StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator: Configuration Guide for Microsoft Windows Server [Hyper-V]
- May 21, 2019
- 16 min read
- Download as PDF
Annotation
Relevant Products
StarWind NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) Initiator
StarWind rPerf utility
Purpose
This guide details the process of creating a Microsoft failover cluster with Windows Server using StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator. It outlines the setup of a cluster involving two Windows Server 2019 nodes and a storage node running CentOS with SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target. The guide includes steps for preparing both the storage and cluster nodes, installing the StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator, and configuring the failover cluster and network preferences.
Audience
The guide is intended for IT professionals, system administrators, and network engineers interested in deploying and managing failover clusters in Windows Server environments, particularly those involving shared NVMe storage using NVMe-oF.
Expected Result
Upon following this guide, users should successfully create a Microsoft failover cluster using StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator. The cluster will involve Windows Server nodes for high availability and a CentOS node as a stable SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target, ensuring high-performance shared storage management.
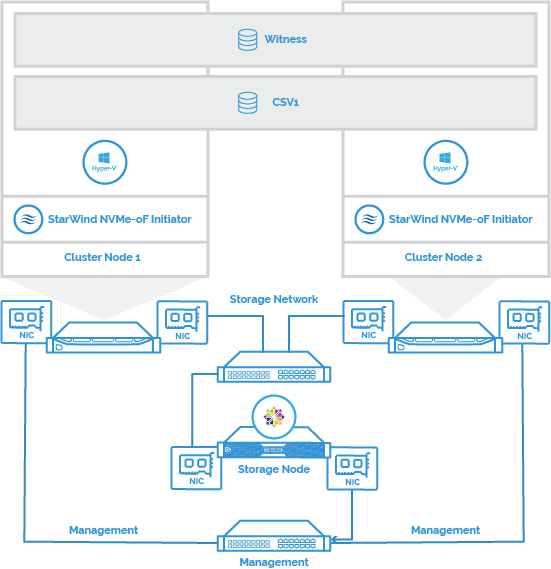
Solution Diagram
The figure below depicts the network diagram of the environment built for this technical paper.
NOTE: This technical paper describes how to configure StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator and SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target for a setup intended exclusively for proof-of-concept and test purposes.
Preconfiguring the Servers
Cluster Node 1 and Cluster Node 2 are running Windows Server 2019; Hyper-V role is installed and Failover Cluster feature is enabled. Storage Node is running CentOS as it is a stable operating system that can be used to create SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target.
StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Initiator is installed on Cluster Nodes 1 and 2. SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target is installed on Storage Node.
Cluster Node 1 and Cluster Node 2 have Mellanox ConnectX-5 adapters installed. The Storage Node has a Mellanox ConnectX-5 network adapter and an NVMe disk installed. That disk is presented as SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target over the Storage Network that has subnet number of 172.16.77.x.
Windows Servers 2019 servers should have the latest Mellanox driver installed, which is available at https://www.mellanox.com/products/adapter-software/ethernet/windows/winof-2
To check the RDMA connectivity and bandwidth between Cluster Nodes and Storage Node, use the StarWind rPerf utility, which can be downloaded at https://www.starwindsoftware.com/starwind-rperf
Preparing the Storage node
In this document, CentOS is used as an operating system of the Storage Node where SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target is configured. Learn more about SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target at https://spdk.io/doc/nvmf.html
Prepare the new CentOS core with multipathing support
Preparation of the Storage Node involves multipath configuration. To configure it, it is necessary to update the OS core and install additional components. Perform the commands below as root on Storage Node.
yum update -y
yum install mc wget tar -y
yum install ncurses-devel git-all openssl-devel gcc bc bison flex elfutils-libelf-devel make -yTo install the new CentOS core, it is necessary to run these commands. Find more details about CentOS core installation at https://wiki.centos.org/Documentation
wget https://cdn.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/linux-5.5.4.tar.xz
tar -xvf linux-5.5.4.tar.xz
cd linux-5.5.4
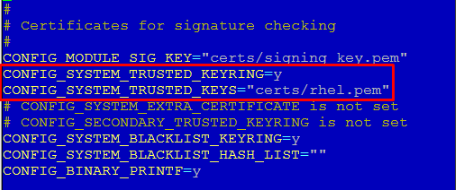
make olddefconfigTo activate multipathing, it is necessary to find and delete the rows below in the .config file.
