StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator: Installation Guide
- November 17, 2020
- 9 min read
- Download as PDF
Annotation
Relevant Products
StarWind NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) Initiator
Purpose
This guide provides instructions for installing and configuring the StarWind NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) Initiator on Windows Server. It details the preconfiguration of servers, checking RDMA connectivity, and the steps to install the StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator. The guide also mentions different ways to work with the initiator, including command-line utility, Microsoft iSCSI initiator GUI, and PowerShell.
Audience
The primary audience includes IT professionals, system administrators, and technology enthusiasts who are interested in configuring high-performance NVMe over Fabrics shared storage solutions in a Windows Server environment.
Expected Result
Following the guide, users should be able to successfully install and configure the StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator on Windows Server, connecting it to a SPDK target with an NVMe drive over an RDMA network. This setup will enable NVMe over Fabrics functionality, providing efficient and fast shared storage access.
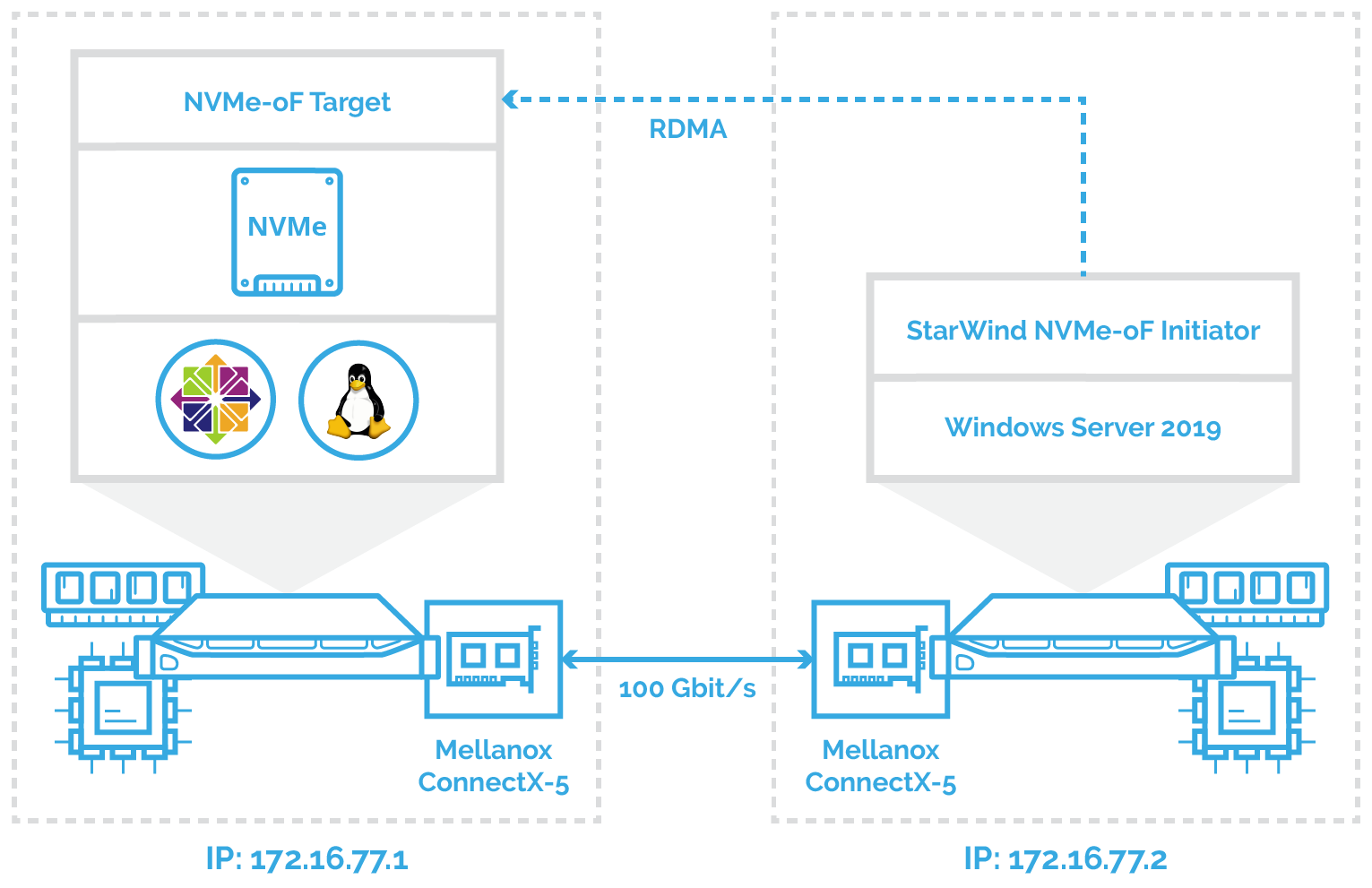
Preconfiguring the Servers
In this document, the first host with Mellanox ConnectX-5 adapter, SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target, and NVMe drive is running CentOS. The second host is running Windows Server 2019 and has Mellanox ConnectX-5 adapter installed accordingly. StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Initiator is deployed on the second Windows Server 2019 and connected to the first CentOS via 172.16.77.x subnet.
