Virtualization technology has revolutionized the way we deploy and manage applications in modern data centers. VMware is one of the most popular virtualization platforms, and it offers a range of features and capabilities to enable organizations to optimize their IT infrastructure.
In this blog post, we will discuss some of the use cases for VMware Raw Device Mapping (RDM), Persistent Memory (PMem), Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe), NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF), and RDMA (iSER) in VMware environments.
Storage plays a vital role in any virtualization deployment, and if not managed properly, it can create performance bottlenecks that can significantly affect the overall performance of the virtual environment.
Use cases for VMware Raw Device Mapping (RDM)
VMware Raw Device Mapping (RDM) is a feature that allows virtual machines to directly access storage devices connected to the ESXi host.
An RDM is a mapping file in a separate VMFS volume that acts as a proxy for a raw physical storage device. With the RDM, a virtual machine can access and use the storage device directly. The RDM contains metadata for managing and redirecting disk access to the physical device.
The benefits of using an RDM are for clustering support requirements and to allow disk commands to be sent directly to the storage resource from a VM.
RDM can be used in a variety of use cases, including:
- Clustering – RDM can be used to enable clustering of applications such as Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle RAC, or VMware vSphere High Availability (HA) in virtualized environments. With RDM, virtual machines can access shared storage devices directly, providing low latency and high performance.
- SAN Management – RDM can also be used to manage Storage Area Networks (SANs) by allowing VMs to directly access LUNs (Logical Unit Numbers) on the SAN. This allows administrators to manage the SAN from a single point and eliminates the need for multiple virtual disks.
Use cases for Persistent Memory (PMem)
Persistent Memory (PMem) is a new technology that combines the benefits of memory and storage to provide high performance and persistence.
PMem allows data to be stored in memory even when the system is turned off, providing faster access to data and faster data recovery in the event of a system failure.
PMem can be consumed in two ways by your virtual machines (VMs):
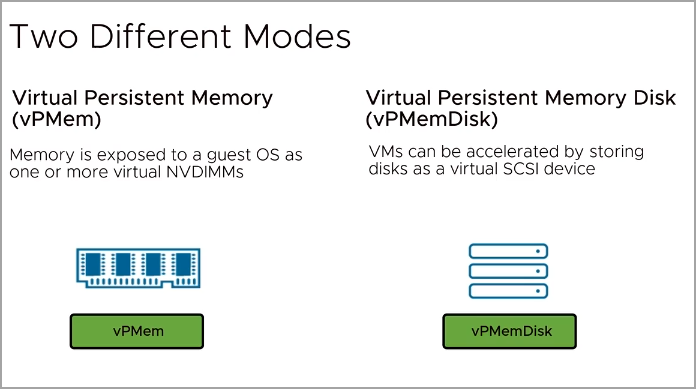
Virtual Persistent Memory (vPMem) – Using vPMem, the memory is exposed to a guest OS as a virtual NVDIMM. This enables the guest OS to use PMem in byte addressable random mode.
Virtual Persistent Memory Disk (vPMemDisk) – Using vPMemDisk, the memory can be accessed by the guest OS as a virtual SCSI device, but the virtual disk is stored in a PMem datastore.
VMware PMem – Two different Modes
PMem can be used in a variety of use cases, including:
- In-Memory Databases – PMem can be used to provide faster access to in-memory databases, such as SAP HANA, by extending the memory capacity of the server.
- Tiered Storage – PMem can be used to create a tiered storage architecture where frequently accessed data is stored in PMem and less frequently accessed data is stored in traditional storage devices. The PMem also provides the fastest access to data compared to NVMe or SATA.
- Big Data Analytics – PMem can be used to accelerate big data analytics workloads, such as Apache Spark, by providing faster access to data.
Use cases for Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe)
NVM Express (NVMe) is a standardized protocol designed specifically for high-performance multi-queue communication with NVM devices. VMware ESXi supports the NVMe protocol to connect to local and networked storage devices.
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) is a high-performance storage interface that provides low latency and high throughput. NVMe can be used in a variety of use cases, including:
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) – NVMe can be used to improve the performance of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) workloads, such as Citrix XenDesktop, by reducing storage latency and increasing IOPS.
- Database Applications – NVMe can be used to improve the performance of database applications, such as Microsoft SQL Server, by reducing storage latency and increasing IOPS.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) – NVMe can be used to accelerate HPC workloads, such as those used in scientific research, by providing faster access to data.
Use cases for NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF)
NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) is a technology that enables remote access to NVMe storage devices over a network. NVMe over Fabrics is a network protocol. Usually, a host communicates with a storage system over a network (we say “fabric”).
It depends on and requires the use of Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA). There are quite a few RDMAs. NVMe over Fabrics can use any of the RDMA technologies, such as RoCE, iWARP or InfiniBand.
NVMe-oF, compared to iSCSI has much lower latency. It adds just a very few microseconds to reach the other side of the network and reach the storage device. This is what is really great about NVMe-oF and which differentiates from (old) iSCSI technology.