CONFIG_SYSTEM_TRUSTED_KEYRING
CONFIG_SYSTEM_TRUSTED_KEYS
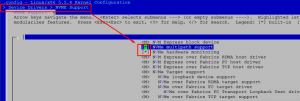
Use the make menuconfig tool to enable NVMe multipath support.
make menuconfigIn Kernel Configuration, select Device Drivers -> NVME Support, choose NVMe multipath support and press the Save button
Confirm the changes.
Compile the core. Use the lscpu command to learn the number of logical CPUs in the system; use that number as the parameter in the make -j command (make-j* where *- the count of logical CPU).
make -j[the number of logical CPUs] && make - j[the number of logical CPUs] modules
make - j[the number of logical CPUs] modules_install && make - j[the number of logical CPUs] installIn this sample, Linux core was compiled with 8 CPUs.
make -j8 && make -j8 modules
make -j8 modules_install && make -j8 installMake the new system the first in the boot menu.
grub2-set-default 0
grub2-editenv listRestart the OS to boot from the new core.
Installing the necessary drivers and components and enabling RDMA
Run the following commands to install the Mellanox drivers and components.
yum -y groupinstall "InfiniBand Support"
dracut --add-drivers "mlx4_en mlx4_ib mlx5_ib" -f
systemctl enable rdma
echo -e "nvme-rdma\nnvme\nnvmet\nnvmet-rdma" > /etc/modules-load.d/nvme-rdma.conf
systemctl enable systemd-modules-load
systemctl start systemd-modules-load
systemctl status systemd-modules-load
dnf install nvmetcli -y
dnf install opensm -y
systemctl enable opensmUse the command below to check that NVMe multipathing support is enabled. The system should return “Y”.
cat /sys/module/nvme_core/parameters/multipathRun the following commands to install the components for SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target.
dnf install epel-release -y
dnf --enablerepo=PowerTools install CUnit-devel -y
dnf --enablerepo=PowerTools install nasm -y
dnf install gcc-c++ rdma-core-devel librdmacm automake libtool python36 numactl-devel libuuid-devel libaio-devel bzip2 -y
dnf --enablerepo=PowerTools install help2man
yum install python2 -y
ln -s /usr/bin/python2 /usr/bin/python
git clone https://github.com/linux-test-project/lcov.git
cd lcov
make install
Installing and starting the SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target
This section describes installing, initialization, and creation of SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target. Find more details at https://spdk.io/doc/getting_started.html
1. SPDK installation
Navigate to the root folder and get the list of available SPDK versions.
cd /
git clone https://github.com/spdk/spdk.git
cd spdk/Select the SPDK version.
git tag
git checkout v20.01
git submodule update --init
./configure --enable-debug --with-rdmamake -j[the number of logical CPUs]2. Starting SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target
In order to start SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target, it is necessary to initialize the NVMe drive. To initialize the NVMe drive, please run setup.sh and gen_nvme.sh from spdk/scripts folder
scripts/setup.sh
scripts/gen_nvme.shNOTE: gen_nvme.sh generates the NVMe namespace that is going to be reused to create an SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target. The generated namespace should look like Nvme0n1 1. Make sure to note this parameter.
SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target requires nvmf.conf file to get all the parameters for its functioning. The file must be created in spdk folder. Please, find the sample of nvmf.conf file below.
