StarWind SAN & NAS CVM 2-node Converged Scenario with VMware vSphere 7
- May 23, 2023
- 26 min read
- Download as PDF
Introduction
StarWind SAN & NAS Controller Virtual Machine (CVM) comes as a prepackaged Linux Virtual Machine (VM) to be deployed on any industry-standard hypervisor. The solution is a fully certified shared storage for VMware vSphere Hypervisor ESXi, allowing you to repurpose your existing hardware running industry-standard hypervisor into high-performing storage.
StarWind SAN & NAS supports hardware and software-based storage redundancy configurations. The solution allows turning your server with internal storage into a redundant storage array presented as NAS or SAN, exposing standard protocols such as iSCSI, SMB, and NFS. It features Web-based UI, Text-based UI, vCenter Plugin, and Command-line interface for your cluster-wide operations.
This guide describes the deployment and configuration process of the StarWind SAN & NAS CVM.
StarWind SAN & NAS virtual machine requirements
Prior to installing StarWind SAN & NAS virtual storage appliance, please make sure that the system meets the requirements, which are available at the following link: https://www.starwindsoftware.com/system-requirements
Pre-Configuring the Servers
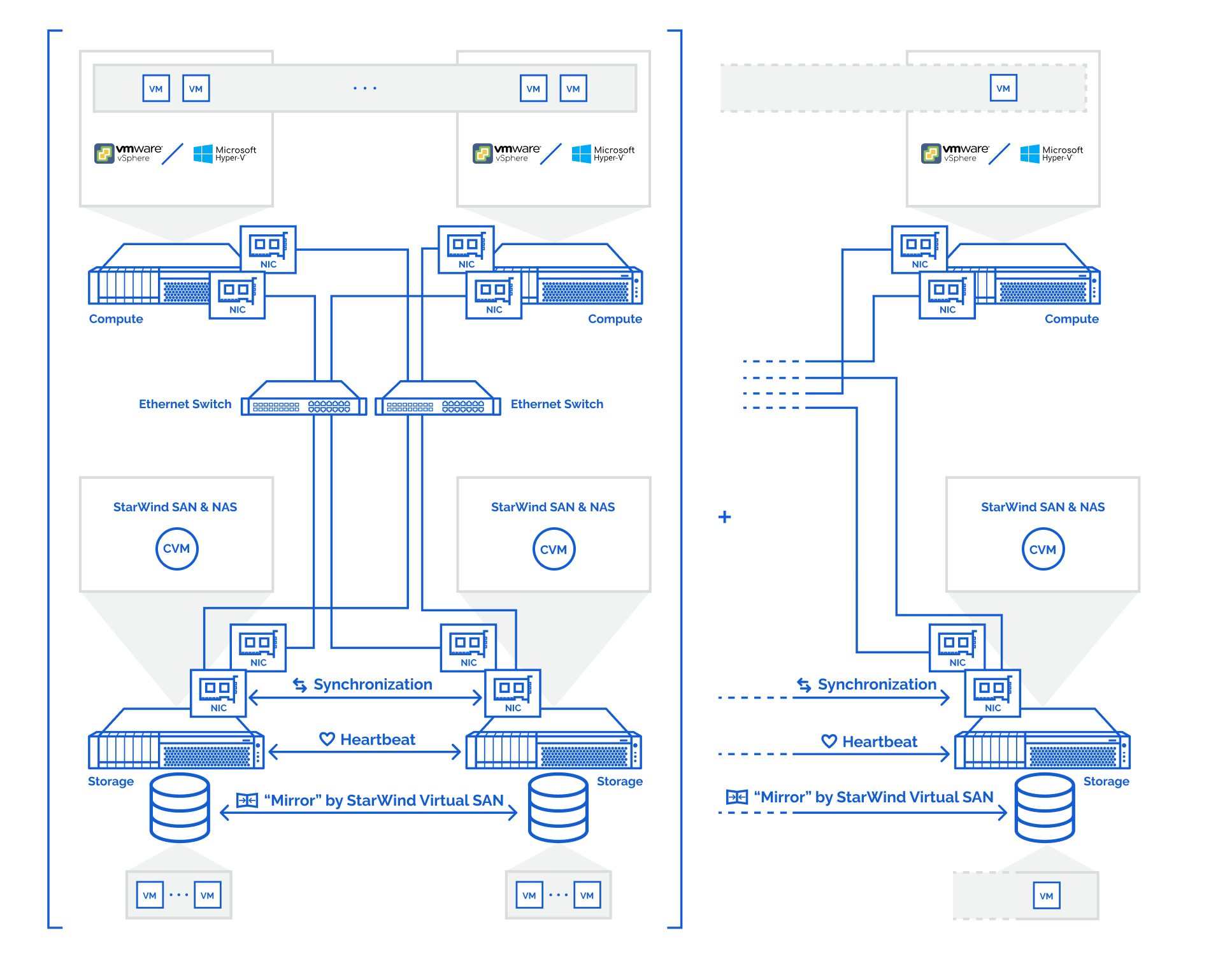
The diagrams below illustrate the common network and storage configurations of the solution for specific deployment configurations.
Please select your deployment scenario:
Highly available shared storage servers
- Dedicated 2 storage servers expose highly available shared storage for vSphere and Hyper-V clusters:
1. Install the hypervisor of your choice, VMware vSphere Hypervisor ESXi or Hyper-V Server, on two dedicated storage servers, and on the compute servers that are intended to connect and utilize the shared storage provisioned by the appliance.
2. StarWind SAN & NAS CVM is deployed on each Hyper-V Server or VMware ESXi server with commodity direct-attached storage.
3. The network interfaces on each node for Management, Data/iSCSI, and Replication interfaces should be connected to different subnets and connected directly according to the network diagram above. Here, the 172.16.10.x subnet is used for the Data (iSCSI) storage traffic, and 172.16.20.x subnet is used for the Replication storage traffic.
NOTE: The vCenter server is recommended for the deployment of multiple ESXi servers.
NOTE: The Failover Cluster feature is recommended for the deployment of multiple Hyper-V servers.
Setting up StarWind SAN & NAS
This part describes how to prepare the environment to deploy and install StarWind SAN & NAS using your hypervisor of choice, either VMware ESXi and VMware vSphere web clients or Microsoft Hyper-V Server.
Please select the required option:
Configuring converged storage server with VMware vSphere
Creating Datacenter in VMware vSphere
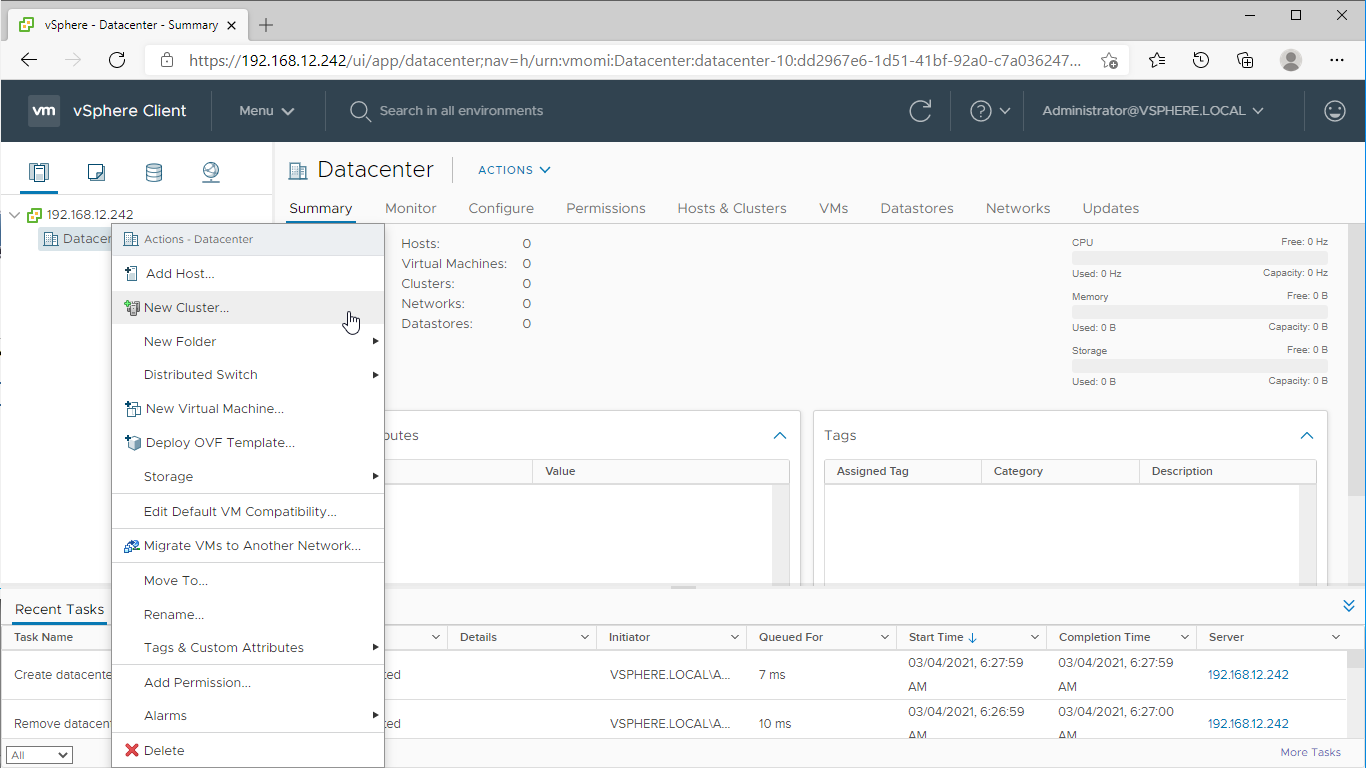
1. Connect to the vSphere Client, right-click on the “vCenter Site” menu, and select the “Create Datacenter” option.
2. Specify the Datacenter Name and click “OK“.
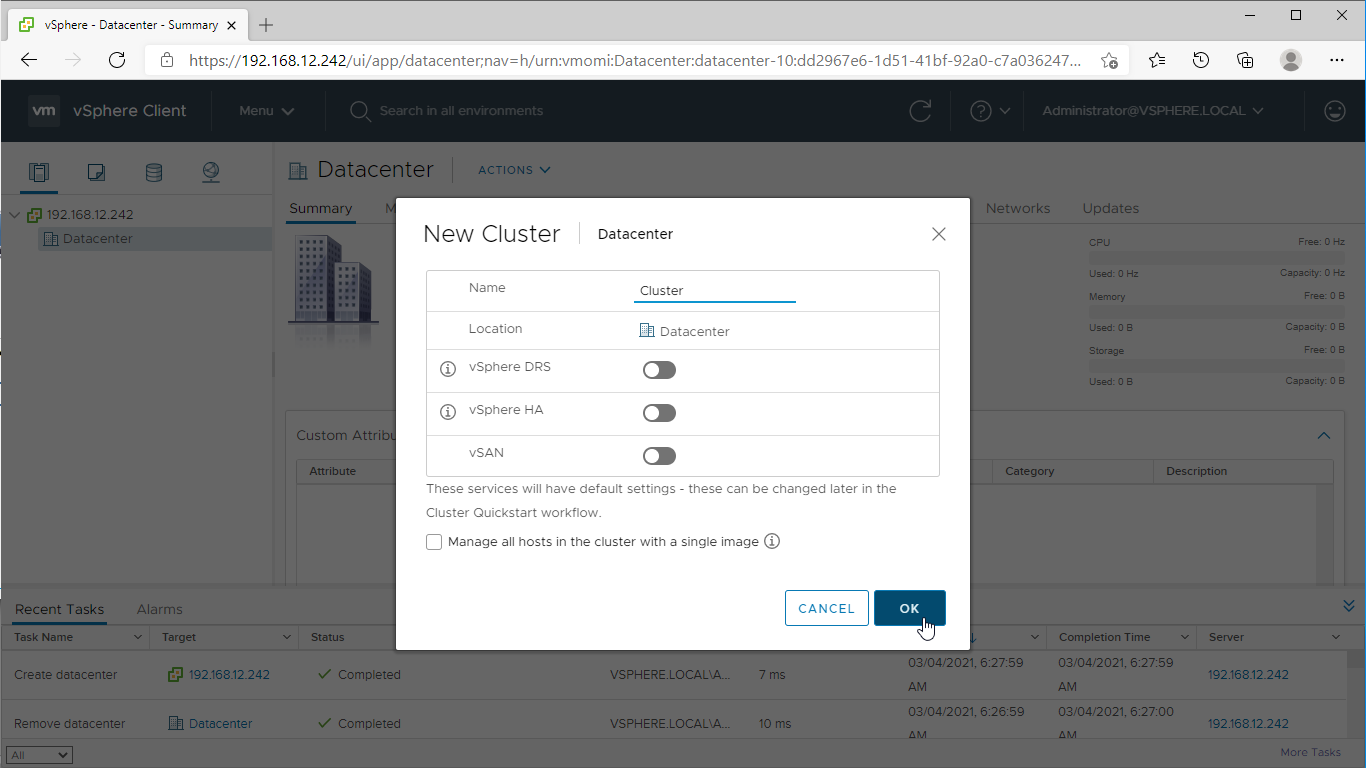
3. Right-click on the Datacenter icon and select the “New Cluster…” action.
4. Specify the cluster name and enable the required services.
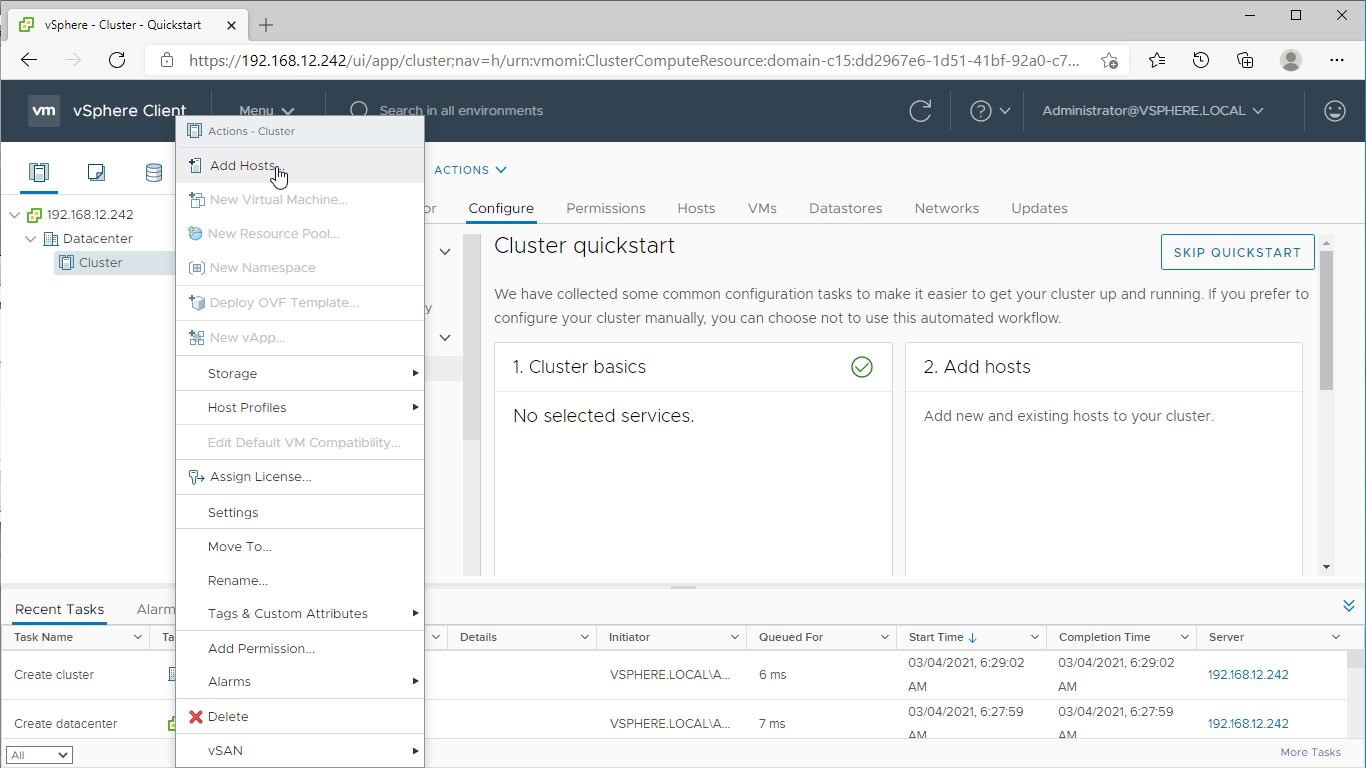
5. Right-click on “Cluster” and select the “Add Hosts” action.
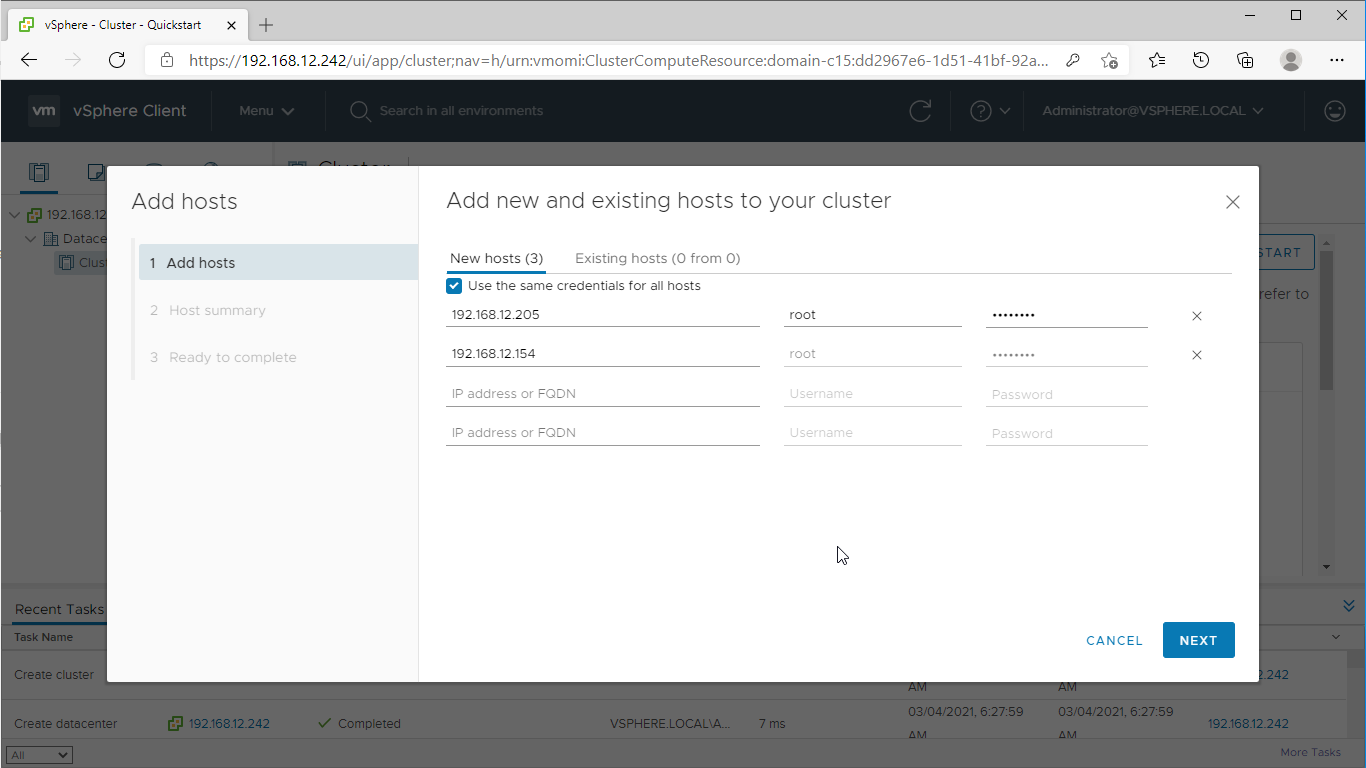
6. In the “Add Hosts” wizard, specify the IPv4 or FQDN, login, and password of each ESXi server intended to be added to the cluster and managed using VMware vSphere.
