Windows 11 is the most advanced Windows client operating system in Microsoft to date. It also contains the best security features of any Windows client operating system. The underlying Windows 11 architecture is built around many layers of security, from hardware operating systems to applications and others. Let’s take a look at some of the advanced security features found in Windows 11.
Hardware security features
Microsoft started from the ground up with Windows 11 and built the operating system’s foundation on hardware-based security, starting with the requirement of a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) device. The Trusted Platform Module is a device that secures secrets and other cryptographic information with encryption to protect that information from further compromise.
TPM 2.0 supports newer algorithms and provides many improvements, including stronger cryptography. Microsoft even has support for its own security processor, Microsoft Pluton.
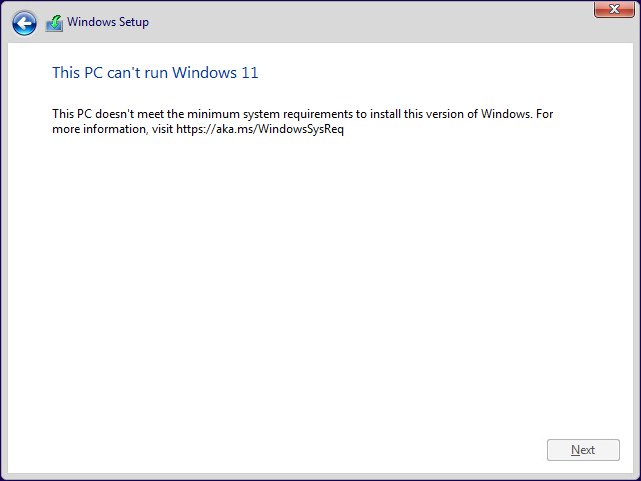
Windows 11 requires a TPM, or the installation will fail. You will see a message similar to the following on your virtual machine or physical host if a TPM is not present in the machine:
Windows 11 TPM required
Another benefit of the TPM requirement is that it enables secure boot, which protects a computer from malicious drivers or other software that may have been tampered with as the computer boots.
Also, with modern hardware running Windows 11, there are additional silicon-assisted security features. Windows 11 can use Virtualization-based Security (VBS) to isolate critical system processes from the rest of the operating system using Hyper-V functionality. This, of course, depends on modern hardware that supports virtualization underneath the hood.
Other hardware-based security features, such as hardware-enforced stack protection, Kernel Direct Memory Access (DMA) Protection, and hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI), are available.
Windows 11 Secured-Core PCs
Microsoft has worked with various OEM partners to introduce PCs that are referred to as Secured-core PCs (SCPCs). What are Secured-core PCs?
Secured-core PCs help prevent cyberattacks and other malicious activity by minimizing the risk of firmware vulnerabilities. With each boot, Secured-core PCs verify a clean and trusted state during startup. It does this by building on top of the hardware capabilities we have discussed, using the hardware-enforced root-of-trust.