[Global]
#[Bdev]
[Rpc]
Enable No
Listen 127.0.0.1
[Nvme]
TransportID "trtype:PCIe traddr:0000:04:00.0" Nvme0
RetryCount 4
TimeoutUsec 0
AcctionOnTimeout None
AdminPollRate 100000
#[Malloc]
#NumberOfLuns 8
#LunSizeInMB 64
[Nvmf]
AcceptorPollRate 10000
ConnectionScheduler RoundRobin
[Transport]
Type RDMA
[Subsystem1]
NQN nqn.2016-06.io.spdk:cnode1
Listen RDMA 172.16.77.1:4420 //The IP address of your target NIC
AllowAnyHost Yes
Host nqn.2016-06.io.spdk:init //the name of your target
SN SPDK001MN
SPDK_Ctrl1
Namespace Nvme0n1 1
NOTE: Nvme0n1 1 is the namespace generated by gen_nvme.sh.172.16.77.1 is the IP address of the target NIC.NQN is the qualified name to identify a storage target.
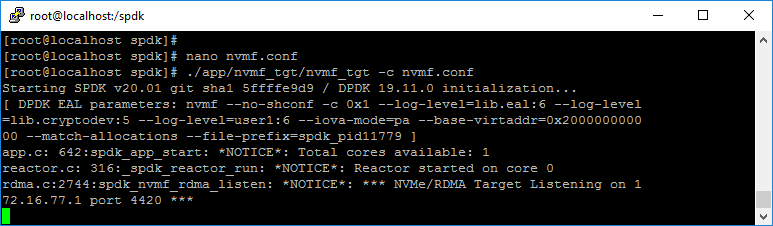
Run the following command to create the SPDK NVMe over Fabrics target based on the previously created nvmf.conf
./app/nvmf_tgt/nvmf_tgt -c nvmf.confNOTE: After the server restarts, the target does not start automatically. The ./app/nvmf_tgt/nvmf_tgt -c nvmf.conf command should be added to autostart of the CentOS server.
Preparing the Cluster nodes
In this document, Windows Server 2019 is used as an operating system of the Cluster Nodes where StarWind NVMe over Fabrics initiator is configured.
Installing StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Initiator
1. Download StarWind NVMe–oF in the link here: https://www.starwindsoftware.com/starwind-nvme-of-initiator
2. Execute the starwind-nvmeof.exe to install StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator and follow the steps in the wizard.
3. Restart the server.
4. Open Device Manager to check that StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator is installed on the system.
Working with StarWind NVMe over Fabrics Initiator
The StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe command-line utility is used to work with the NVMe-oF initiator:
1. Find available NVMe-oF controllers and subsystems (targets). The command will show a list of names and properties of controllers for the address:
StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe discovery <target_ip_addr[:port]> <local_ip_addr>
2. Connect the NVMe-oF controller. The command will create a connection to the target.
StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe insert <target_ip_addr[:port]> <local_ip_addr> <SubNQN> <HostNQN> [<num_io_queues> <io_queue_depth>]
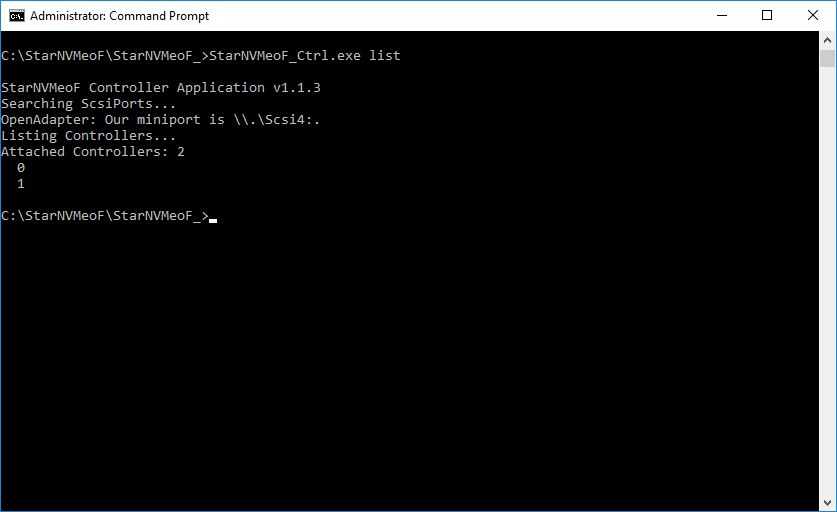
3. Show the list of connected NVMe-oF controllers. The command will show the list of connected controllers:
StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe list
4. Disconnect the NVMe-oF controller that is connected to the system. The command will disconnect the controller. The LUNs will be removed from the system:
StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe remove <controllerId>
Discovering and Connecting NVMe-over-Fabrics Targets on Windows Server
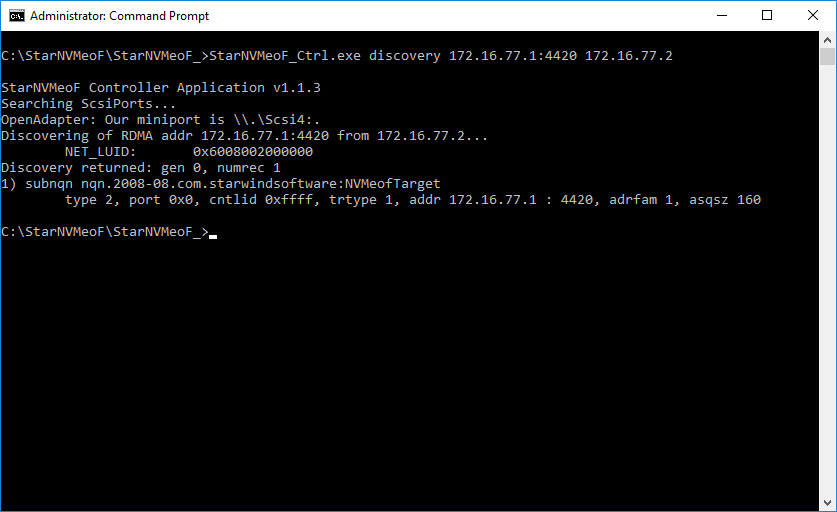
1. To discover the target, run the discovery command: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe discovery <target_ip_addr:[port]> <local_ip_addr> by specifying the protocol, target host IP address and port number:
Example: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe discovery 172.16.77.1:4420 172.16.77.2
Where:
<172.16.77.1:4420> — NVMe-oF target host IP and port;
<172.16.77.2> — local host IP.
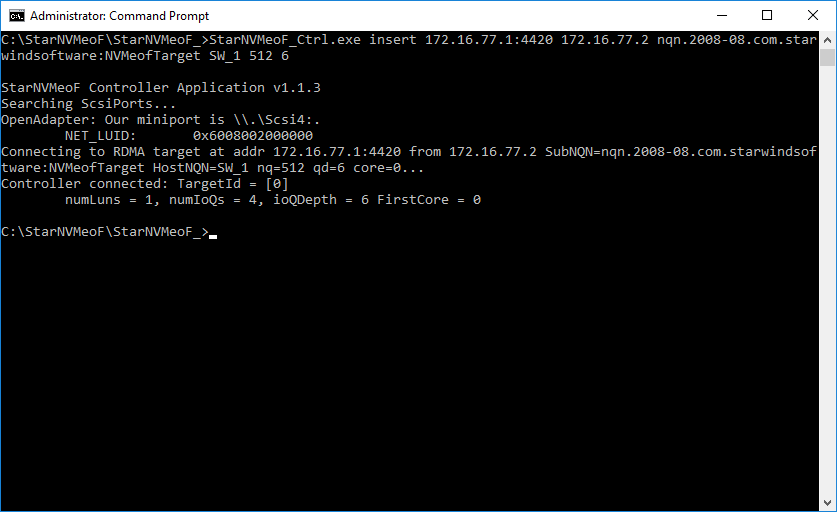
2. To connect the target, run the command: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe insert <target_ip_addr[:port]> <local_ip_addr> <SubNQN> <HostNQN> [<num_io_queues> <io_queue_depth> <first_core>]
Example: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe insert 172.16.77.1:4420 172.16.77.2 nqn.2008-08.com.starwindsoftware:NVMeofTarget SW_1 512 6 0
Where:
- <172.16.77.1:4420 > — target host IP and port;
- <172.16.77.2> — local host IP;
- <nqn.2008-08.com.starwindsoftware:NVMeofTarget> — SubNQN of the target (may be copied from the discovery results screen);
- <SW_1> — local HostNQN;
- <512> — quantity of connections to the target;
- <6> — queue depth;
- <0> — number of the initial core.