NOTE: For the converged deployment with StarWind SAN & NAS CVM running on VMware ESXi servers, it is recommended to add the VMware ESXi servers that host the CVMs.
NOTE: For the converged deployment with StarWind SAN & NAS installed bare metal, make install of StarWind vCenter plugin to manage the SAN & NAS nodes from the vSphere web interface.
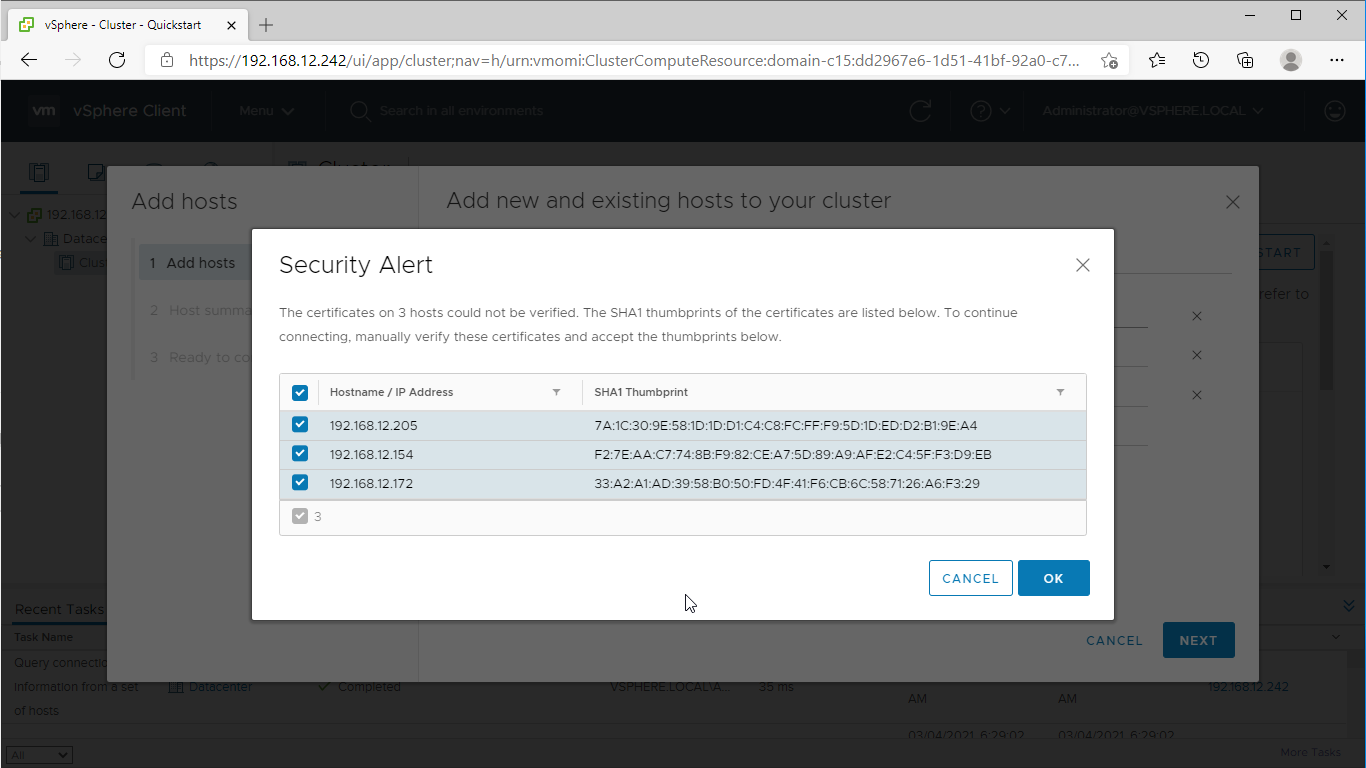
7. Manually verify the ESXi servers’ certificates and accept the thumbprints. Click “OK” to proceed.
8. Review settings and finish adding servers to the cluster.
Configuring Networks on vSphere Servers
Configure network interfaces on each node to ensure that Management and Data/iSCSI interfaces are in different subnets and connected physically according to the network diagram above. All actions below should be applied to each ESXi server for running StarWind SAN & NAS.
NOTE: Virtual Machine Port Group should be created for the Data/iSCSI and Replication vSwitches. VMKernel port should be created only for Data/iSCSI traffic. Static IP addresses should be assigned to VMKernel ports.
NOTE: It is recommended to set jumbo frames to 9000 on vSwitches and VMKernel ports for Data/iSCSI and Replication traffic. Additionally, vMotion can be enabled on VMKernel ports.
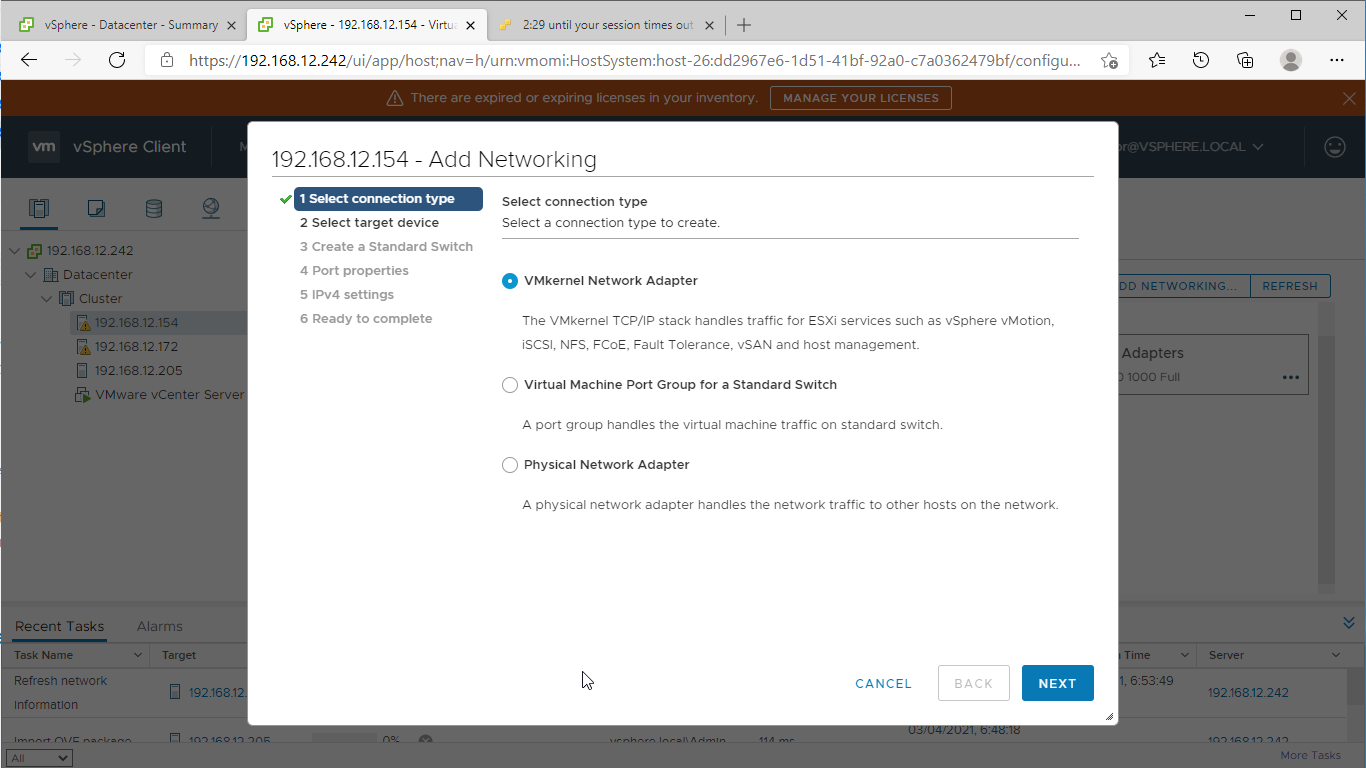
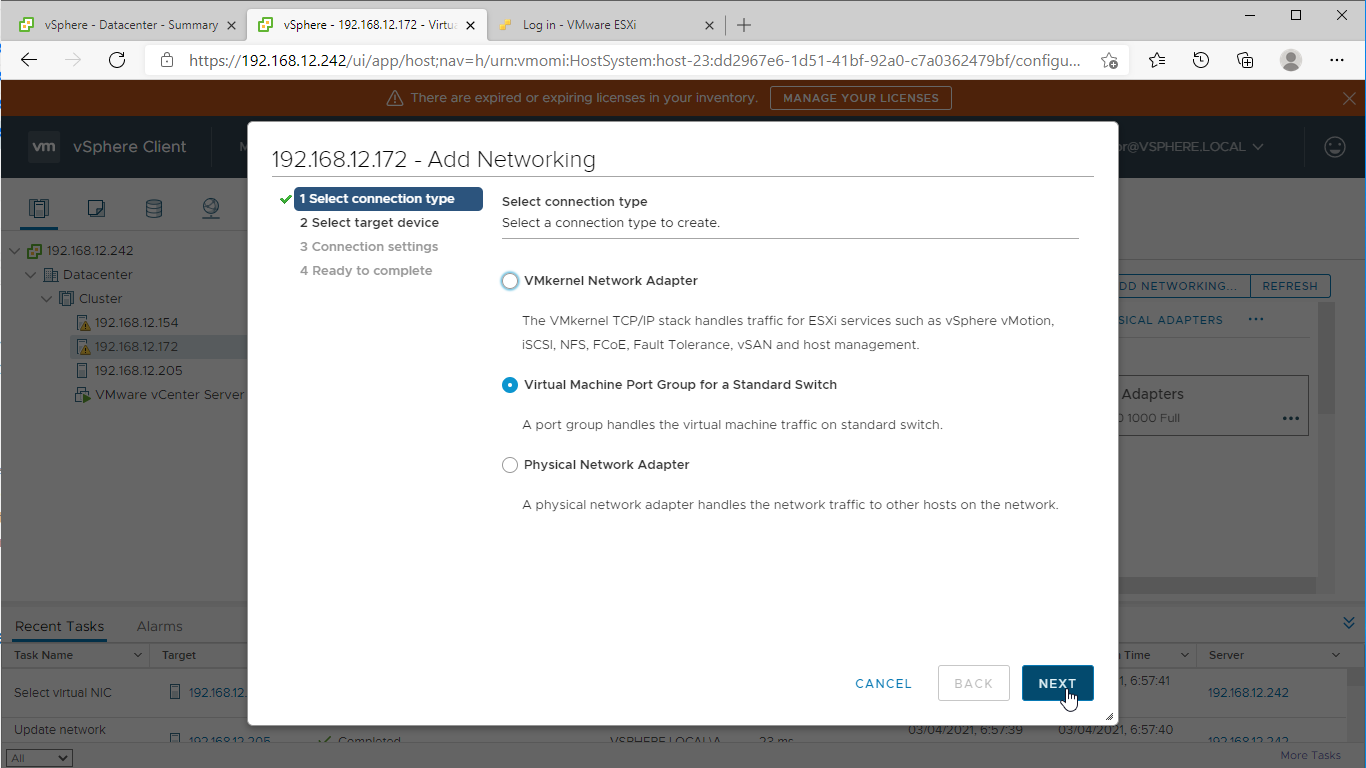
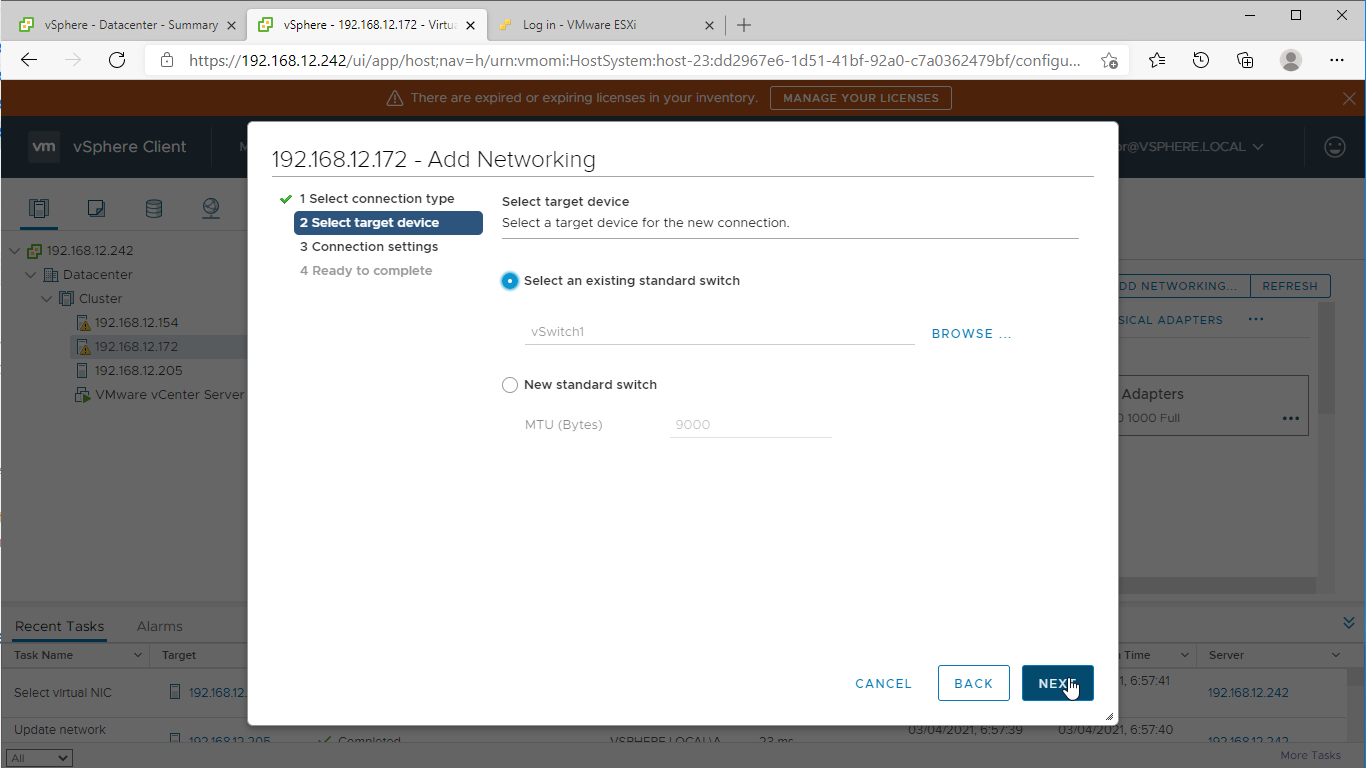
1. Using the VMware vSphere Client console, start the “Add Networking” wizard. Add a new VMKernel network adapter for the Data/iSCSI channel.