Windows Servers 2019 should have the latest Mellanox driver installed, which is available here:
https://www.mellanox.com/products/adapter-software/ethernet/windows/winof-2
To check the RDMA connectivity and bandwidth between the initiator server and target server, use the StarWind rPerf utility, which can be downloaded here: https://www.starwindsoftware.com/starwind-rperf
The article on how to install and configure SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target could be found here: https://www.starwindsoftware.com/resource-library/starwind-nvme-of-initiator-creating-microsoft-failover-cluster-with-windows-server/
Installing StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Initiator
1. Download StarWind NVMe–oF in the link here: https://www.starwindsoftware.com/starwind-nvme-of-initiator
2. Execute the starwind-nvmeof.exe to install StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator and follow the steps in the wizard.
3. Restart the server.
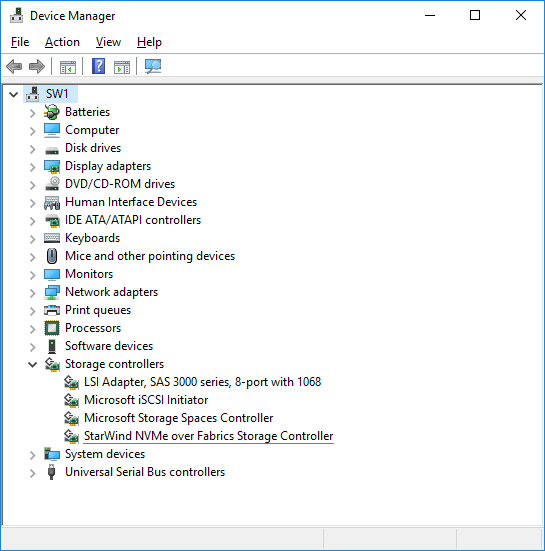
4. Open Device Manager to check that StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator is installed on the system.
Working with StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Initiator
There are three ways to work with StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Initiator: using StarNVMeoF_Ctrl command-line utility (preferred), from Microsoft iSCSI initiator GUI and via PowerShell commandlets:
Using command-line utility
The StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe command-line utility is used to work with the NVMe-oF initiator.
Discovering targets
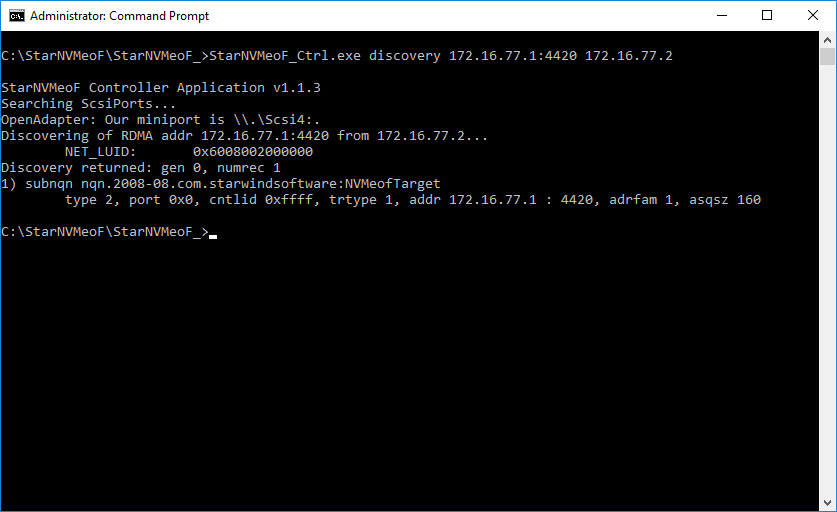
1. To discover the target, run the discovery command: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe discovery <target_ip_addr:[port]> <local_ip_addr> by specifying the protocol, target host IP address and port number:
Example: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe discovery 172.16.77.1:4420 172.16.77.2
Where:
<172.16.77.1:4420> — NVMe-oF target host IP and port;
<172.16.77.2> — initiator host IP.