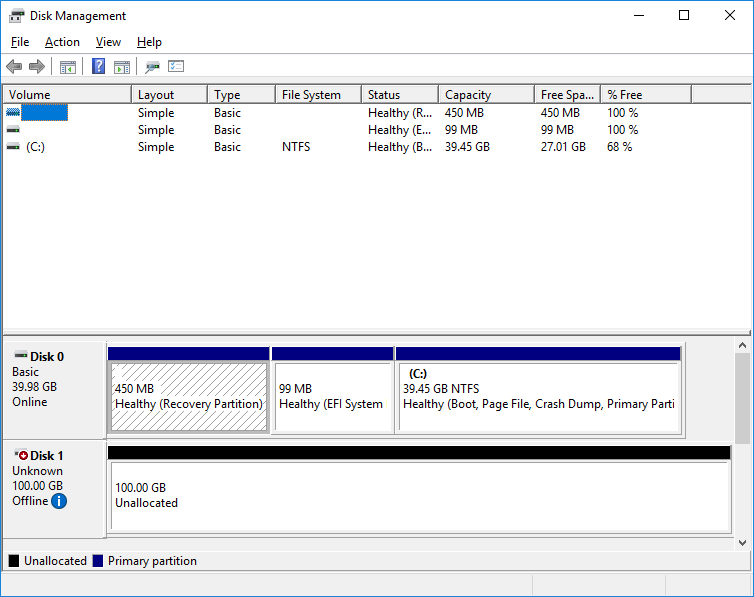
3. After the “insert” command is executed, disk LUNs for the connected controller namespaces should appear in the system.
4. To show the list of connected NVMe-oF controllers, run the “StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe list” command.
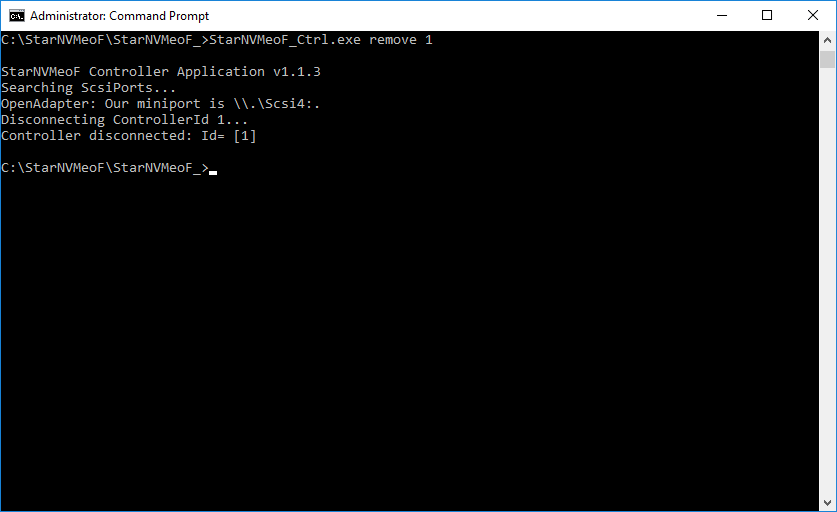
5. To disconnect LUNs from the system, run the the controller disconnection command StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe remove <controllerId>
Example: StarNVMeoF_Ctrl.exe remove 1
Where:
- <1> — controller Id
NOTE: Make sure that LUNs are not used by other applications at the moment of disconnection, as removing LUNs with active file operations may lead to data corruption.