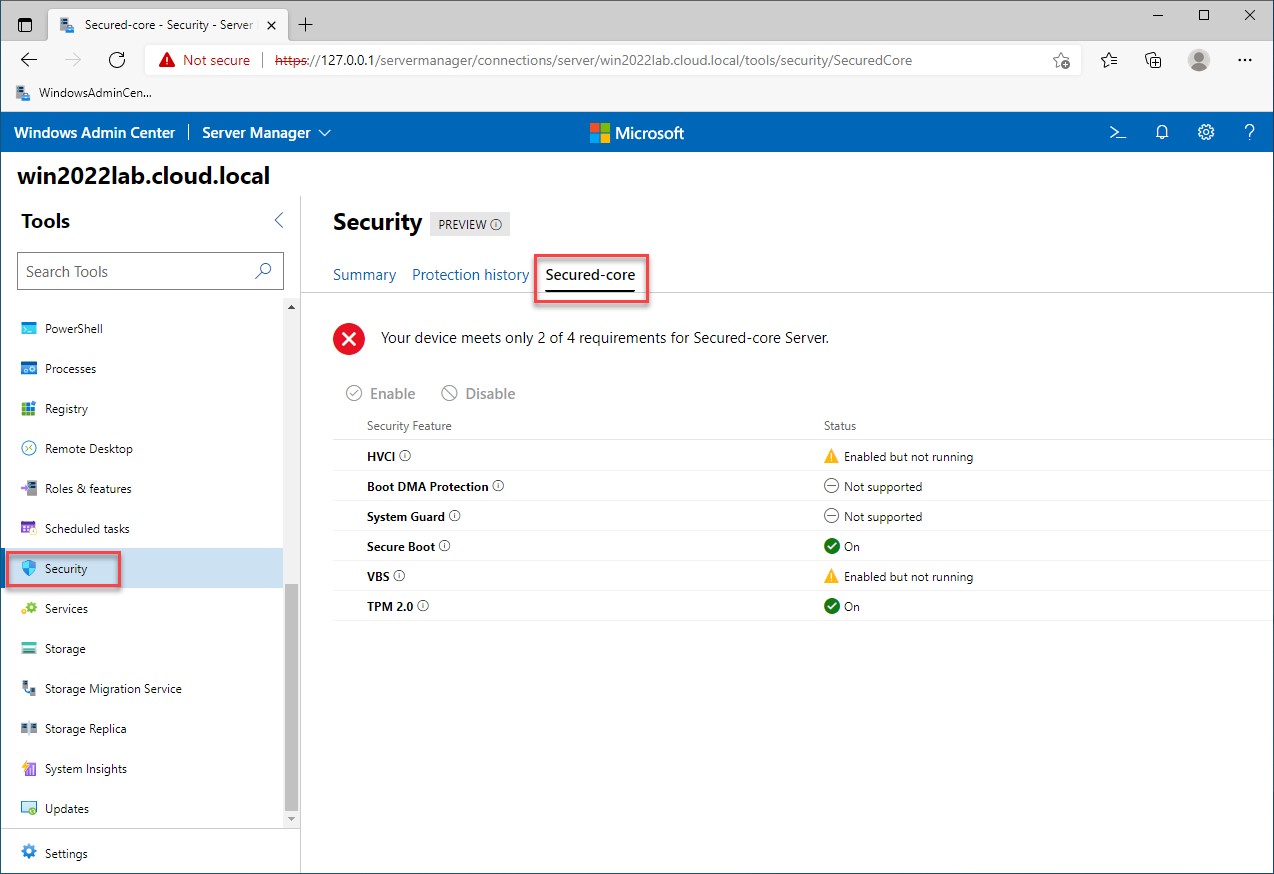
You can easily view your Secured-core capabilities in Windows Admin Center. Under the Security tab for your Windows PC or Server, you can see the Secured-core tab, which shows six categories of compliance:
- HVCI
- Boot DMA Protection
- System Guard
- Secure Boot
- VBS
- TPM 2.0
Below, we can see a machine that is not supported for a full Secured-core implementation.
Viewing secured-core capabilities in Windows Admin Center
Trusted boot
One of the requirements of Windows 11 is that a PC use UEFI with the Secure Boot feature. Secure Boot works with Trusted Boot to ensure malware and other attacks cannot inject themselves into the boot process before loading the operating system.
First, Secure Boot kicks in to provide the initial protection to the PC. Secure Boot takes the PC through a trusted path to when the Windows kernel instantiates the Trusted Boot process. Trusted Boot blocks any malware attacks on the Windows boot sequence by using signature enforcement throughout the boot sequence.
The OS checks the bootloader’s digital signature and the code that runs during the operating system’s start procedures and makes sure the signature is not compromised.
Encryption and Data Protection
Windows 11 has strong encryption and data protection features built into the operating system. BitLocker Drive Encryption makes sure that if a device is stolen or exposed. BitLocker enables encryption for the OS, data, and removable data drives. BitLocker To Go is a technology that refers to BitLocker Drive Encryption on removable data drives. It supports removable media encryption like USB flash drives, SD cards, and external hard drives.