The NVMe protocol is a NUMA-optimized protocol and was developed to address many shortcomings of SCSI. It supports tens of thousands of parallel command queues which can be used as submission and completion queues on different CPUs.
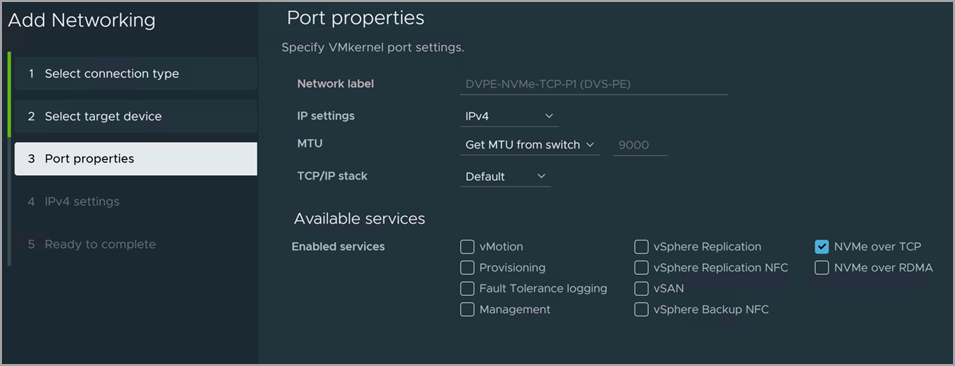
VMware vSphere supports NVMe-oF as it uses standard Ethernet HW and can be converged with other traffic. Make sure that your network card can carry enough bandwidth as NVMe-TCP with other traffic without enough bandwidth could impact other network traffic.
NVMe over TCP
NVMe-oF can be used in a variety of use cases, including:
- Remote storage – NVMe-oF can be used to provide remote access to NVMe storage devices in data centers or between datacenters in different geographic regions.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) – NVMe-oF can be used to enable distributed computing clusters, where data is accessed remotely over a network.
In the ESXi environment, the NVMe storage devices appear similar to SCSI storage devices, and can be used as shared storage.
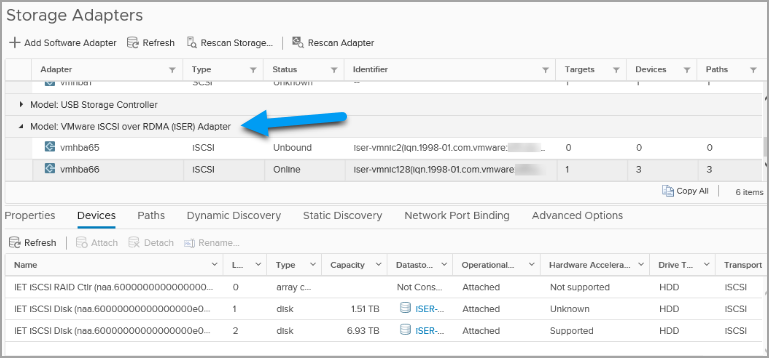
Use cases for RDMA with iSER in VMware environments:
ISER, or iSCSI Extensions for Remote Direct Memory Access, is a protocol that enables RDMA-based data transfers over iSCSI networks. iSER provides faster data access and lower latency than traditional iSCSI protocols, making it ideal for high-performance storage environments.
VMware iSER Adapter
- High-Performance Storage – RDMA with iSER is ideal for high-performance storage environments that require fast data access and low latency. By taking advantage of the speed and low latency of RDMA, iSER can provide better storage performance than traditional storage protocols.
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) – RDMA with iSER can also be used for virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) environments, where multiple users access virtual desktops simultaneously. By improving storage performance, RDMA with iSER can improve the overall user experience for VDI users.
- Big Data Analytics – RDMA with iSER can be used for big data analytics, where large amounts of data need to be processed quickly. By providing faster data access and low latency, RDMA with iSER can improve the performance of big data analytics applications.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) – RDMA with iSER can be used for high-performance computing (HPC) environments, where fast data access and low latency are essential. By taking advantage of the speed and low latency of RDMA, iSER can improve the performance of HPC applications.
- Cloud Computing – RDMA with iSER can be used in cloud computing environments, where multiple virtual machines need to access shared storage. By improving storage performance, RDMA with iSER can improve the overall performance of cloud computing environments.
Whether you are running high-performance storage environments, virtual desktop infrastructure, big data analytics, high-performance computing, or cloud computing, RDMA with iSER can help you achieve faster data access and lower latency. VMware’s integration of RDMA with iSER in its vSphere platform provides administrators with a powerful tool for optimizing storage performance in virtualization deployments.
Final Words
All those technologies that we have talked today are part of VMware vSphere 8. VMware keeps integrating new technologies into their flagship product. New storage technologies are rising every year and as such, with every new release of VMware vSphere, those technologies are supported so users can benefit from faster workloads. Latest VMware vSphere 8 has added suppot for clustered VMDK feature for clustered applications such as Microsoft WSFC on an NVMeoF Datastore.