Configuring a Failover Cluster
NOTE: To avoid issues during the cluster validation configuration, it is recommended to install the latest Microsoft updates on each node.
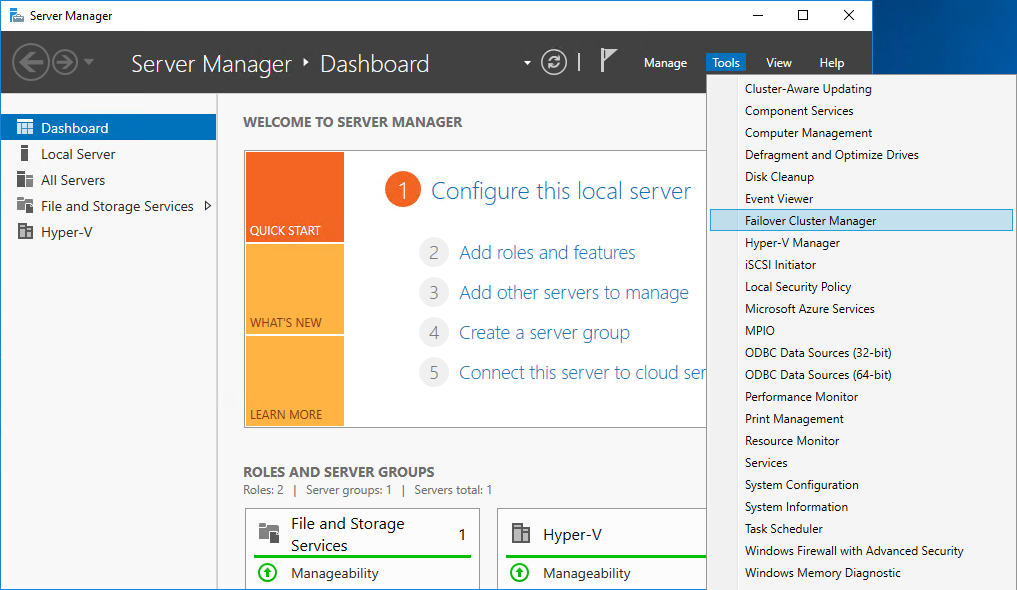
1. Open Server Manager. Select the Failover Cluster Manager item from the Tools menu.
2. Click the Create Cluster link in the Actions section of Failover Cluster Manager.
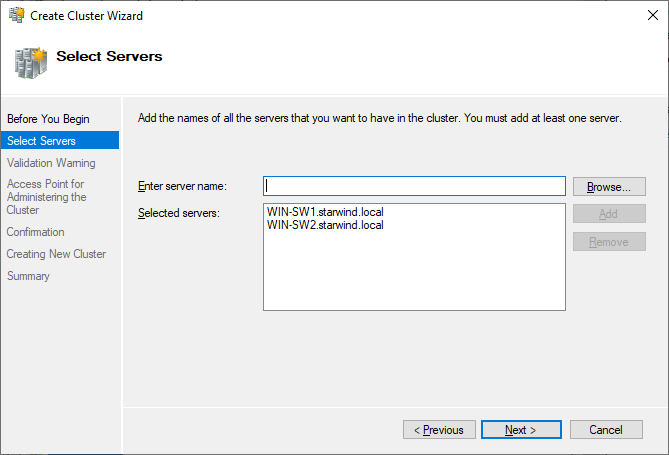
3. Specify the servers to be added to the cluster. Click Next to continue.
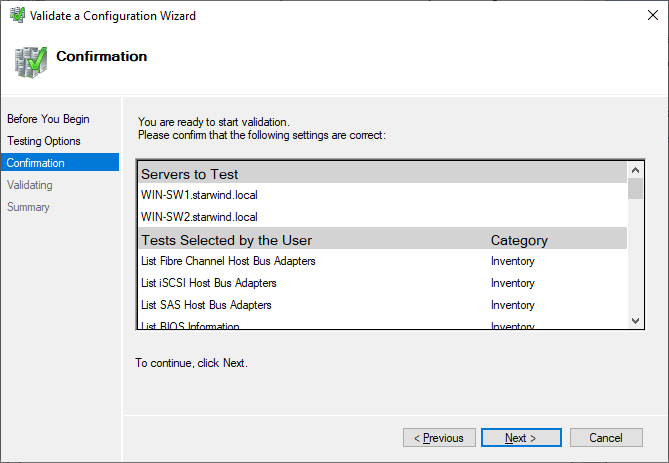
4. Validate the configuration by running the cluster validation tests: select Yes… and click Next to continue.
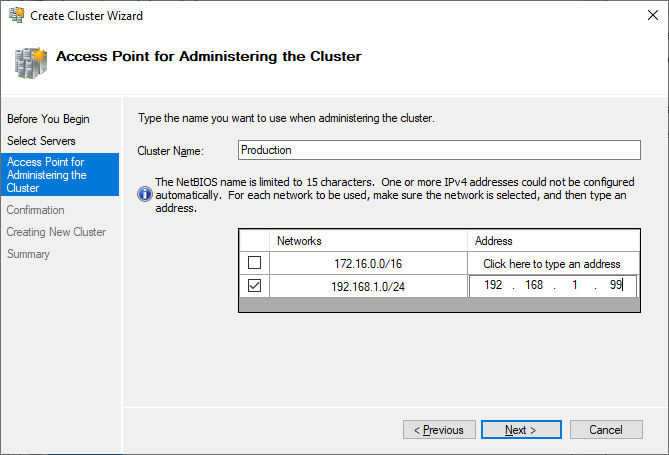
5. Specify Cluster Name.
NOTE: If the cluster servers get IP addresses over DHCP, the cluster also gets its IP address over DHCP. If the IP addresses are set statically, set the cluster IP address manually.
6. In Confirmation, make sure that all settings are correct. Click Previous to make any changes or Next to proceed.
NOTE: If checkbox Add all eligible storage to the cluster is selected, the wizard will add all disks to the cluster automatically. The device with the smallest storage volume will be assigned as a Witness. It is recommended to uncheck this option before clicking Next and add cluster disks and the Witness drive manually.
7. The process of the cluster creation starts. Upon the completion, the system displays the summary with the detailed information. Click Finish to close the wizard.
Adding Storage to the Cluster
1. In Failover Cluster Manager, navigate to Cluster -> Storage -> Disks. Click Add Disk in the Actions panel, choose StarWind disk from the list and confirm the selection.