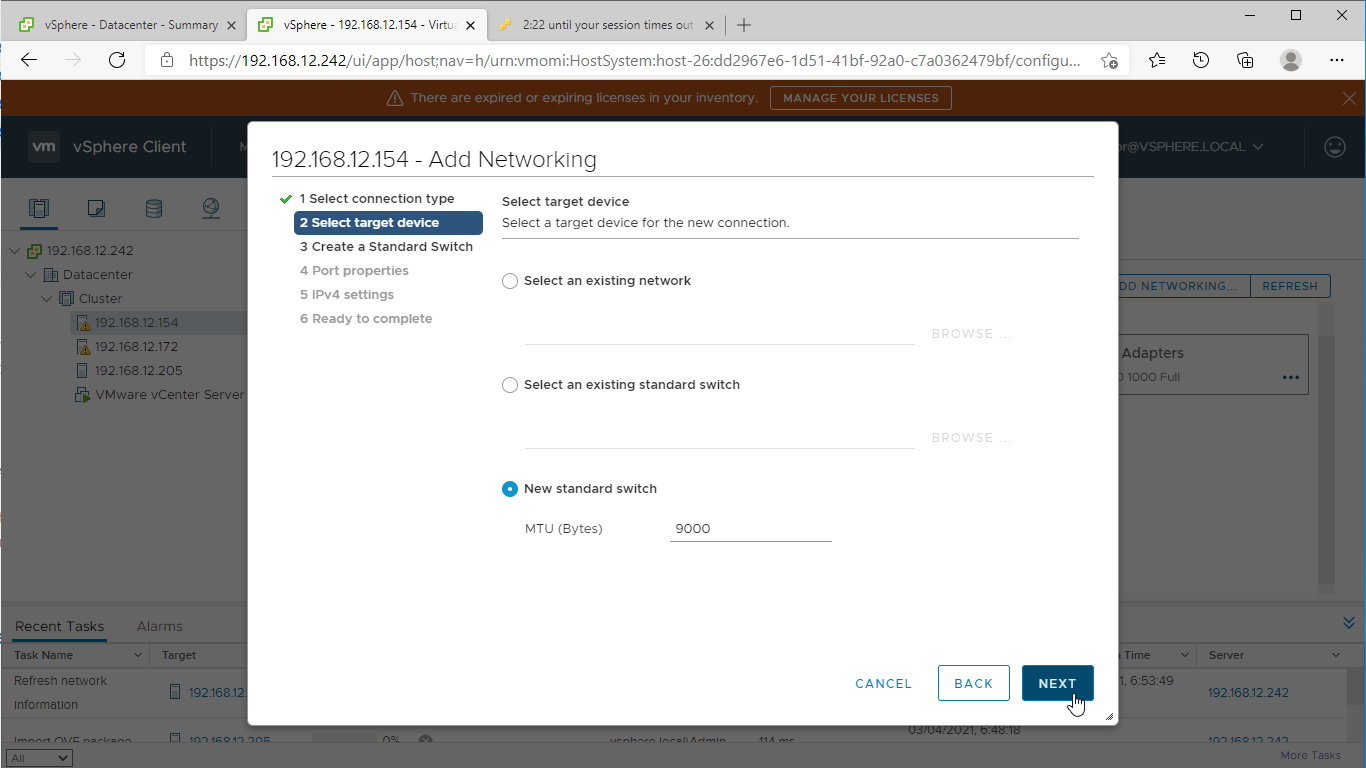
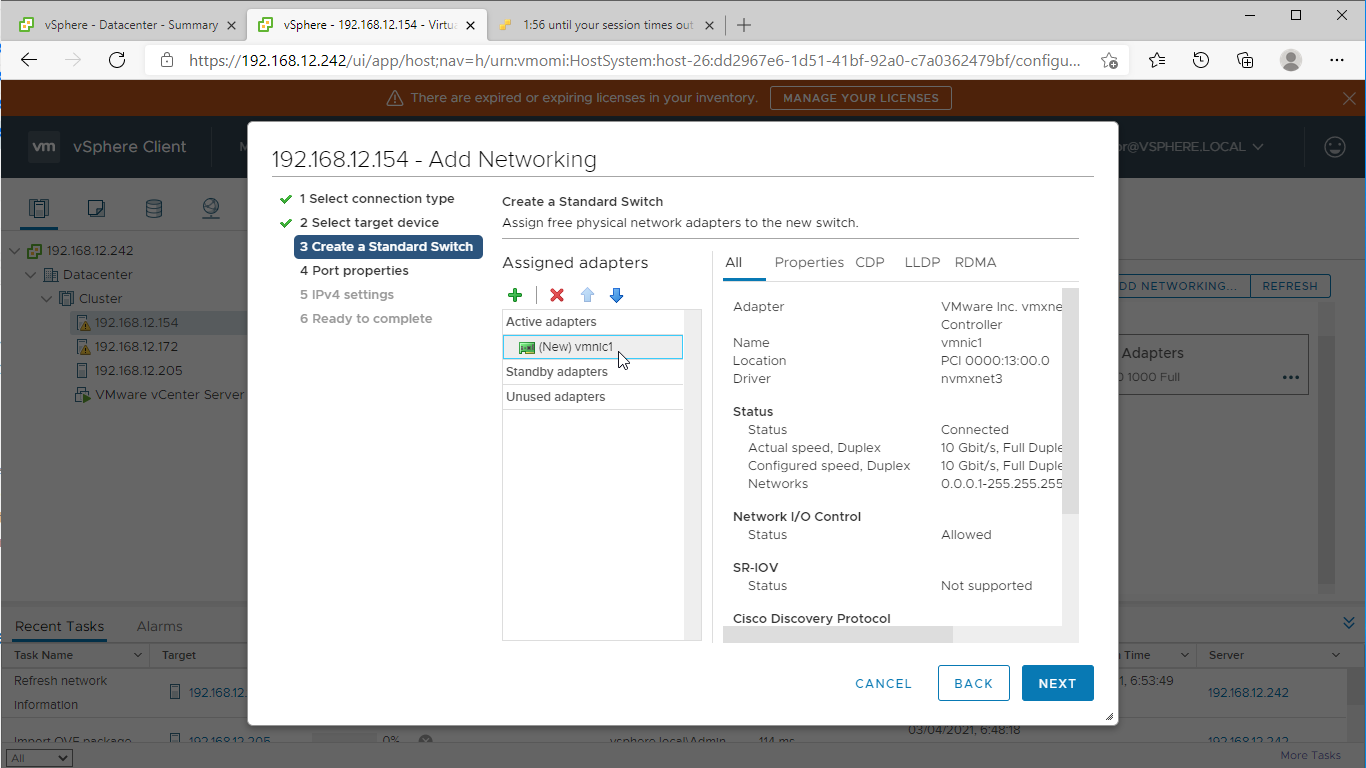
2. Create a new standard switch for the Data/iSCSI channel. Set MTU accordingly.
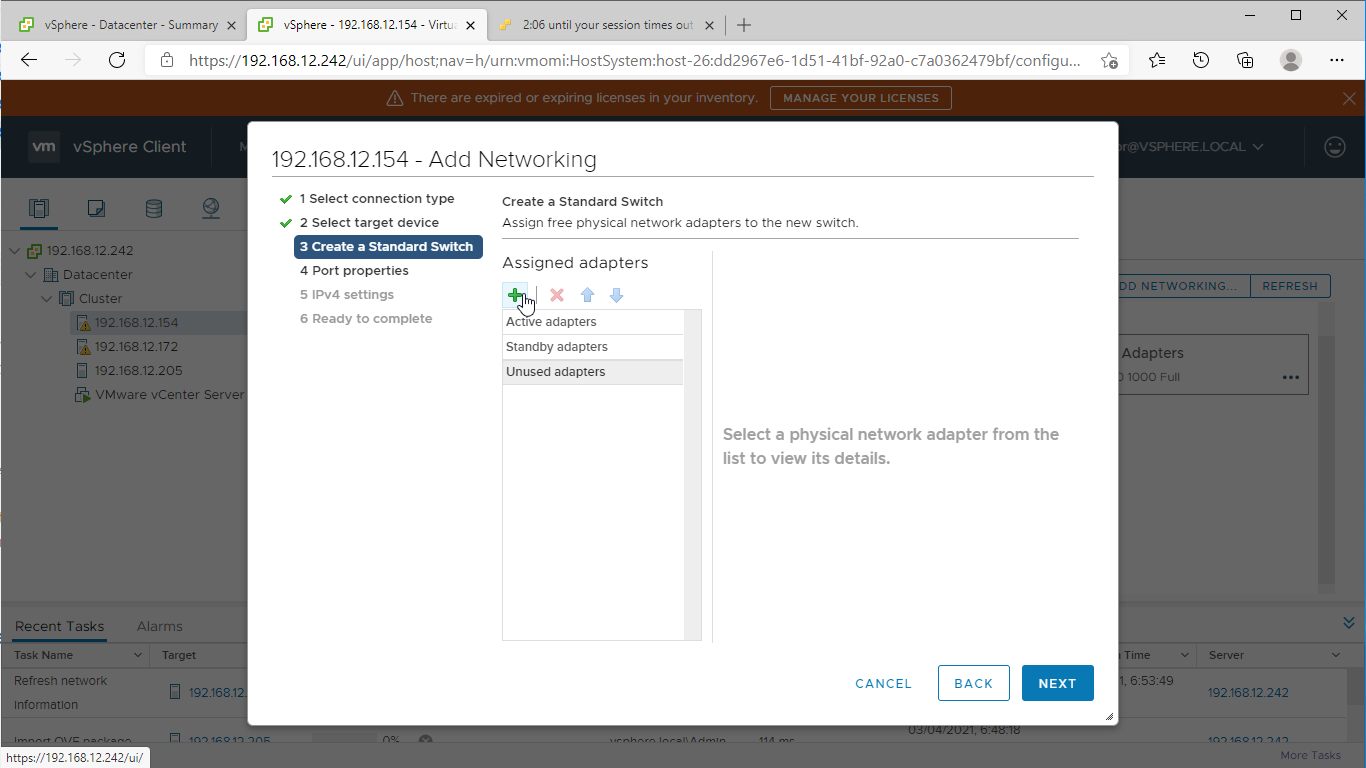
3. Assign the second network adapter to the virtual switch. Click Next.
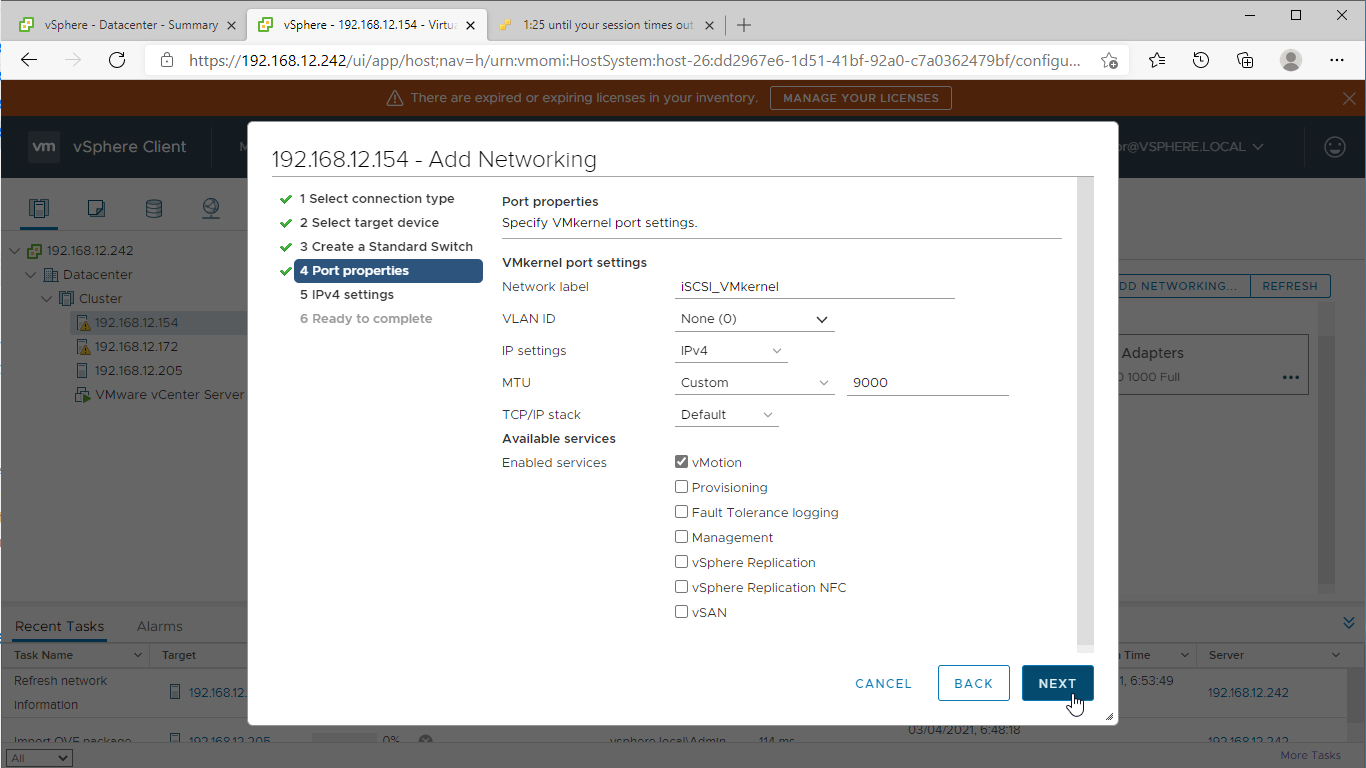
4. Specify port properties such as Network Label, MTU, and enable required services. Click Next.
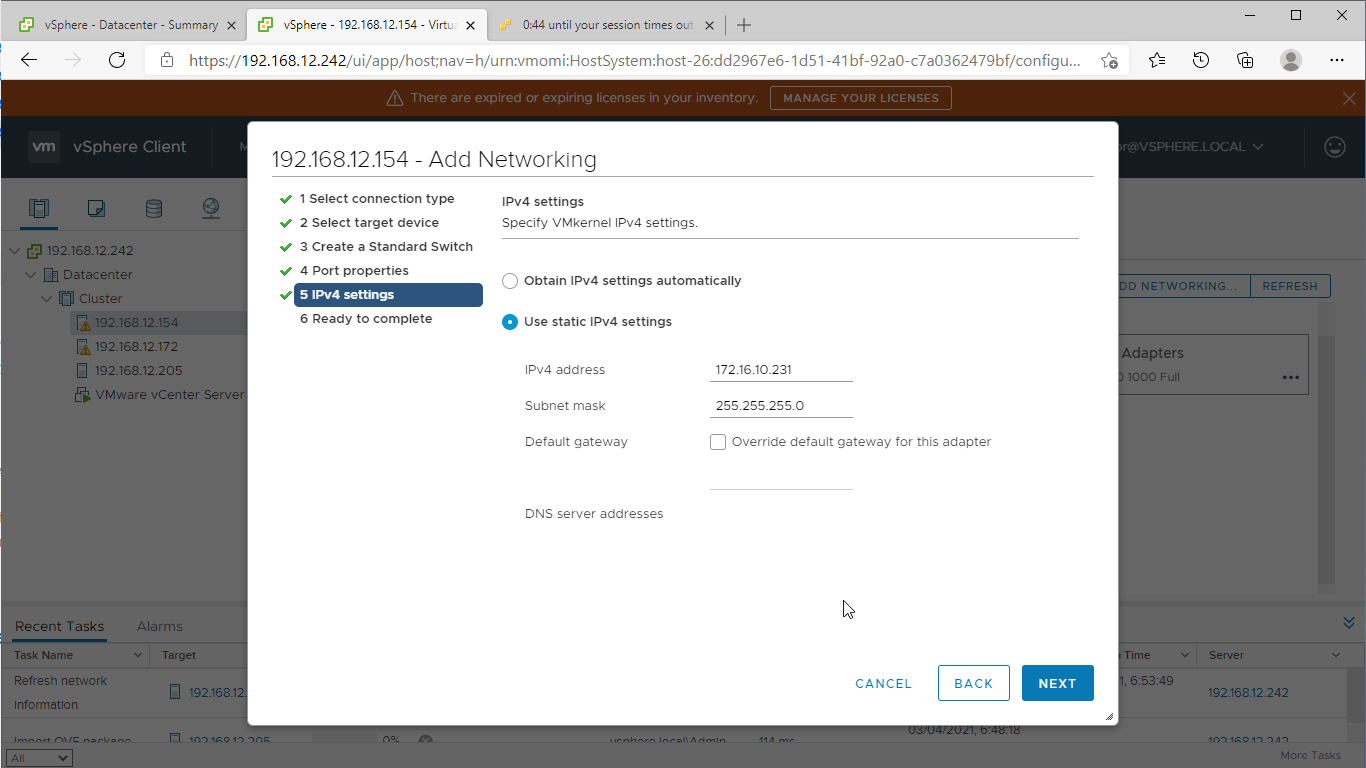
5. Assign static IPv4 address settings to the virtual switch. Click Next.
NOTE: In this document, the 172.16.10.x subnet is used for Data traffic and 172.16.20.x subnet is used for Replication traffic.