Device Encryption is also a type of encryption implemented at the consumer level that can’t be managed. It can be turned on for devices with all the required hardware components. It needs a combination of TPM 2.0, UEFI Secure Boot, Hardware Security Test Interface, and Modern Standby. Commercial devices can turn off device encryption in favor of BitLocker encryption.
Network security
Like Windows Server 2022, Windows 11 implements new network security features. It has new DNS and TLS protocol versions that provide protection for sensitive applications and help implement a zero-trust networking environment.
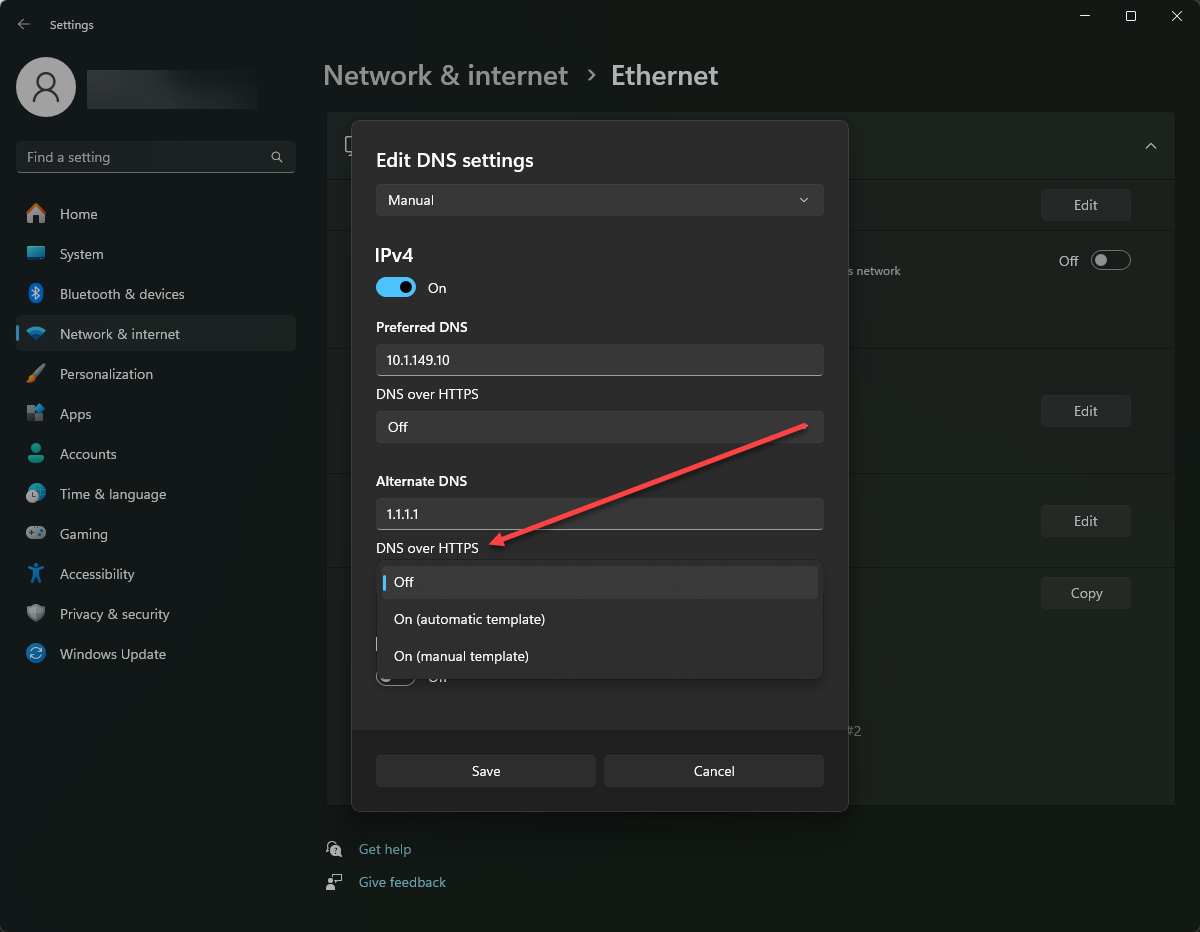
Windows 11 DNS supports DNS over HTTPS and DNS over TLS, two types of DNS encryption. It protects network communications from network snooping of DNS queries by attackers on the same network segment. This type of configuration is important in a zero-trust scenario where there is no trust placed on the network boundary where clients reside.