Connecting targets
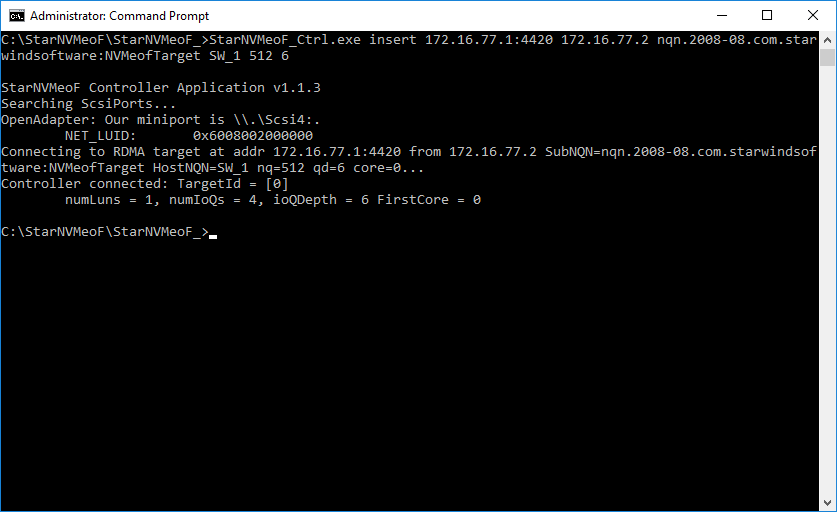
1. To connect the target, run the command: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe insert <target_ip_addr[:port]> <local_ip_addr> <SubNQN> <HostNQN> [<num_io_queues> <io_queue_depth> <first_core>]
Example: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe insert 172.16.77.1:4420 172.16.77.2 nqn.2008-08.com.starwindsoftware:NVMeofTarget SW_1 512 6 0
Where:
- <172.16.77.1:4420 > — target host IP and port;
- <172.16.77.2> — initiator host IP;
- <nqn.2008-08.com.starwindsoftware:NVMeofTarget> — SubNQN of the target (may be copied from the discovery results screen);
- <SW_1> — local HostNQN;
- <512> — quantity of connections to the target;
- <6> — queue depth;
- <0> — number of the initial core.
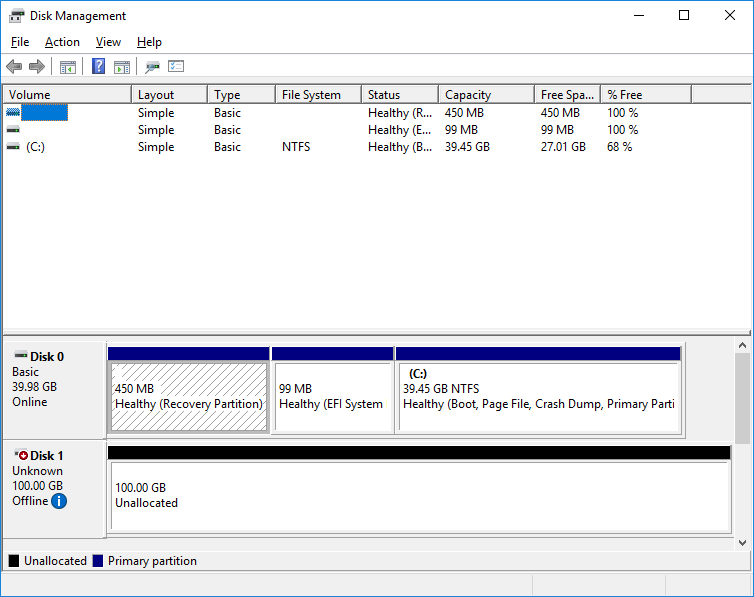
2. After the “insert” command is executed, disk LUNs for the connected controller namespaces should appear in the Disk Management.