6. Review the summary of your settings and click “Finish” to add networking.
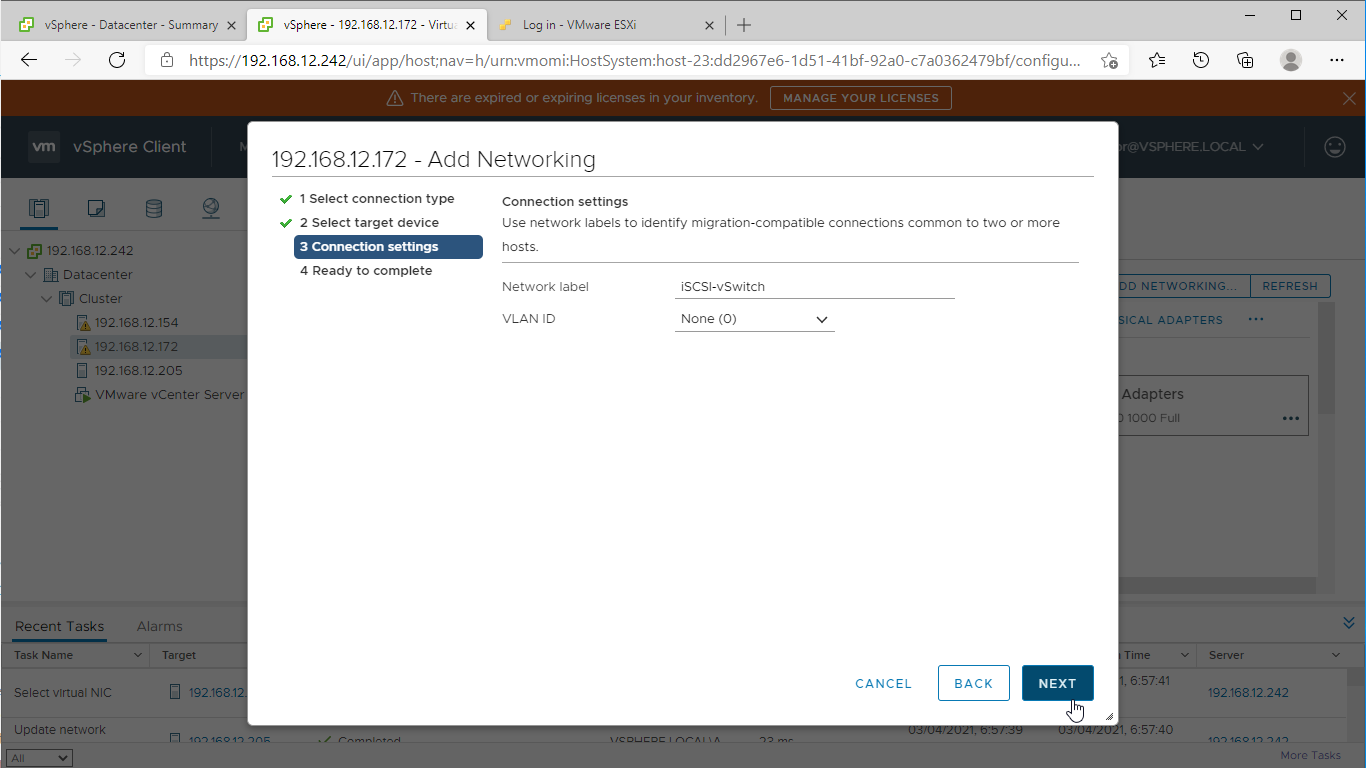
7. Start the “Add Networking” wizard again to create a “Virtual Machine Port Group for a Standard Switch“.
8. Specify the previously created vSwitch. Click Next.
9. Set the Network label and click Next. Optionally, set VLAN ID if used.
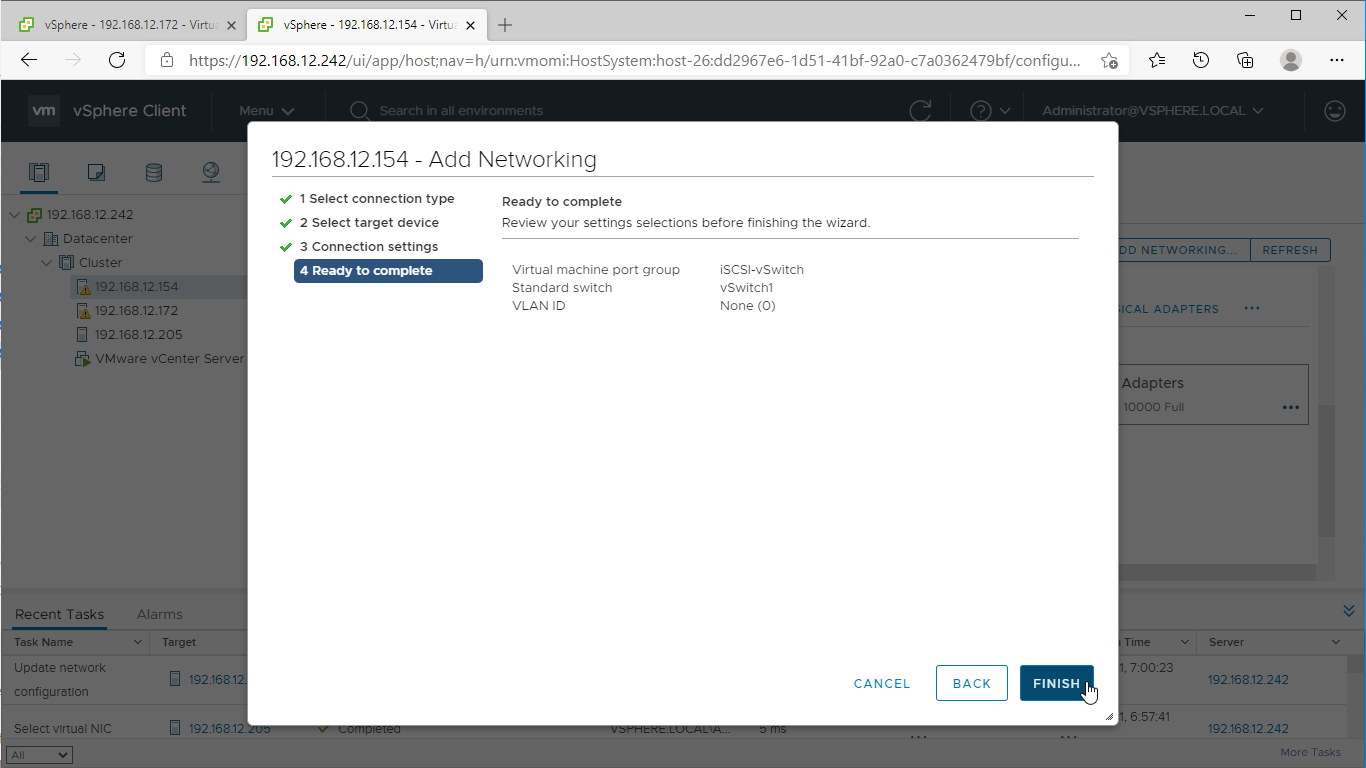
10. Review the port group setting and click Finish to apply.
10. Repeat steps 7-9 to configure the network for Replication traffic on each vSphere server.
11. Repeat steps 1-9 for any other links intended for the Data/iSCSI and Replication connections on each vSphere server.
Deploying StarWind SAN & NAS CVM on vSphere servers
1. Download the zip archive that contains StarWind SAN & NAS CVM
https://www.starwindsoftware.com/san-and-nas#download
2. Extract the virtual machine files.
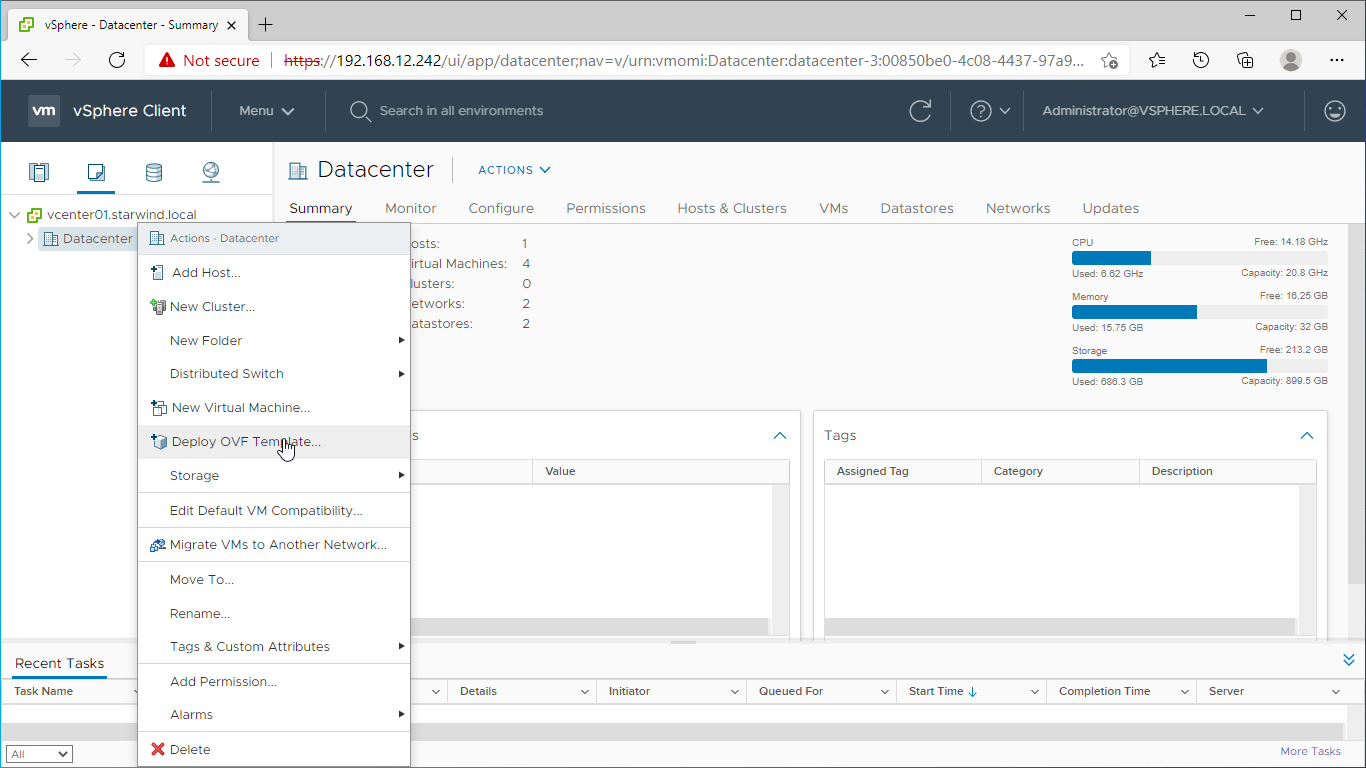
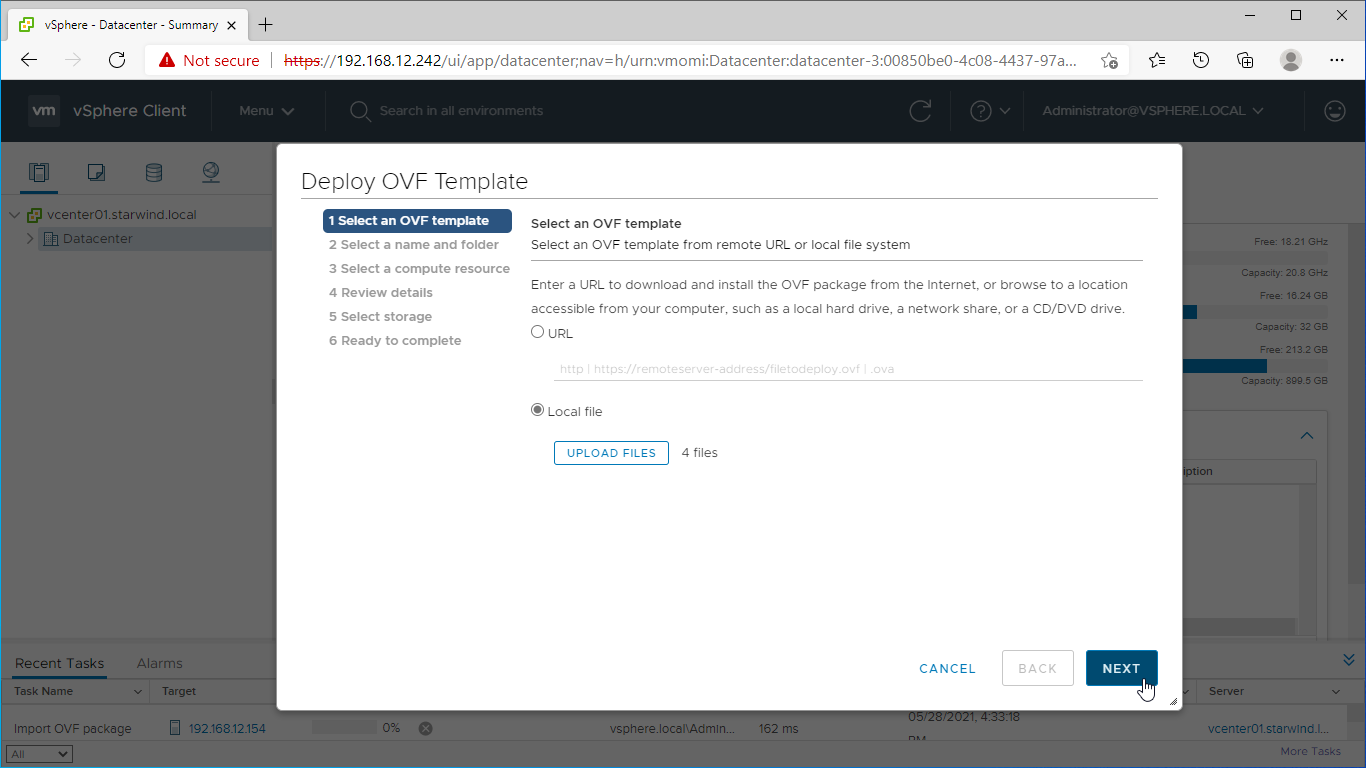
3. Deploy the control virtual machine to the VMware vSphere. Right-click on the Datacenter, cluster, or node menu and select the “Deploy OVF Template…” option from a drop-down menu.