Below, you can see the Network & internet > Ethernet > DNS settings properties that shows the option to turn on DNS encryption for the DNS configuration. You have a few options here:
- Off
- On (automatic template)
- On (manual template)
Viewing the DNS encryption options in Windows 11
Built-in virus and threat protection
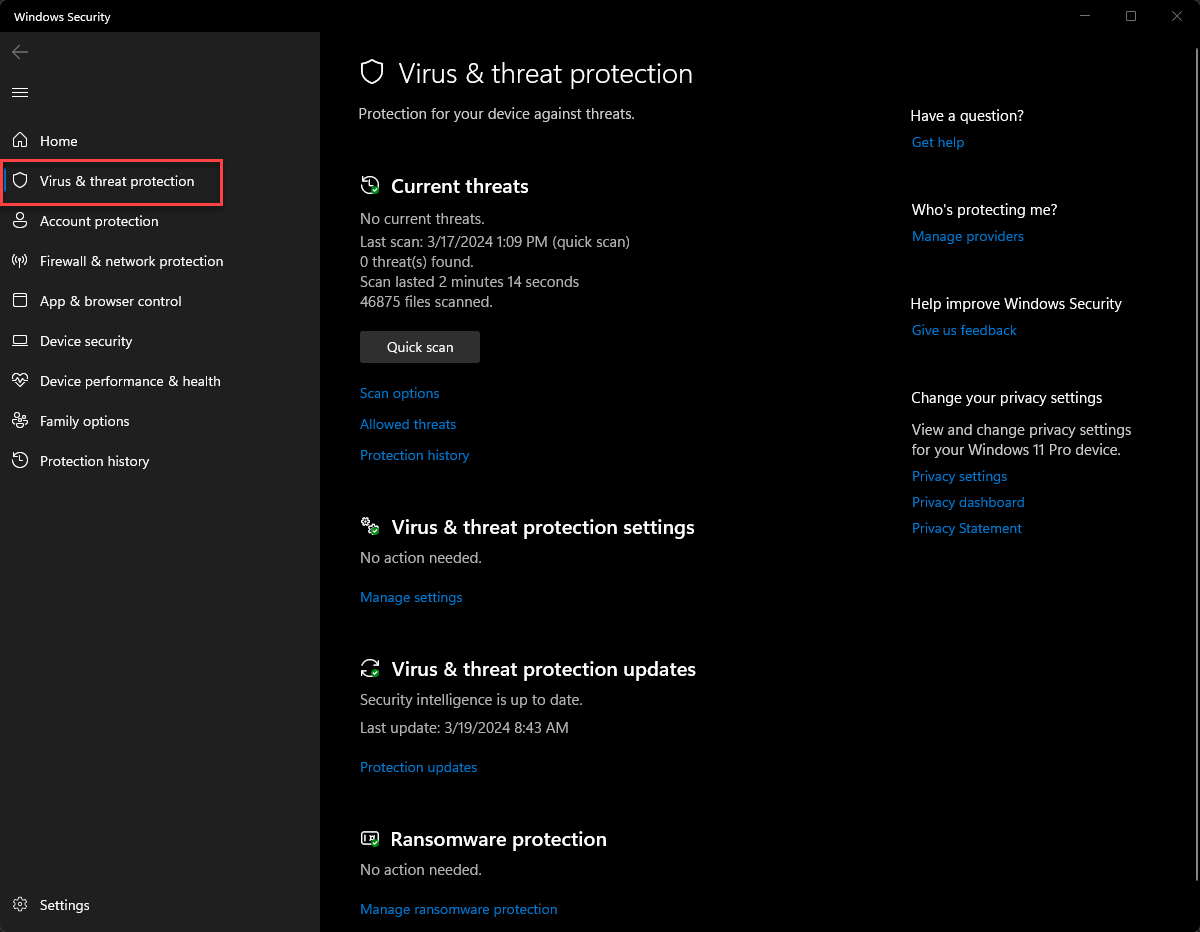
Windows 11 actually has very robust virus and threat protection built into the operating system by default. It includes Microsoft Defender SmartScreen that protects against phishing, malware websites, and applications. It also protects against malicious downloads.