Getting information about targets
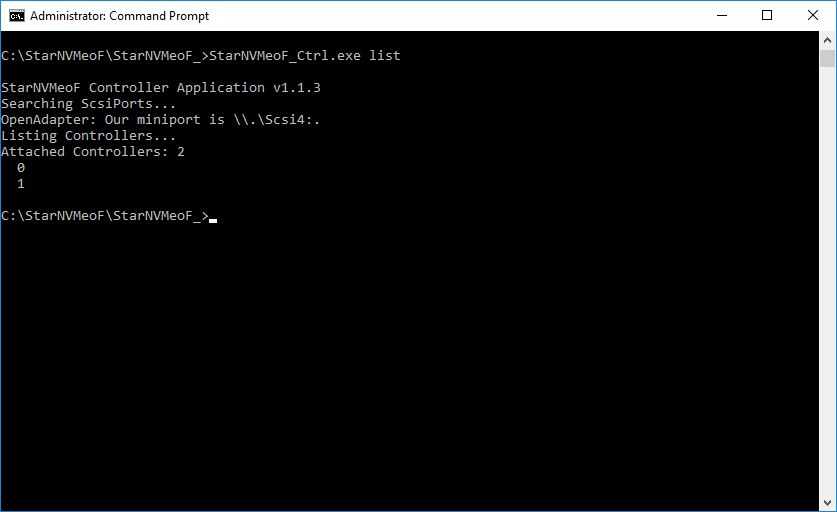
1. To show the list of connected NVMe-oF controllers, run the “StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe list” command.
Disconnecting targets
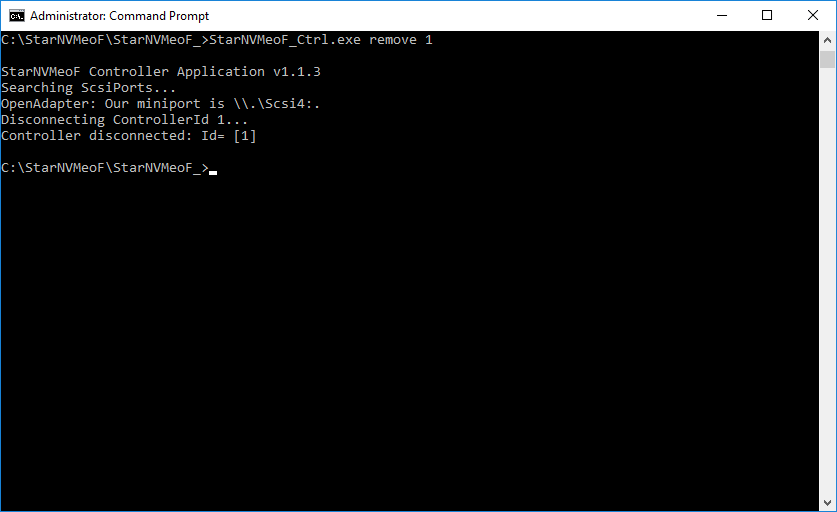
1. To disconnect LUNs from the system, run the controller disconnection command: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe remove <controllerId>
Example: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe remove 1
Where:
- <1> — controller Id
NOTE: Make sure that LUNs are not used by other applications at the moment of disconnection, as removing LUNs with active file operations may lead to data corruption.
Using MS iSCSI Initiator GUI
Discovering targets
1. Launch Microsoft iSCSI Initiator: Start -> Windows Administrative Tools -> iSCSI Initiator. Alternatively, launch it using the command below in the command line interface:
iscsicpl2. Navigate to the Discovery tab.