4. In the first step of the wizard, point to the location of the OVF template. Select the VM files and click Next.
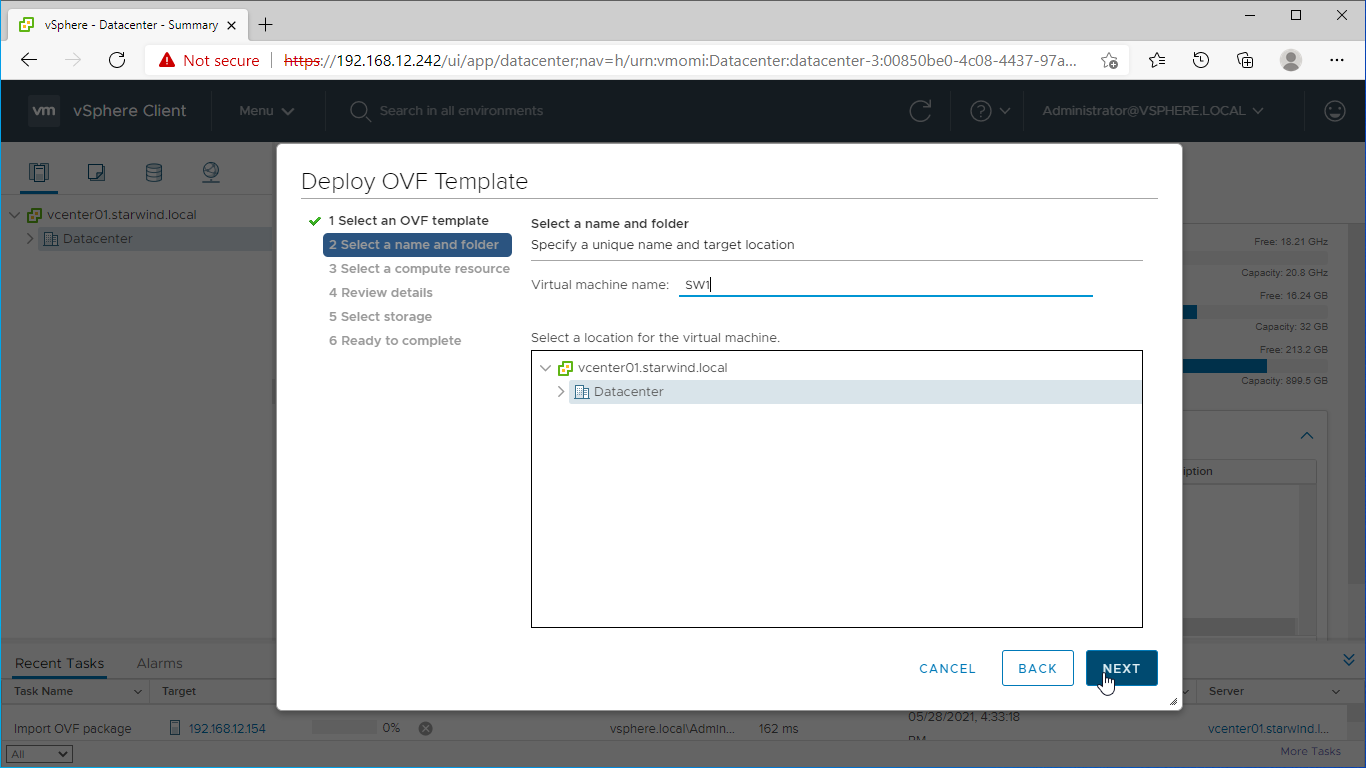
5. Specify the VM name and target location.
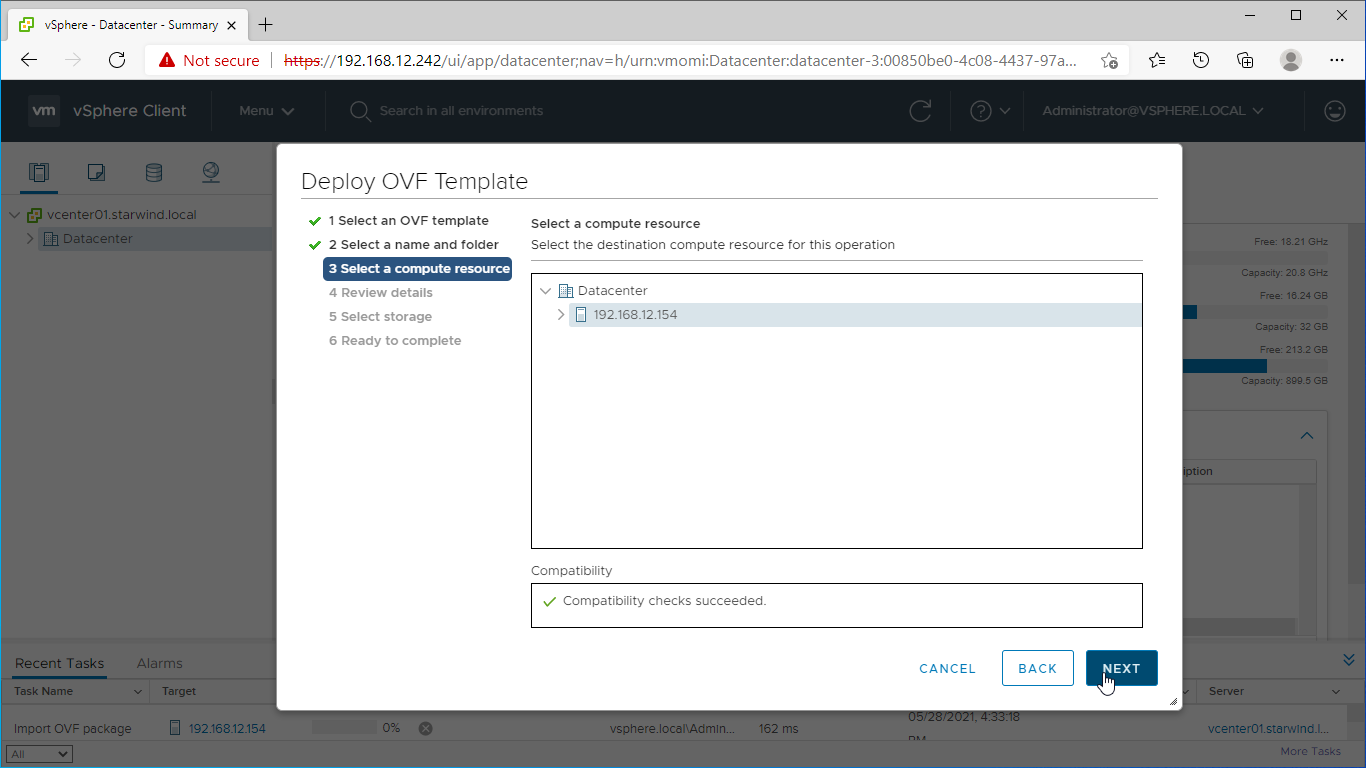
6. Select a compute resource intended to run the StarWind SAN & NAS CVM
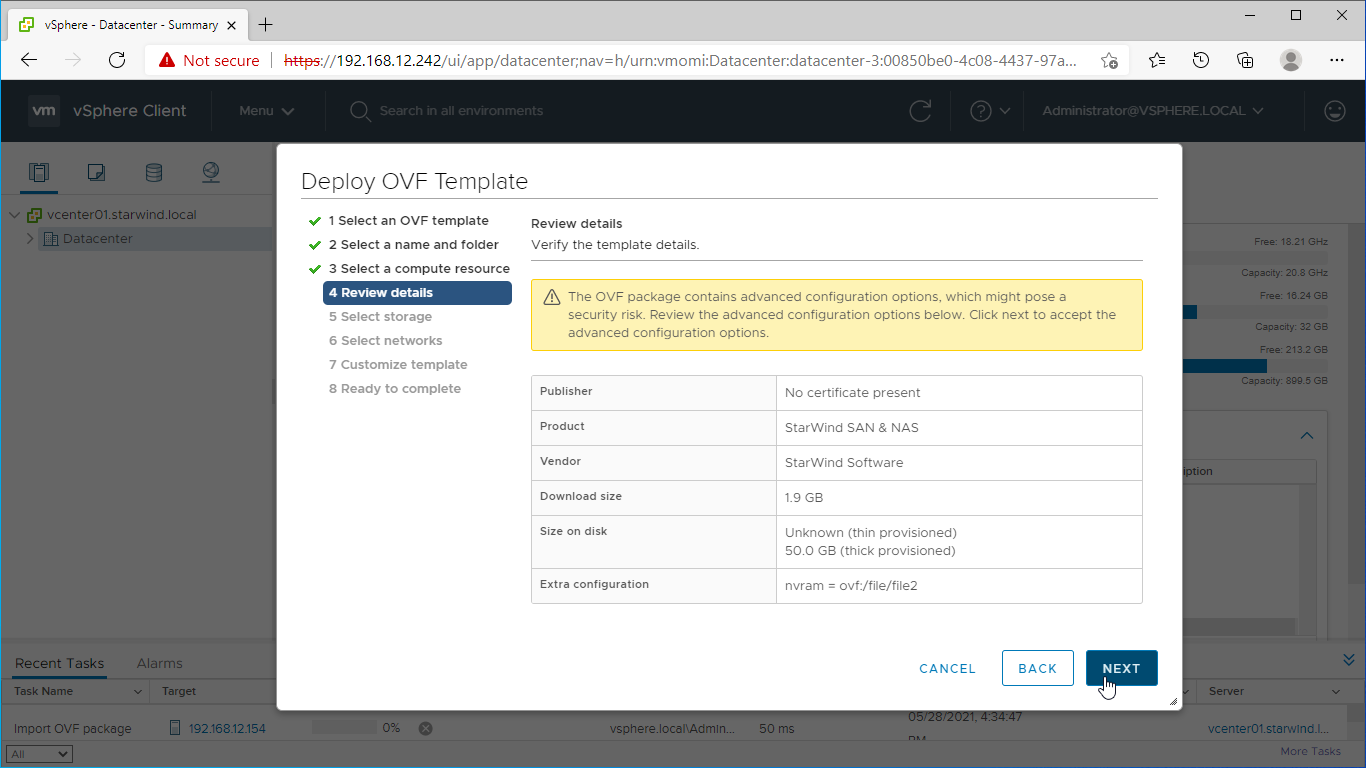
7. Review the template details. Click Next.
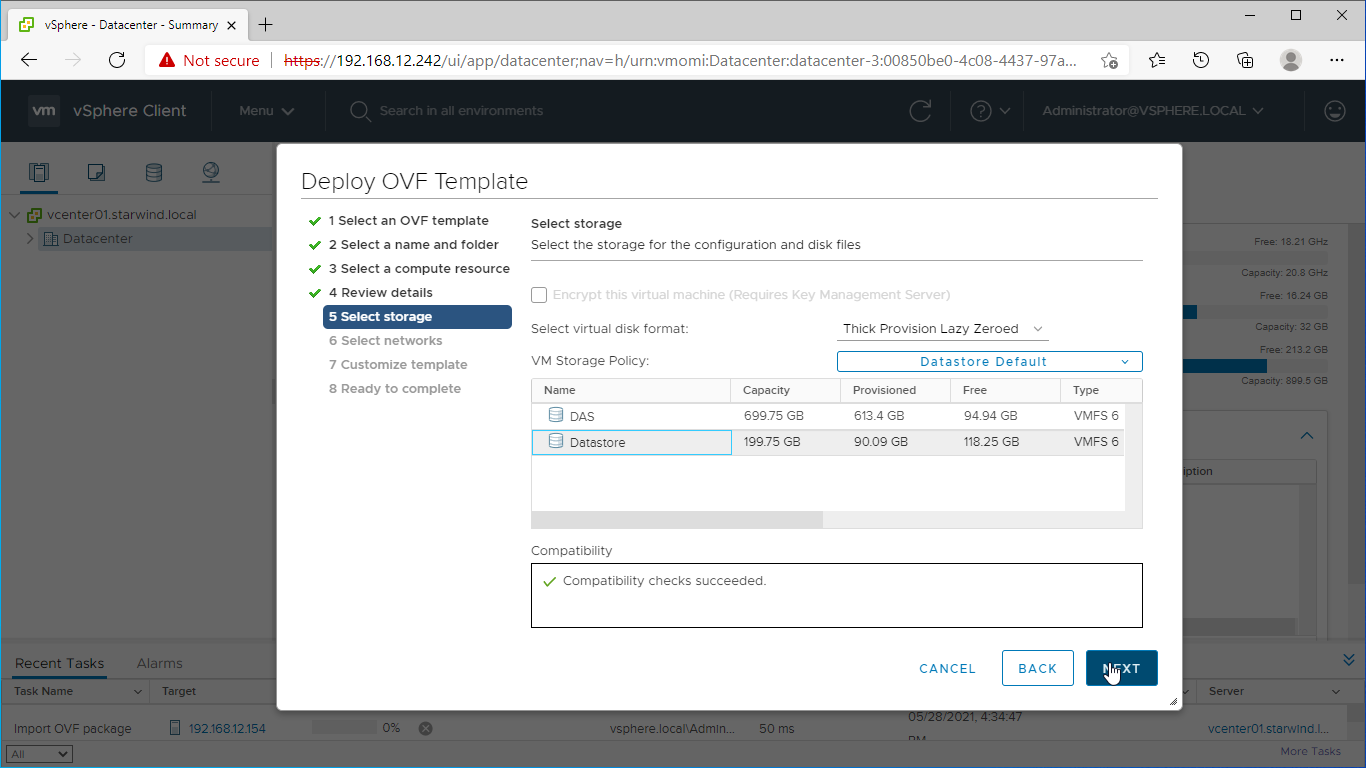
8. In the second step of the wizard, specify the virtual machine provisioning type, VM Storage Policy, and select the direct-attached storage for the appliance system drive. Click Next.
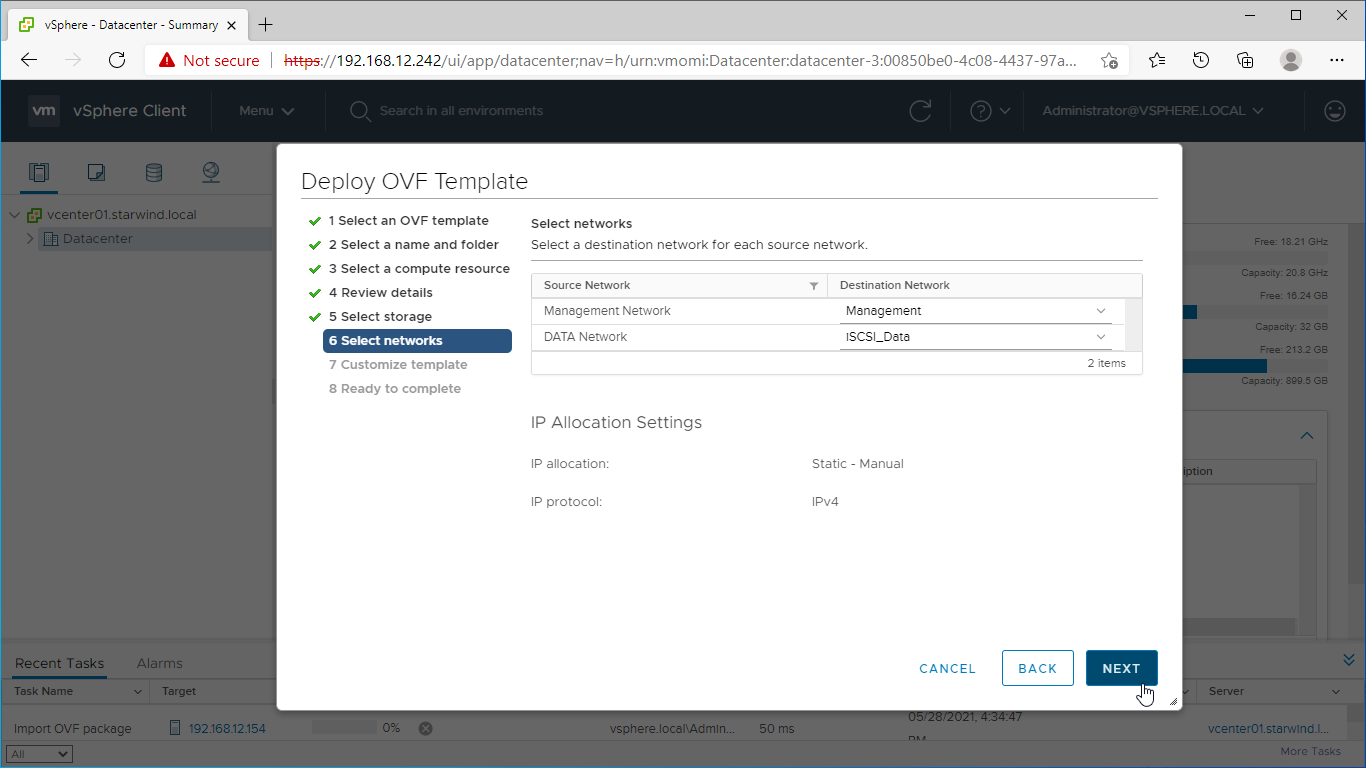
9. Select the destination network for each network adapter assigned to the VM.
The default naming for virtual switches:
- the Management virtual switch is “Management vSwitch”,
- the iSCSI virtual switch is “Data/iSCSI vSwitch”,
- the Synchronization virtual switch is “Replication/Sync vSwitch “.
Specify corresponding network connections according to your virtual network naming. Click Next.
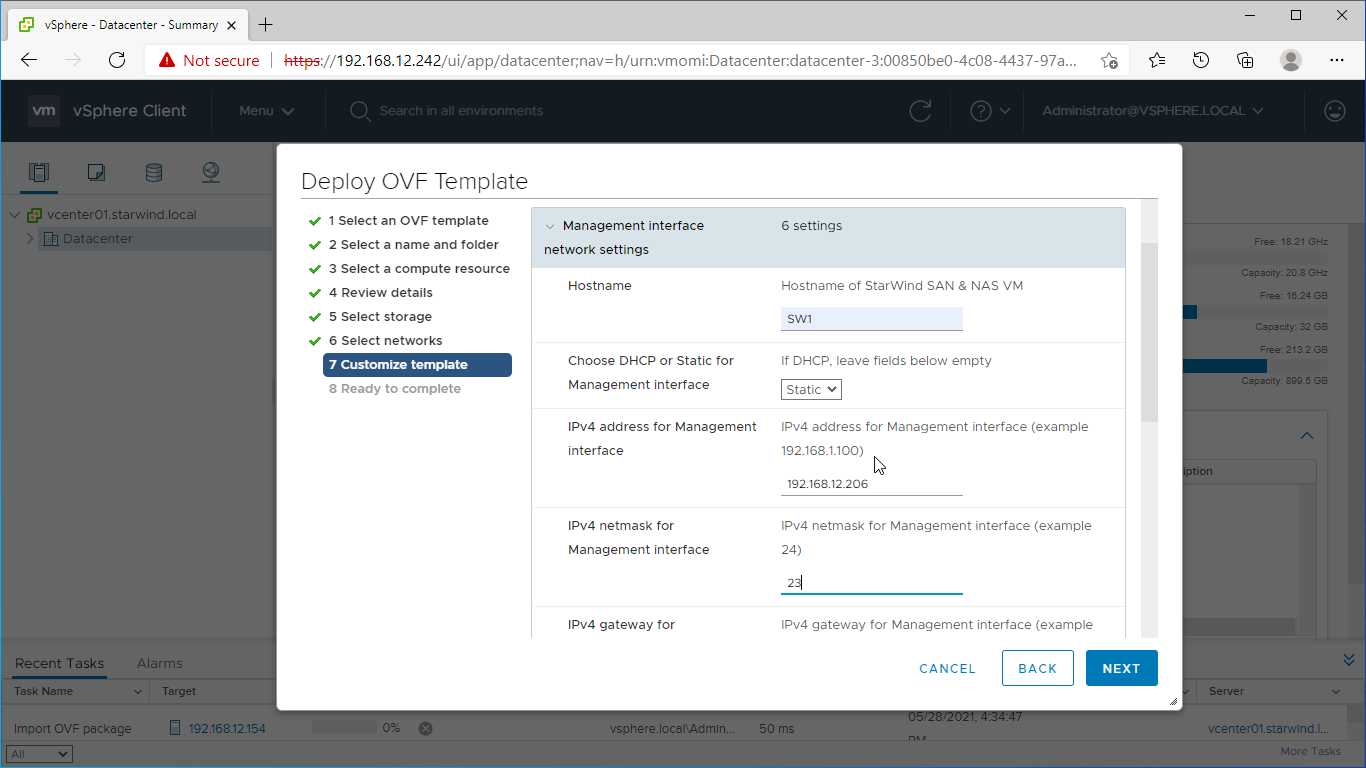
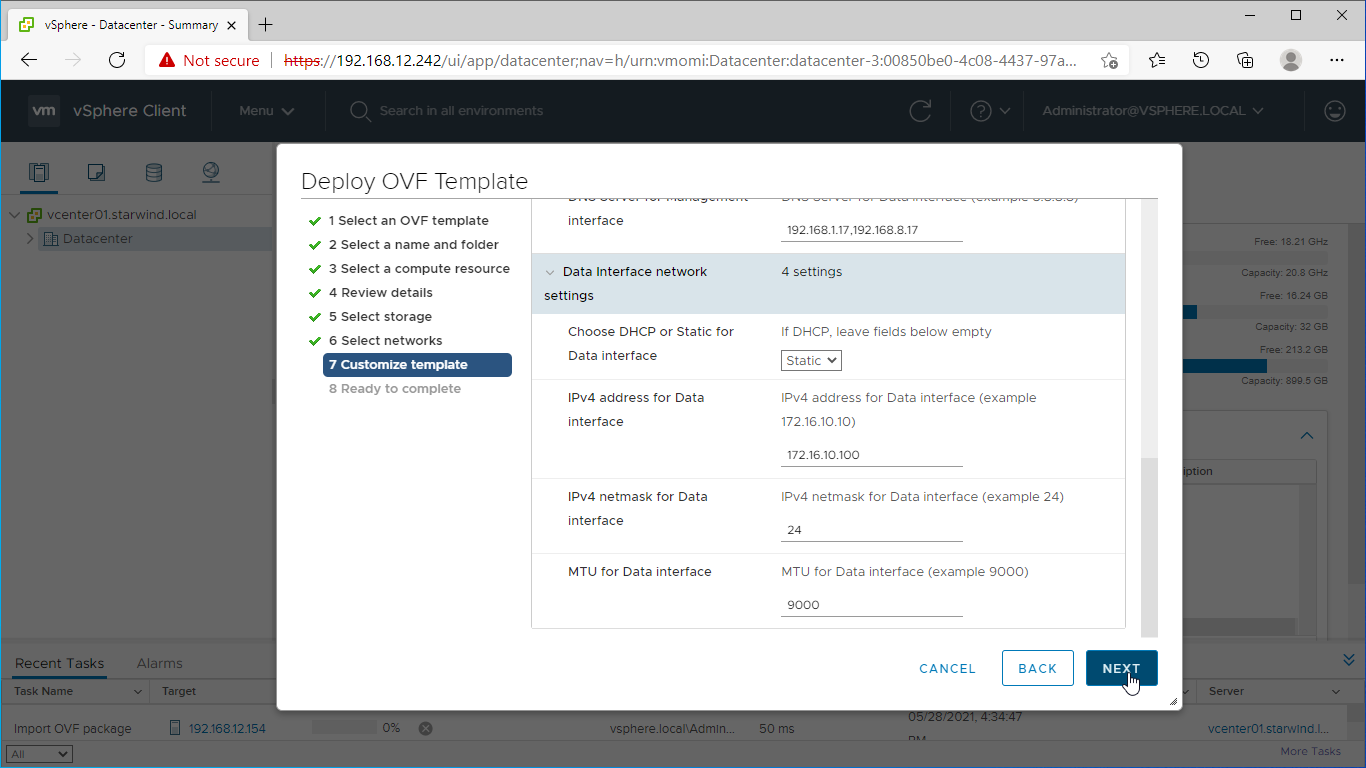
10. Specify the hostname, static IPv4 address, gateway, DNS, and additional network settings for Management and iSCSI/Data network interfaces:
NOTE: To manage the SAN & NAS appliance via StarWind vCenter plugin, the static IPv4 address must be assigned.
