001 | 0,326 | 103% | 103% | 95% |
| 64k random write | 118000 | 7375 | 1,081 | 85255 | 5330 | 5,992 | 72% | 72% | 554% |
| 1M read | 11900 | 11900 | 5,393 | 11709 | 11709 | 5,442 | 98% | 98% | 101% |
| 1M write | 6938 | 6938 | 2,300 | 7221 | 7221 | 2,167 | 104% | 104% | 94% |
GRAID:
| GRAID5 – local | GRAID5 – FCP | Comparison | |||||||
| Pattern | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) | IOPs | MiB\s | Latency (ms) |
| 4k random read | 10800000 | 42188 | 0,377 | 4563635 | 17827 | 0,430 | 42% | 42% | 114% |
| 4k random write | 975000 | 3809 | 2,100 | 514719 | 2011 | 1,980 | 53% | 53% | 94% |
| 4k random read/write 70/30 | 3140000 | 12266 | 1,529 | 1109071 | 4332 | 0,554 | 35% | 35% | 36% |
| 64k random read | 740000 | 46250 | 1,382 | 397736 | 24859 | 0,634 | 54% | 54% | 46% |
| 64k random write | 135000 | 8438 | 1,895 | 132669 | 8292 | 1,915 | 98% | 98% | 101% |
| 1M read | 47000 | 47000 | 5,442 | 25150 | 25150* | 2,520 | 54% | 54% | 46% |
| 1M write | 11100 | 11100 | 11,530 | 10493 | 10493 | 12,117 | 95% | 95% | 105% |
* – throughput limitation of our FC adapters (3200MB\s * 8 ports = 25600MB\s).
Conclusions
Essentially, the most impressive shared storage performance was presented by a redundant GRAID storage array full of PBlaze6 6920 Series NVMe SSDs with StarWind SAN & NAS on top and running over Fibre Channel to client nodes, using Marvell Qlogic 2772 Fibre Channel adapters. GRAID is the only technology to guarantee probably the highest performance software-defined shared storage can get as of now. The GRAID build has managed to receive around 50% of the local RAID array performance with the approximately same latency as with the local storage. The only reason the results on 64k/1M large block reads were different is the natural technical limitations of achieving near or at maximum bandwidth speeds for 32G Fibre Channel environment.
Locally, GRAID shows outstanding results with high data values: it was capable of receiving the seemingly impossible number of 10,8M IOPs with the latency of just 0,377 ms on a 4k random read pattern. Also, since GRAID offloads IO requests processing to GPU, the CPU usage on the storage node is 2-10 times lower than that of MDRAID which allows using free CPU resources for other tasks. With MDRAID, we have managed to practically achieve the full performance that the RAID array could provide locally but at a cost of significantly higher latency.
If you want to unleash the full GRAID performance potential, we would advise looking into NVMe-oF and RDMA which will be added in the subsequent StarWind SAN & NAS new builds. You can find more about the NVMe-oF and StarWind NVMe-oF initiator performance in one of the following articles.