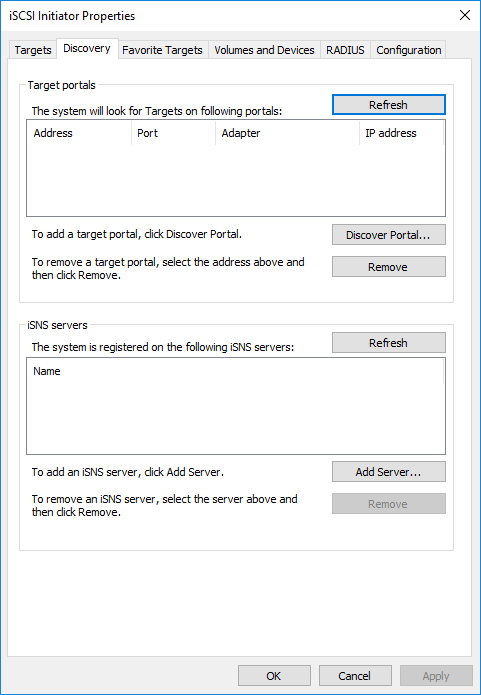
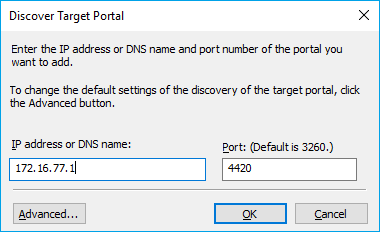
3. In Discover Target Portal dialog, type in the IP address of the NVMe-oF target server that will be used to connect the provisioned targets and port number (4420). Click Advanced.
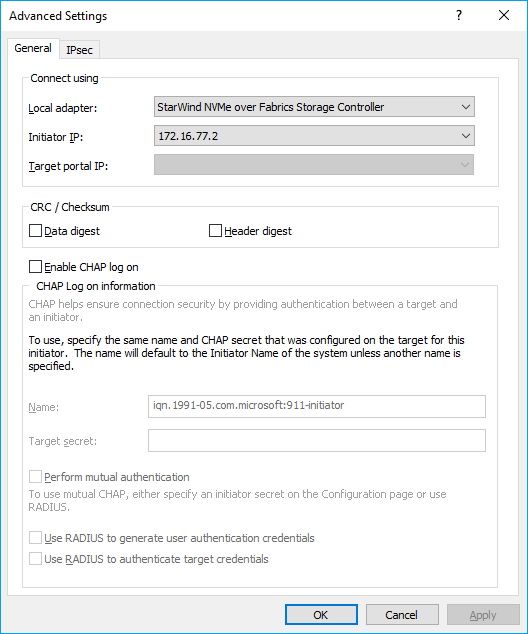
4. Select StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Storage Controller as the Local adapter, select the Initiator IP in the same subnet as the IP address of the target server from the previous step. Confirm the actions to complete the Target Portal discovery.
5. Now, the target portal is added to the initiator server.
Connecting targets
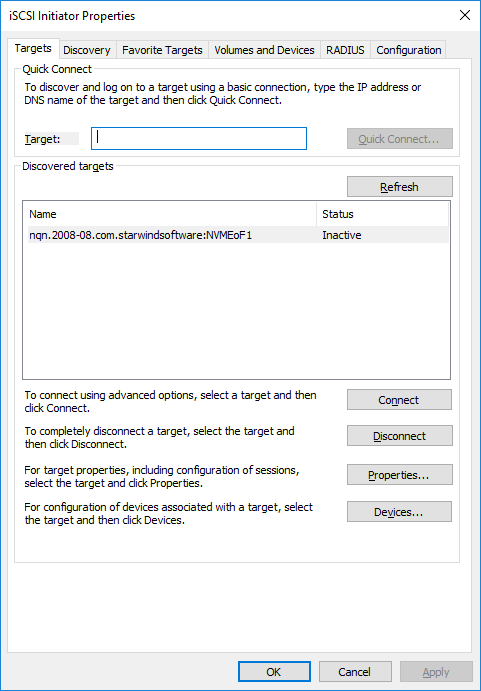
1. Click the Targets tab. The previously created target is listed in the Discovered Targets section.
2. Press Connect and select StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Storage Controller in the Local adapter dropdown menu.
In the Initiator IP field select the IP address for the initiator.