NOTE: if a DHCP server is available on the given network, you can skip setting the additional parameters for that interface.
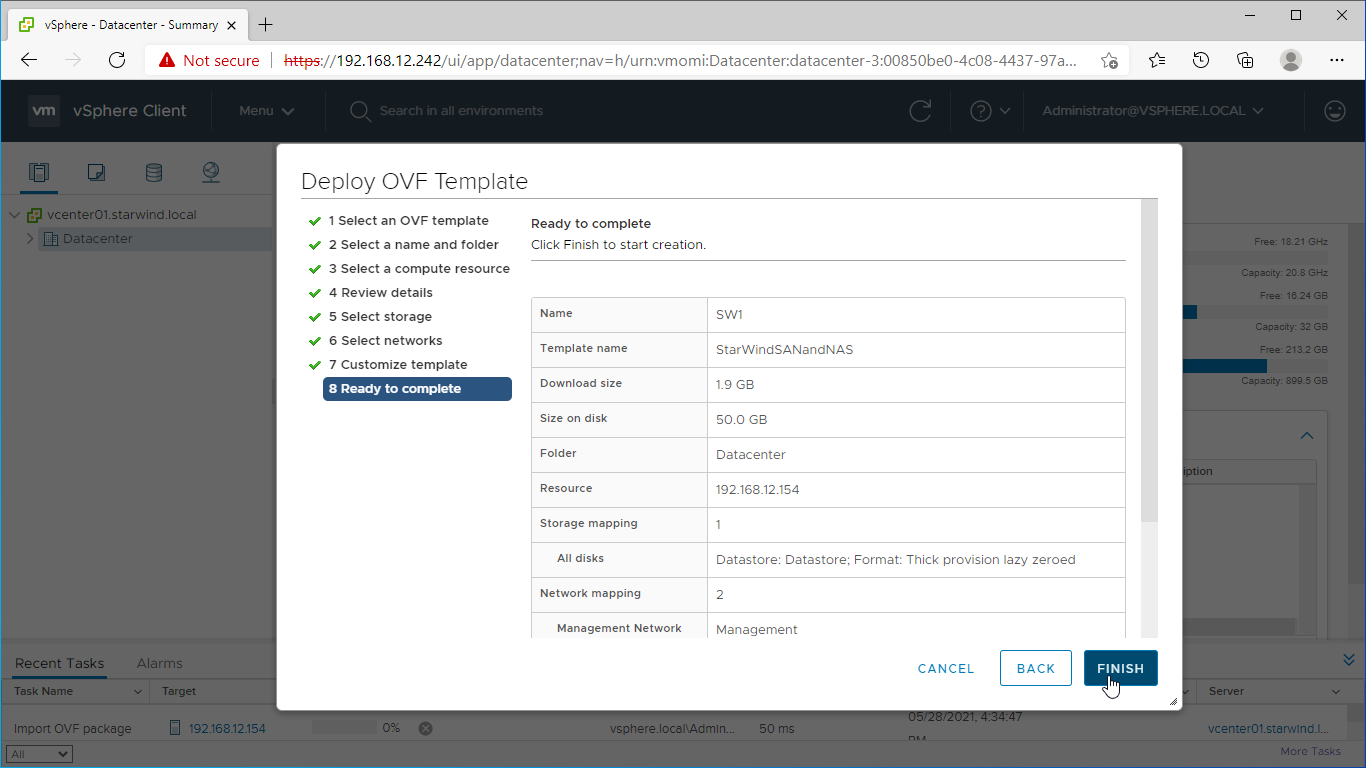
11. Review the deployment summary information and click to start the VM creation.
12. Repeat the VM deployment on each partner server which is used for configuring 2-node or 3-node highly available storage according to your licensing.
Configuring Appliances
Getting started with StarWind SAN & NAS
1. Start StarWind SAN & NAS CVM.
2. Launch Console to see the VM boot process and get the IPv4 address of the Management network interface.
Note: in case VM has no IPv4 address obtained from a DHCP server, use the Text-based User Interface (TUI) to set up a Management network.
3. Using the web browser, open a new tab and enter the VM IPv4 address to open StarWind SAN & NAS Web Interface. Click “Advanced” and then “Continue to…”
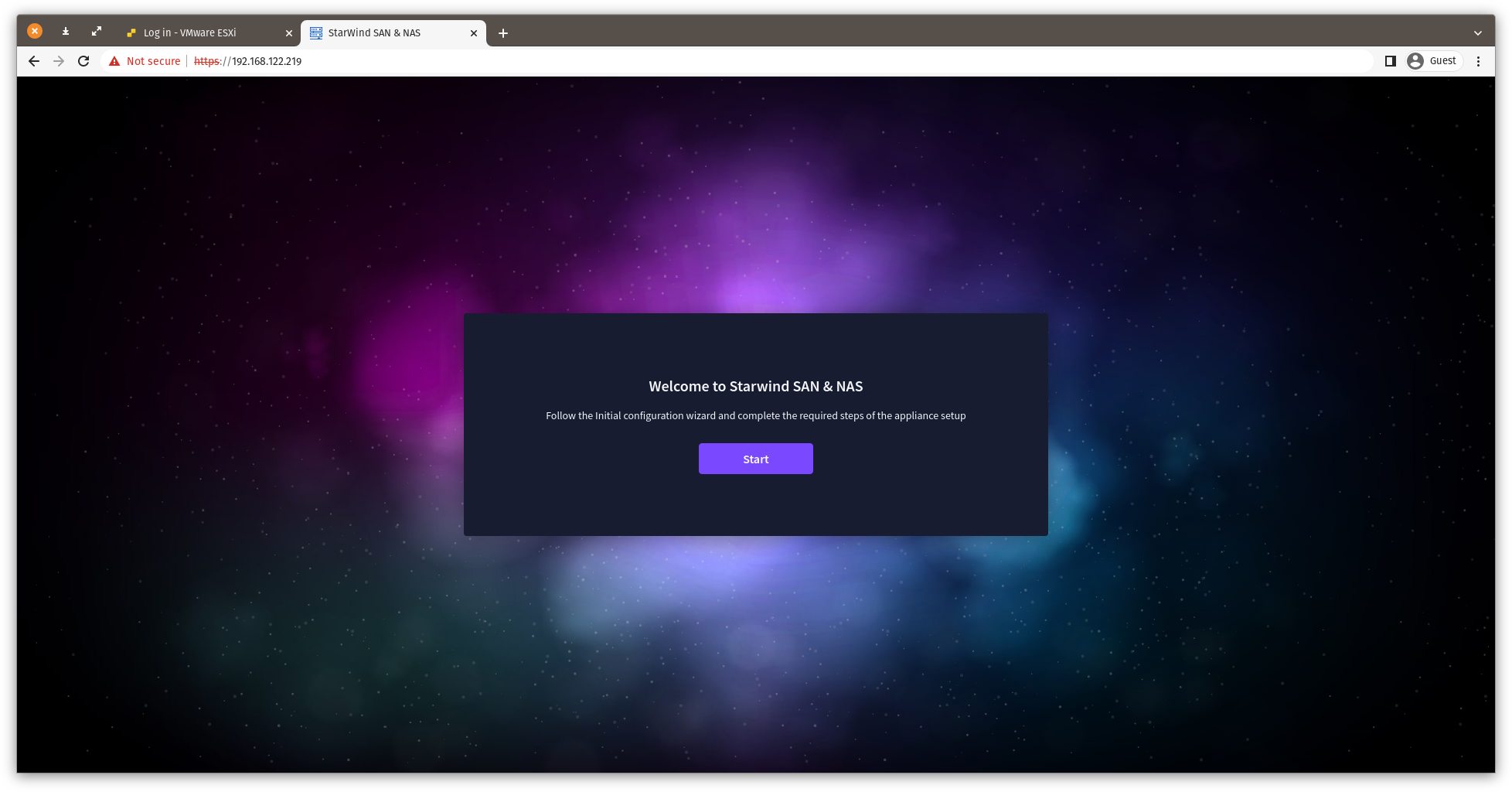
4. StarWind SAN & NAS welcomes you, and the “Initial configuration” wizard will guide you through the deployment process.