2. To configure the cluster witness disk, right-click on Cluster and proceed to More Actions -> Configure
3. Follow the wizard and choose the Select the quorum witness option. Click Next.
4. Select Configure a file share witness. Click Next.
5. Select the file share to be assigned as the cluster witness. Click Next and press Finish to complete the operation.
6. In Failover Cluster Manager, right-click the disk and select Add to Cluster Shared Volumes.
7. If renaming of the cluster shared volume is required, right-click on the disk and select Properties. Type the new name for the disk and click Apply followed by OK
Configuring Cluster Network Preferences
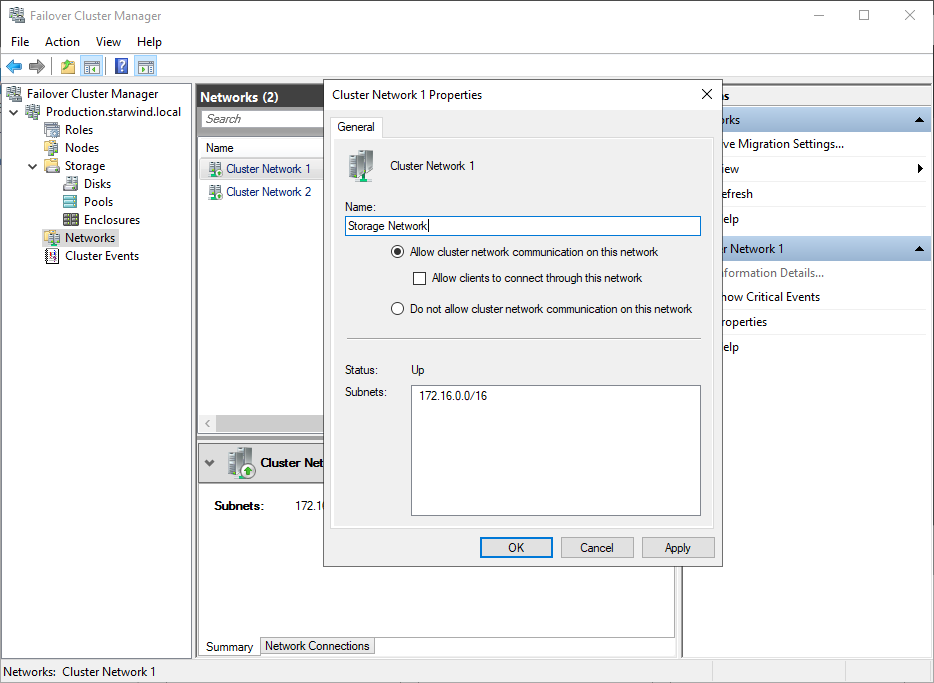
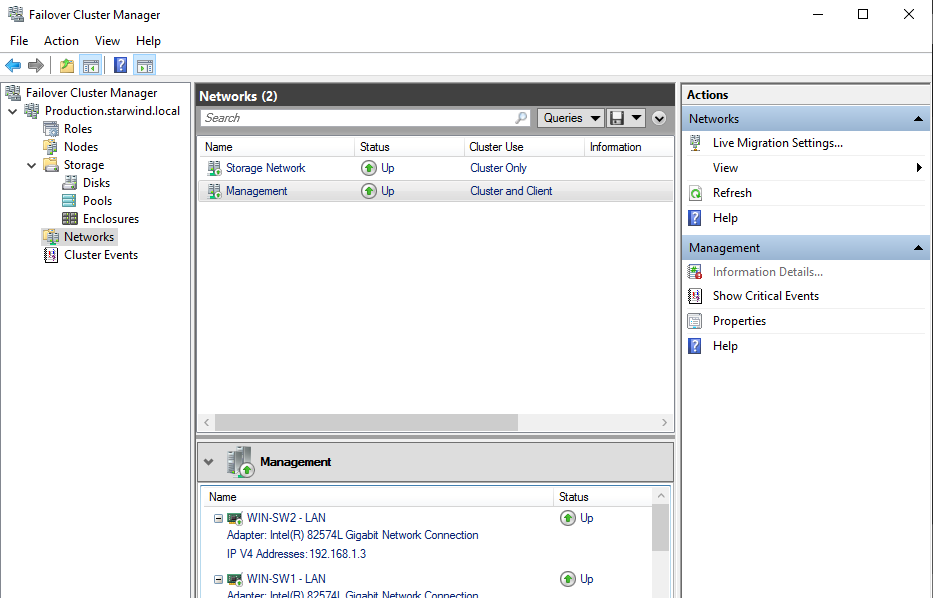
1. In the Networks section of the Failover Cluster Manager, right-click on the network from the list. If required, set its new name to identify the network by its subnet. Apply the change and press OK.
NOTE: Please double-check that cluster communication is configured with redundant networks: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/failover-clustering/smb-multichannel
2. Rename other networks as described above, if required.
The cluster configuration is completed and it is ready for virtual machines deployment. Select Roles and in the Action tab, click Virtual Machines -> New Virtual Machine. Complete the wizard.
.
Conclusion
The StarWind NVMe-oF Initiator installation guide provides a comprehensive method for IT professionals to set up a Microsoft failover cluster with enhanced performance and reliability using NVMe over Fabrics technology. This setup is crucial for environments requiring high-speed shared storage and failover capabilities, contributing significantly to the efficiency of server infrastructures.