In the Target portal IP, select the corresponding portal IP from the same subnet. Confirm the actions.
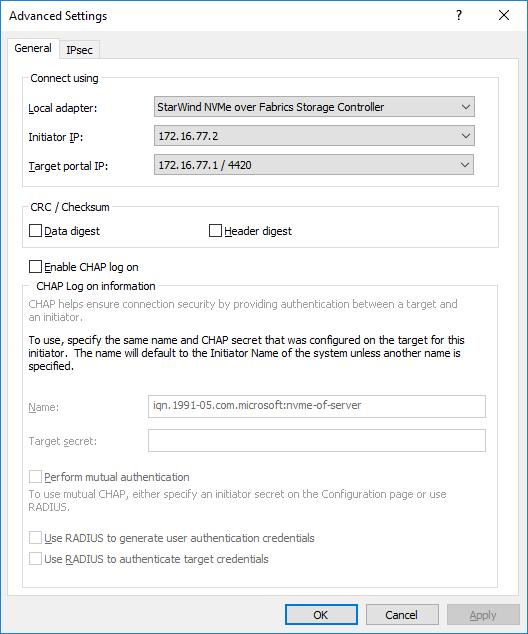
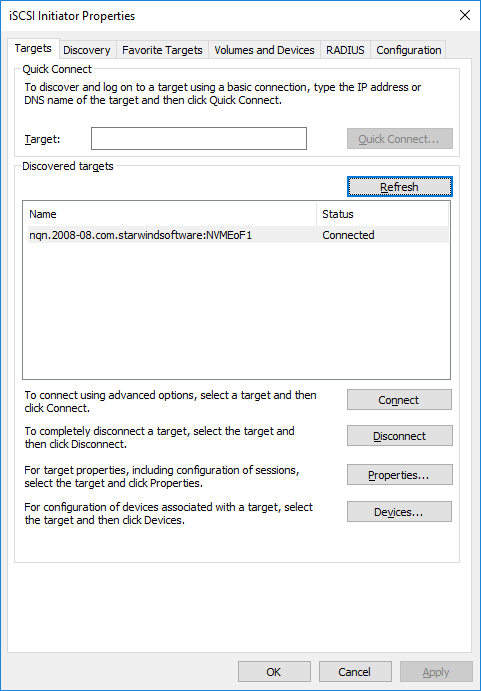
3. Target is connected
4. Open the Disk Management snap-in. The connected disk(s) will appear as unallocated and offline.
5. Bring the disks online by right-clicking on them and selecting the Online menu option.
Disconnecting targets
1. To disconnect the NVMe-oF target choose the specified target from the Discovered Targets list a press the Disconnect button.
NOTE: Make sure that LUNs are not used by other applications at the moment of disconnection, as removing LUNs with active file operations may lead to data corruption.
Using PowerShell
Discovering targets
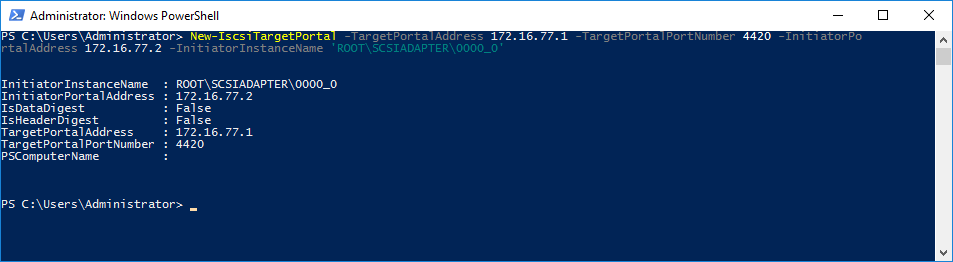
1. To discover the target, run the discovery commandlet in Powershell: New-IscsiTargetPortal -TargetPortalAddress <target IP> -TargetPortalPortNumber <target port> -InitiatorPortalAddress <initiator IP> -InitiatorInstanceName <‘initiator controller‘> by specifying target host IP address and port number:
Example:
New-IscsiTargetPortal -TargetPortalAddress 172.16.77.1 -TargetPortalPortNumber 4420 -InitiatorPortalAddress 172.16.77.2 -InitiatorInstanceName 'ROOT\SCSIADAPTER\0000_0'Where:
<172.16.77.1> -TargetPortalAddress;
<4420> -InitiatorPortalAddress