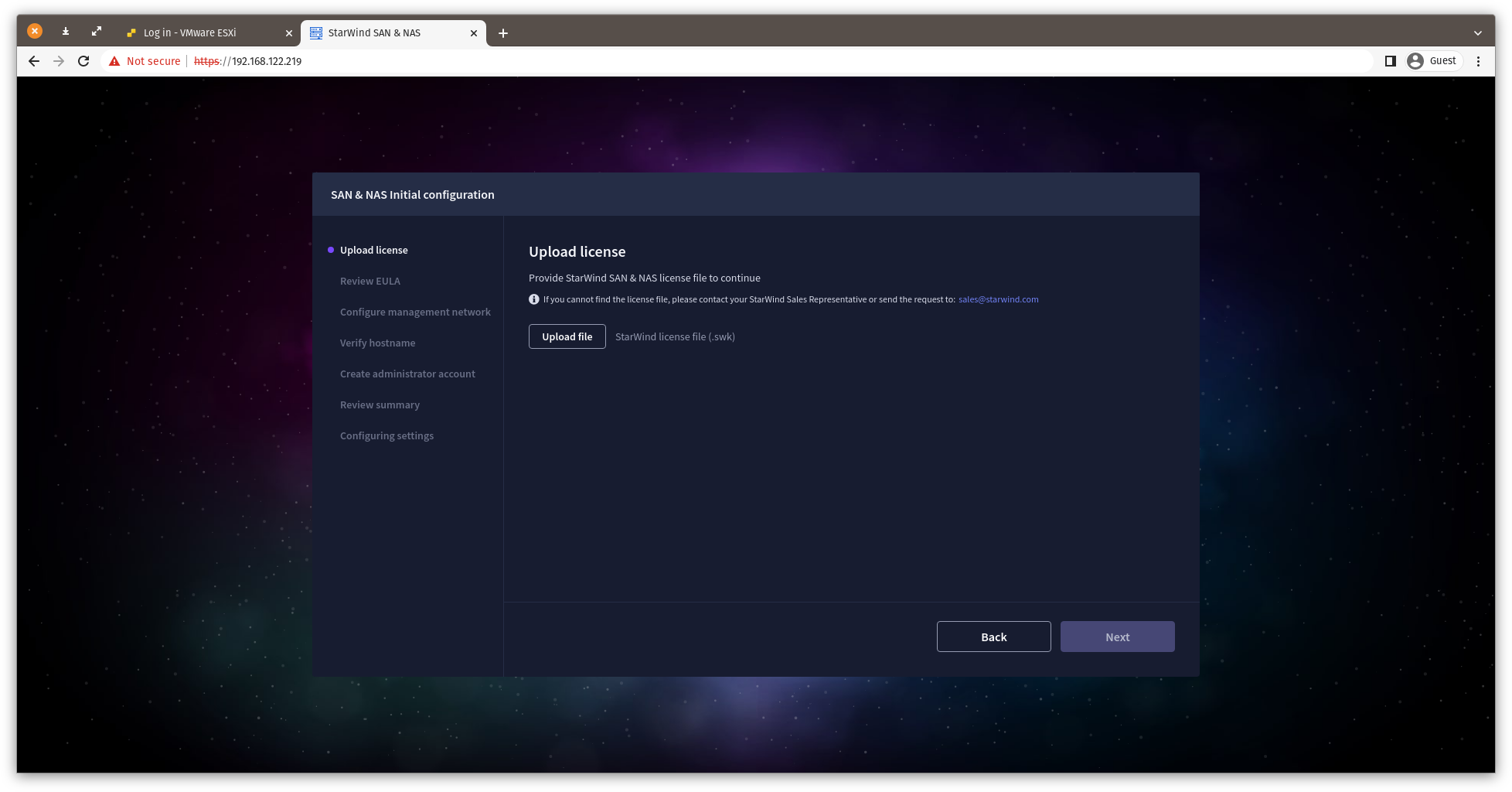
5. In the following step, upload the license file.
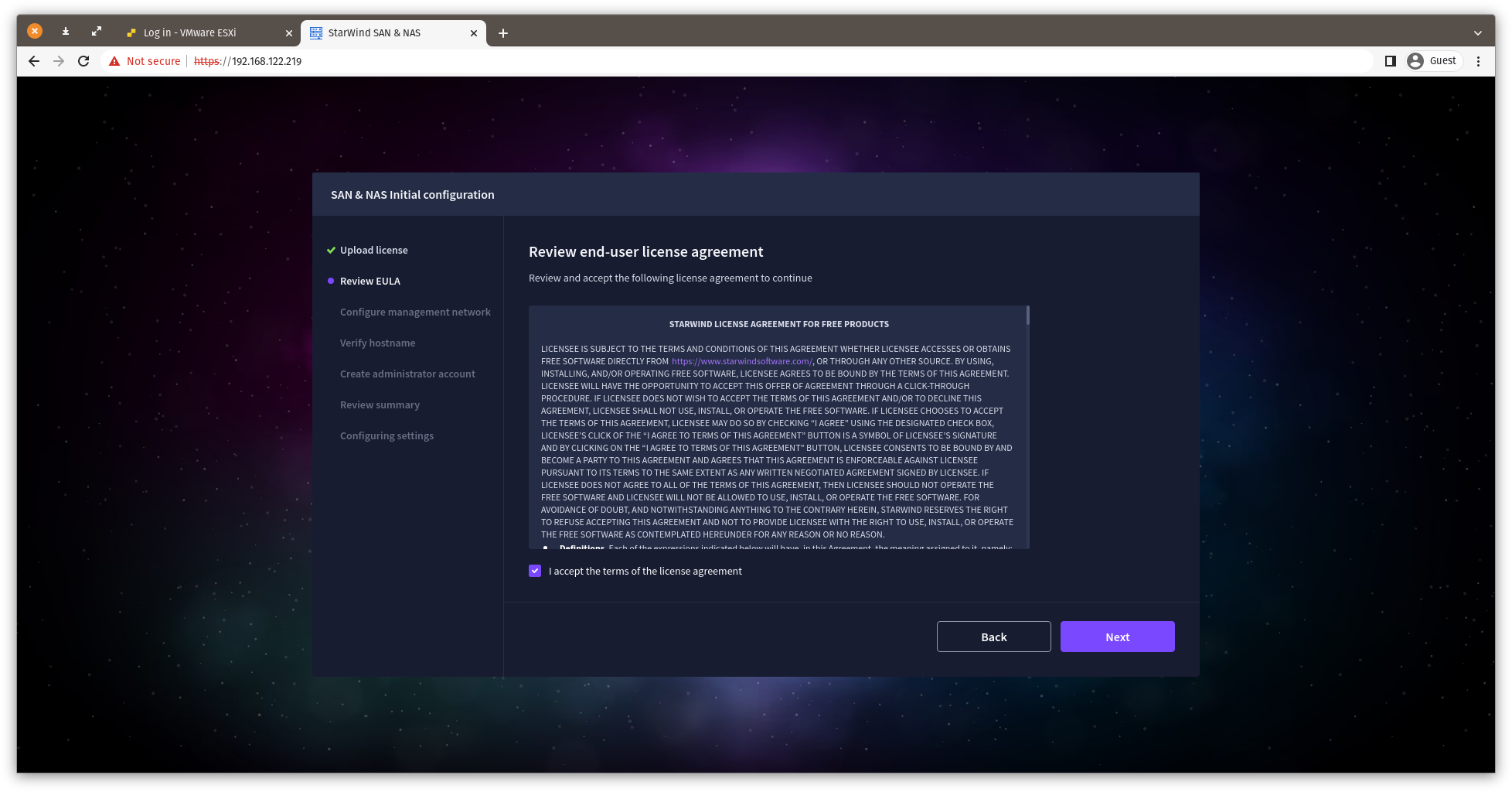
6. Read and accept the End User License Agreement to proceed.
7. Review or edit the Network settings and click Next.
Note: Static network settings are recommended for the configuration.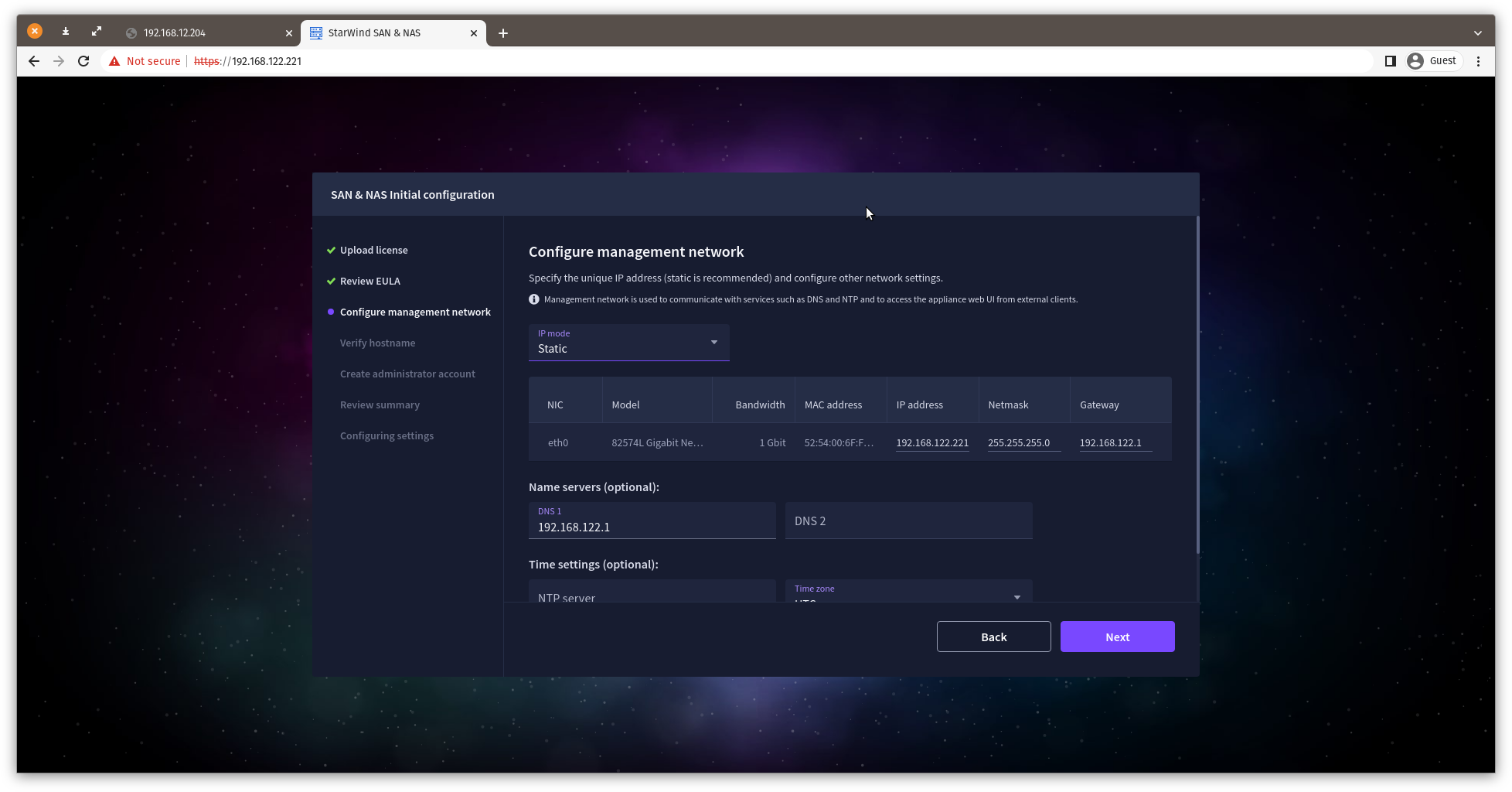
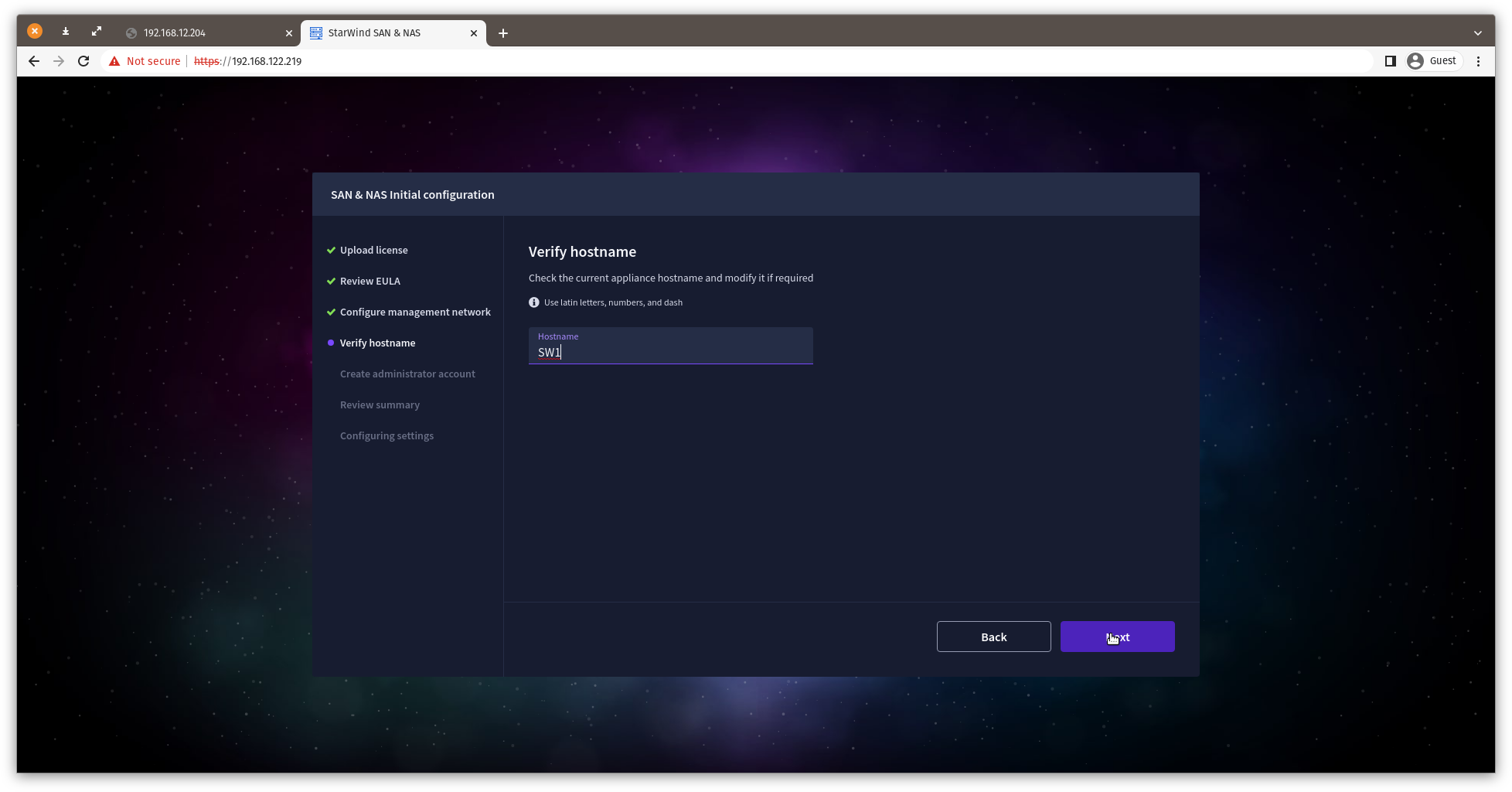
8. Specify the hostname for the virtual machine and click Next.
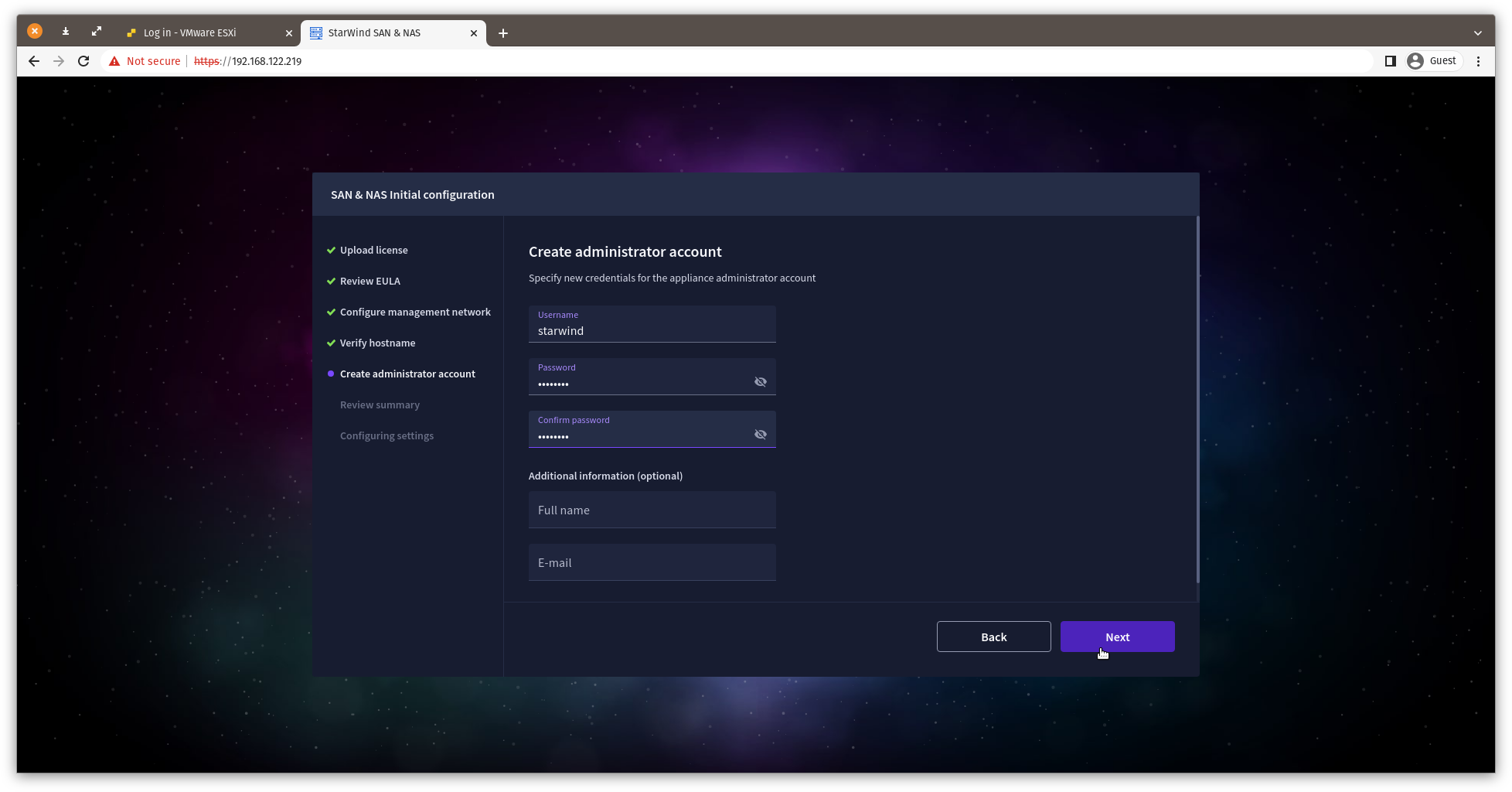
9. Create an administrator account. Click Next.
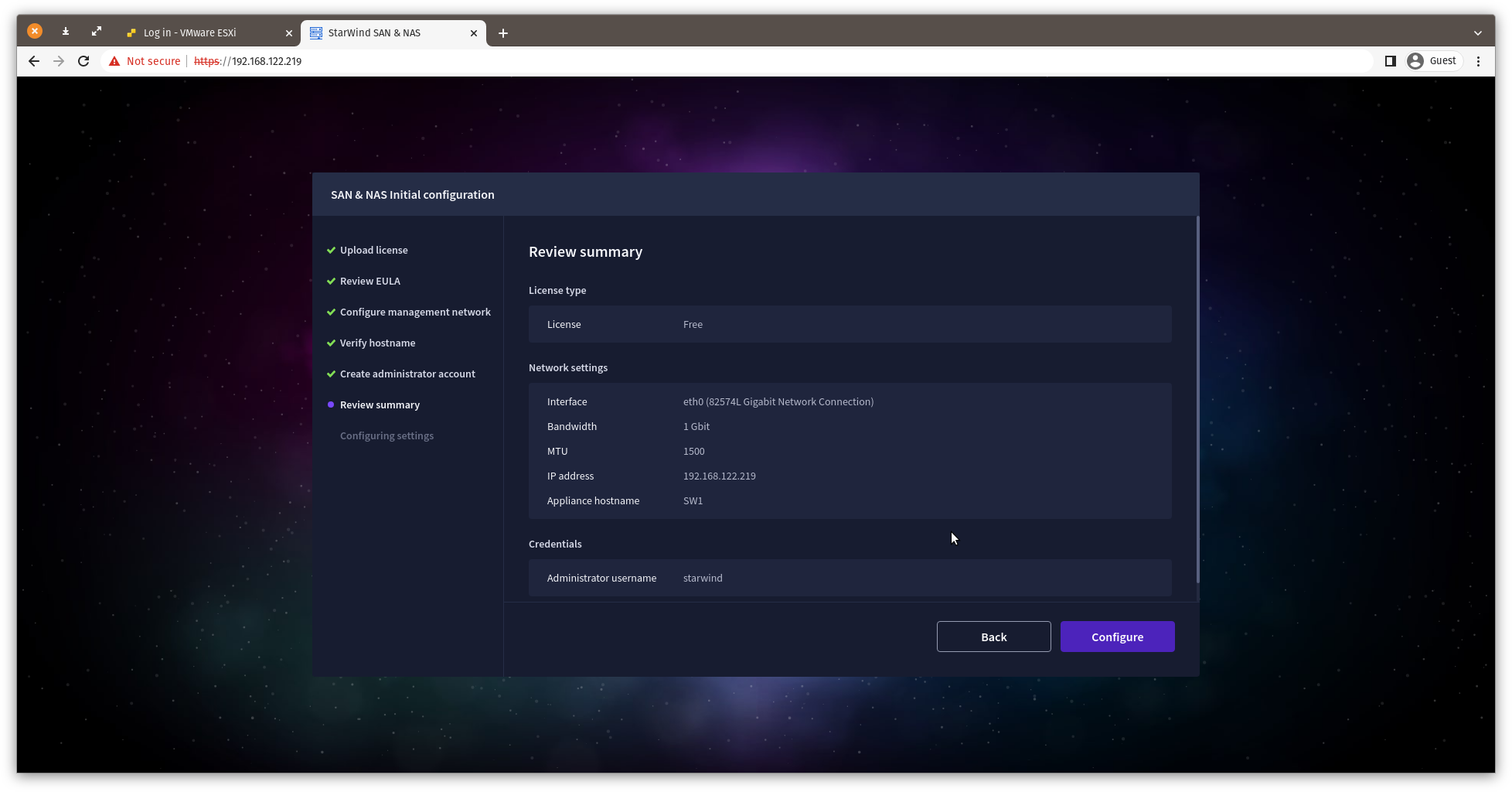
10. Review your settings selection before setting up StarWind SAN & NAS.
11. Please standby until the Initial Configuration Wizard configures StarWind SAN & NAS for you.
12. The appliance is set and ready. Click on the Done button to install StarWind vCenter Plugin right now or uncheck the checkbox to skip this step and proceed to the Login page.
13. Repeat the initial configuration on other StarWind SAN & NAS CVMs that will be used to create 2-node or 3-node HA shared storage.
Installing StarWind vCenter Plugin
NOTE: This step is optional. StarWind vCenter plugin integrates the Controller Virtual Machines management into VMware vSphere user interface allowing managing compute and storage resources from a single web console.
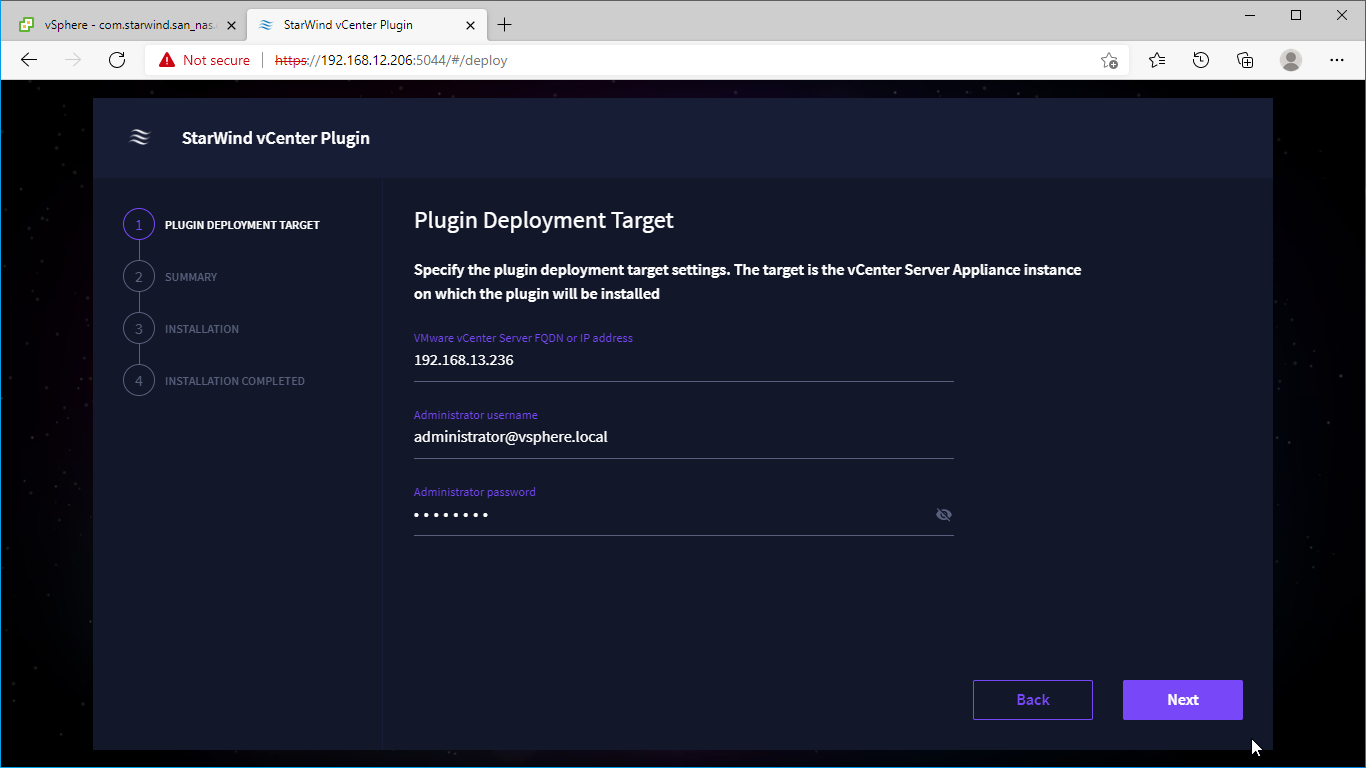
1. To install the StarWind Plugin ensure that the version of your VMware vCenter Server Appliance 7.o or newer, then click Next.