Microsoft Defender Antivirus is a next-generation malware protection platform that can continually monitor your Windows 11 PC for malware, viruses, and other security threats. The solution provides real-time scanning benefits along with next-generation capabilities like behavior-based and heuristic antivirus analysis. It can detect malware and threats as well as potentially unwanted applications (PUAs).
With Windows 11 and Microsoft Defender Antivirus, you get cloud-delivered virtus and malware protection that provides almost real-time protection of new and emerging threats. This is thanks to Microsoft’s massive cloud environment that can collect various risk signals and translate these into security defenses across the board.
Viewing security and virus protection in Windows 11 using Microsoft Defender
Enabling passwordless sign-in
One of the most compromised components of the overall security scheme for an organization is passwords. Windows 11 provides many passwordless sign-in options that can help completely get rid of passwords in the enterprise.
Windows 11 includes the Windows Hello capability that enables passwordless sign-in using biometric or PIN verification and provides built-in support for FIDO2 passwordless sign-in.
Using the TPM device and asymmectric keys, Windows Hello protects authentication by binding a user’s credentials to their device. It protects against replay attacks, phishing, and spoofing, and alsop password resuse and leaks.
Organizations can use Windows Hello with Active Directory and Microsoft Entra ID accounts for single sign-on to work or school resources.
Credential protection
For organizations that are still using passwords, Windows 11 provides built-in protetctions that help safeguard traditional passwords. These include:
Local security authority LSA protection – This mechanism is responsible for authenticating users and verifying Windows logins. In Windows 11, it only loads trusted, signed code which helps protect against LSA credential theft.
Credential guard – It is a hardware-based virtualization-based technology that provides protection against credential theft. Credentials are stored in an isolated environment that is not accessible to the rest of the operating system.
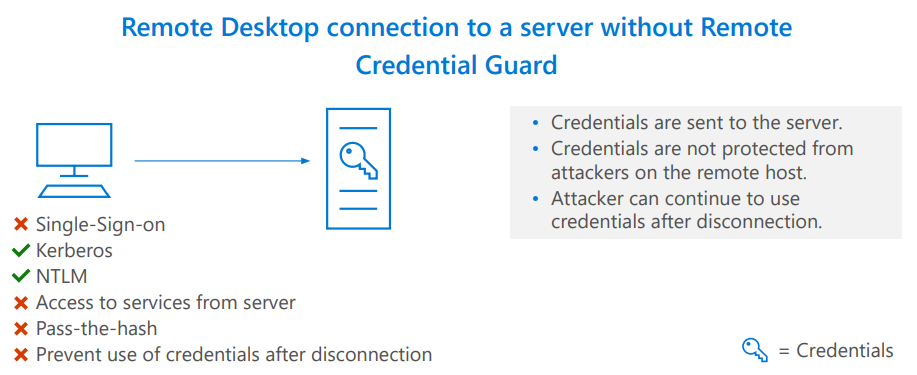
Remote credential guard – It protects Kerberos requests by redirecting the request back to the device that is requesting the connection. It also allows for single sign-on for Remote Desktop sessions. Remote Desktop credential guard makes sure the credentials or credential hashes are never passed over the network to the target device.
Viewing security and virus protection in Windows 11 using Microsoft Defender
Wrapping up
Windows 11 has a wealth of security features and capabilities that come in the box. These help organizations to meet modern cybersecurity challenges successfully. It also gives admins the tools needed to protect traditional passwords, secure network connectivity, and use modern hardware capabilities to secure sensitive system processes.