<172.16.77.2> -InitiatorPortalAddress
<‘ROOT\SCSIADAPTER\0000_0’> -InitiatorInstanceName – StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Storage Controller
2. To get NVME targets name, run the commandlet Get-IscsiTarget:
Get-IscsiTargetConnecting targets
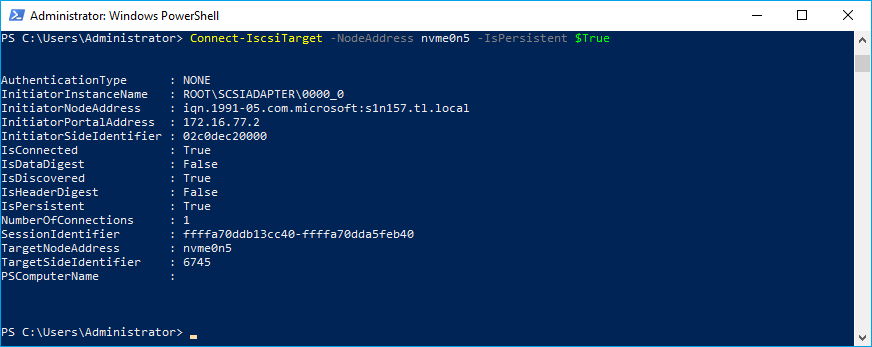
1. To connect the target, run the commandlet: Connect-IscsiTarget -NodeAddress <NodeAddress>-IsPersistent $True
Example:
Connect-IscsiTarget -NodeAddress nvme0n5 -IsPersistent $True4. To get information about the sessions, run the command:
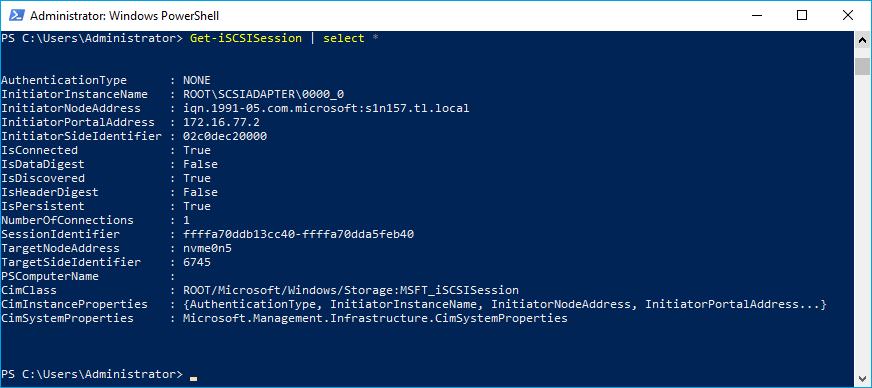
Get-iSCSISession | select *Disconnecting targets
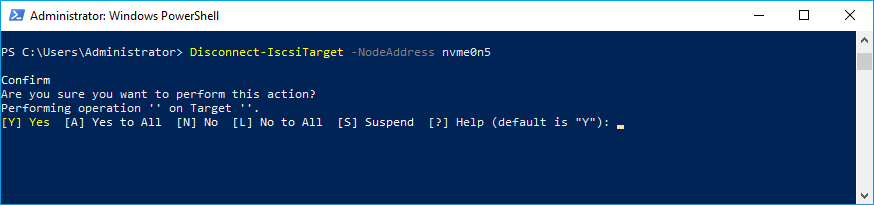
1. To disconnect the target, run the command: Disconnect-IscsiTarget -NodeAddress <NodeAddress>
Example:
Disconnect-IscsiTarget -NodeAddress nvme0n5NOTE: Make sure that LUNs are not used by other applications at the moment of disconnection, as removing LUNs with active file operations may lead to data corruption.
Conclusion
The installation guide for StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator offers a comprehensive approach to setting up NVMe over Fabrics in a Windows Server environment. By following these instructions, users can significantly enhance their server’s storage performance, leveraging the speed and efficiency of NVMe technology over a network fabric.