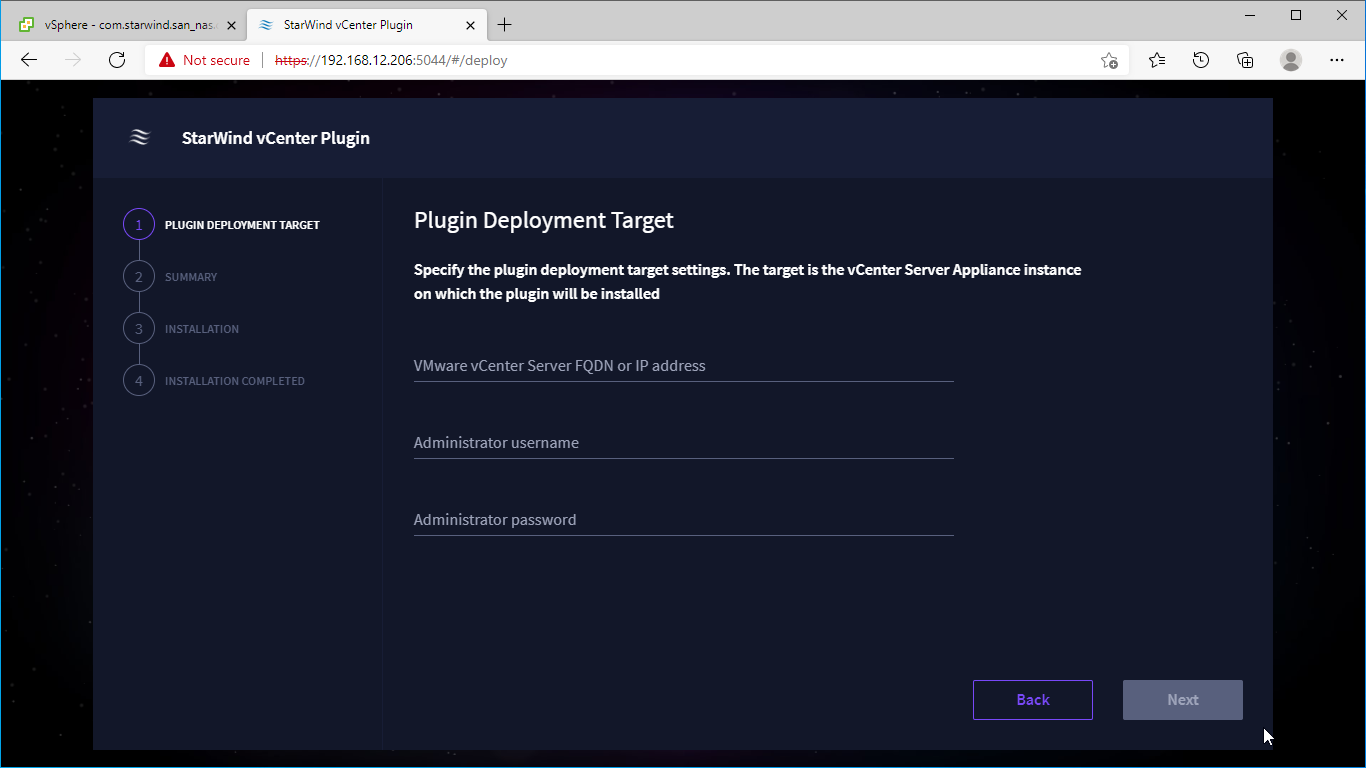
2. Specify the vCenter Server FQDN or IP Address and administrator credentials and click Next.
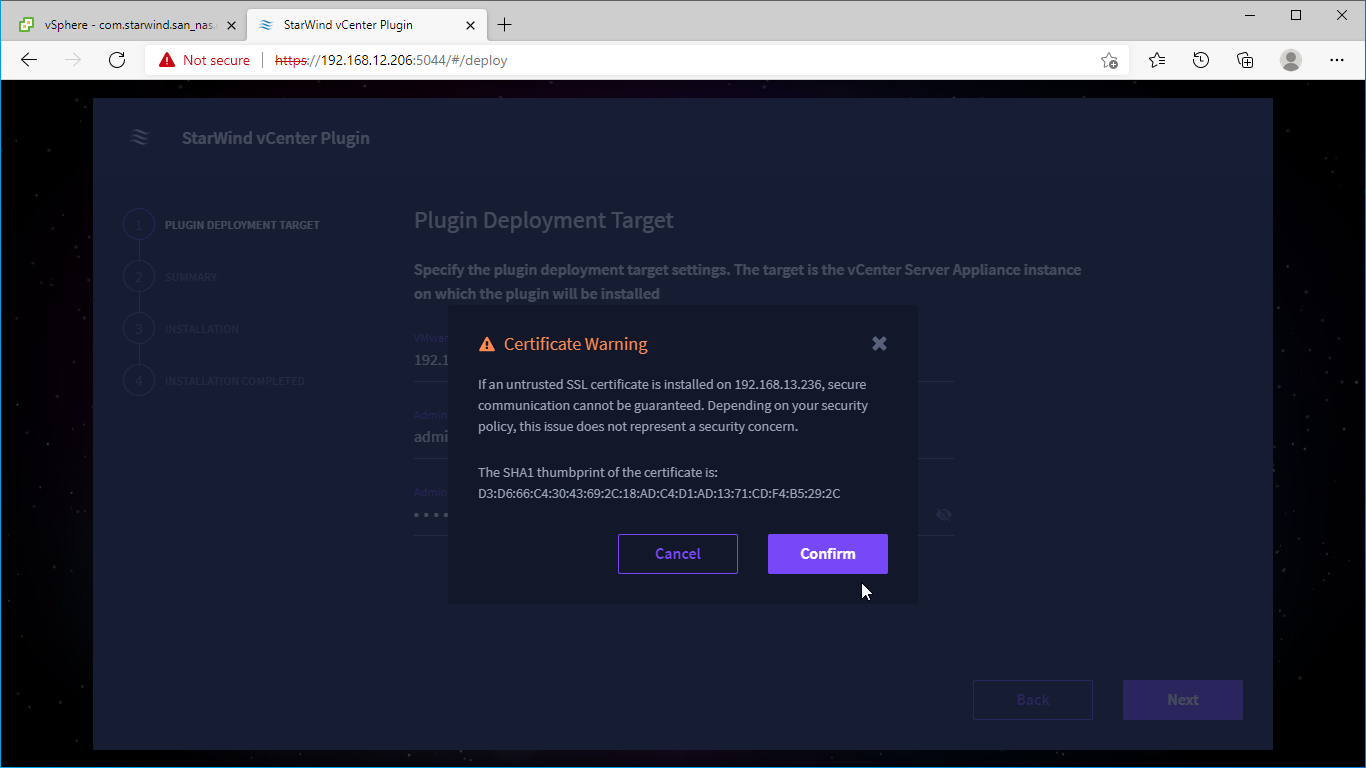
3. Confirm the connection to your vCenter Server Appliance.
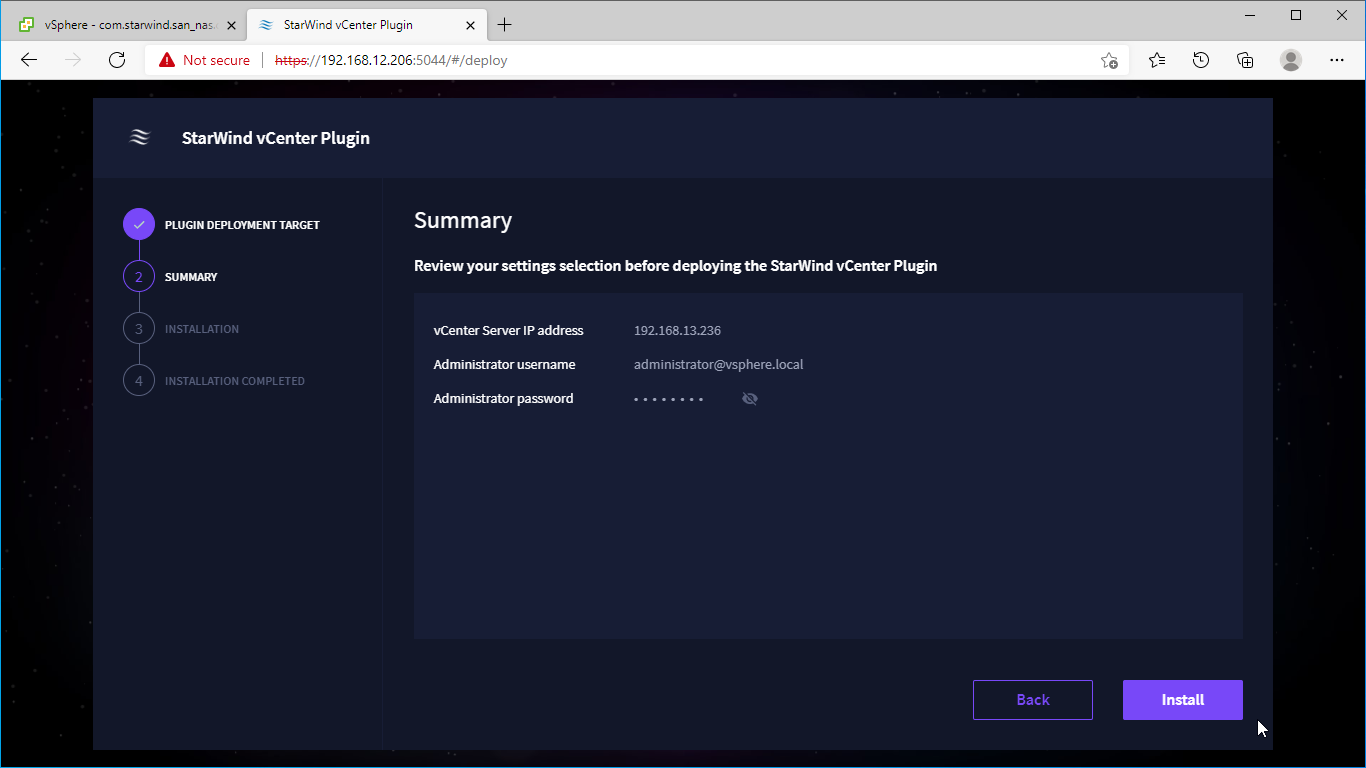
4. Review Summary and click the Install button.
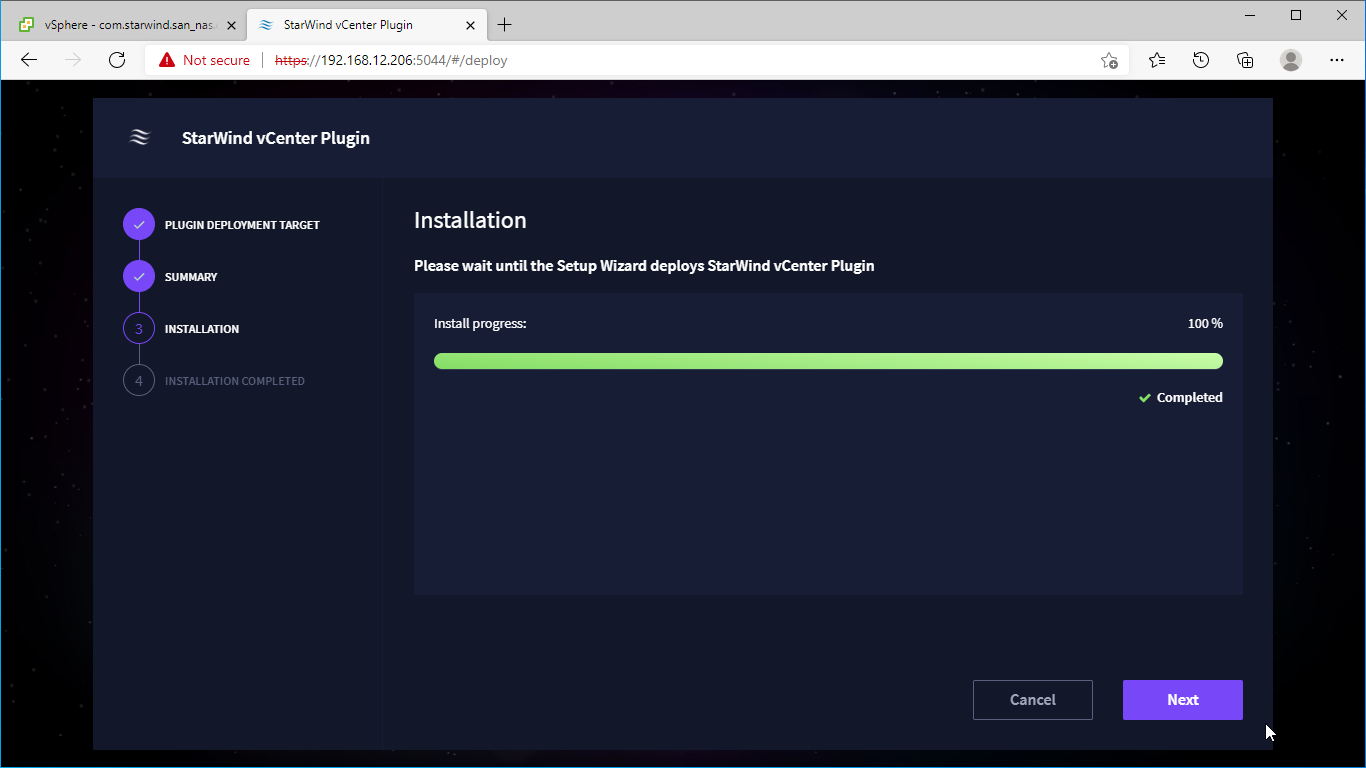
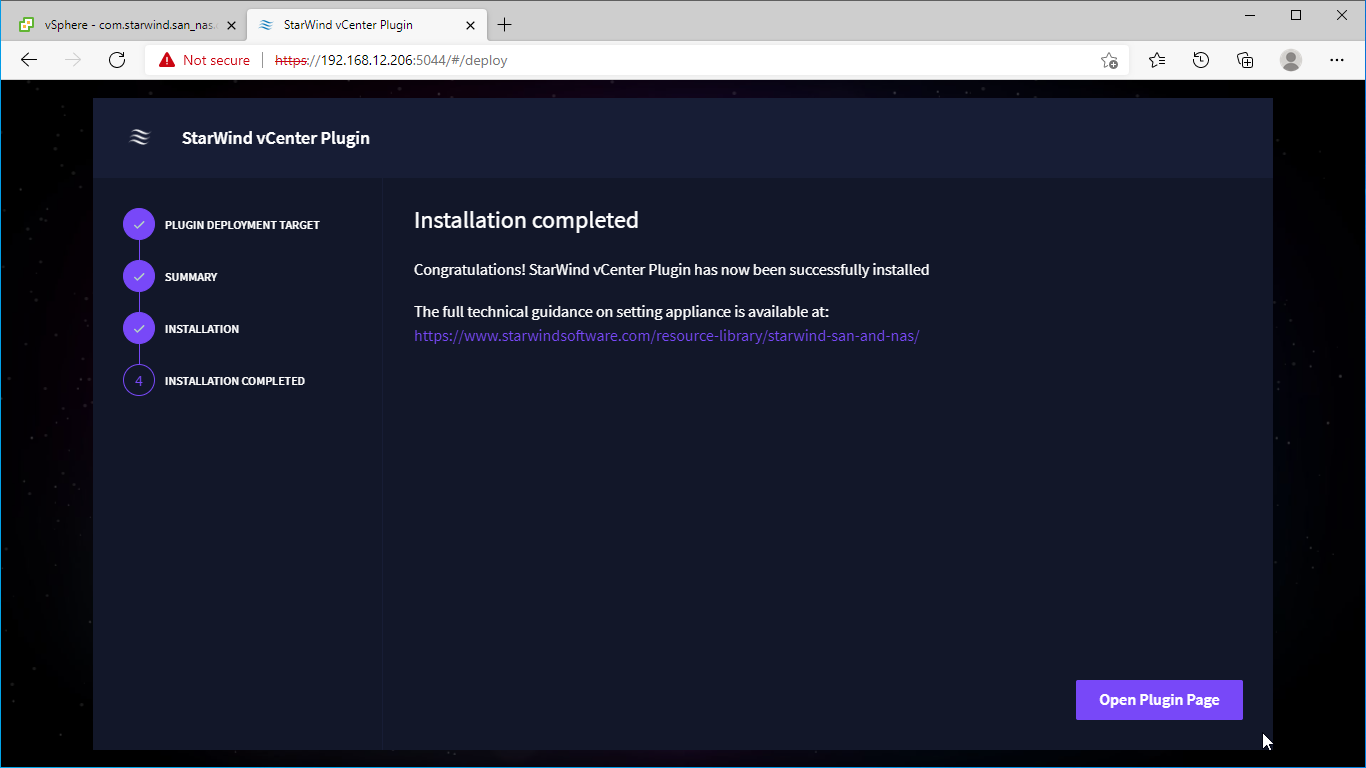
5. Wait until the plugin is installed.
6. Click the Open Plugin page to start using StarWind SAN & NAS via the vCenter Plugin interface.
7. Repeat the plugin installation on each StarWind Controller Virtual Machine that will be managed using the StarWind Plugin in the VMware vSphere web interface.
Add Appliance
To create replicated, highly available storage, add partner appliances that use the same StarWind Virtual SAN license key.
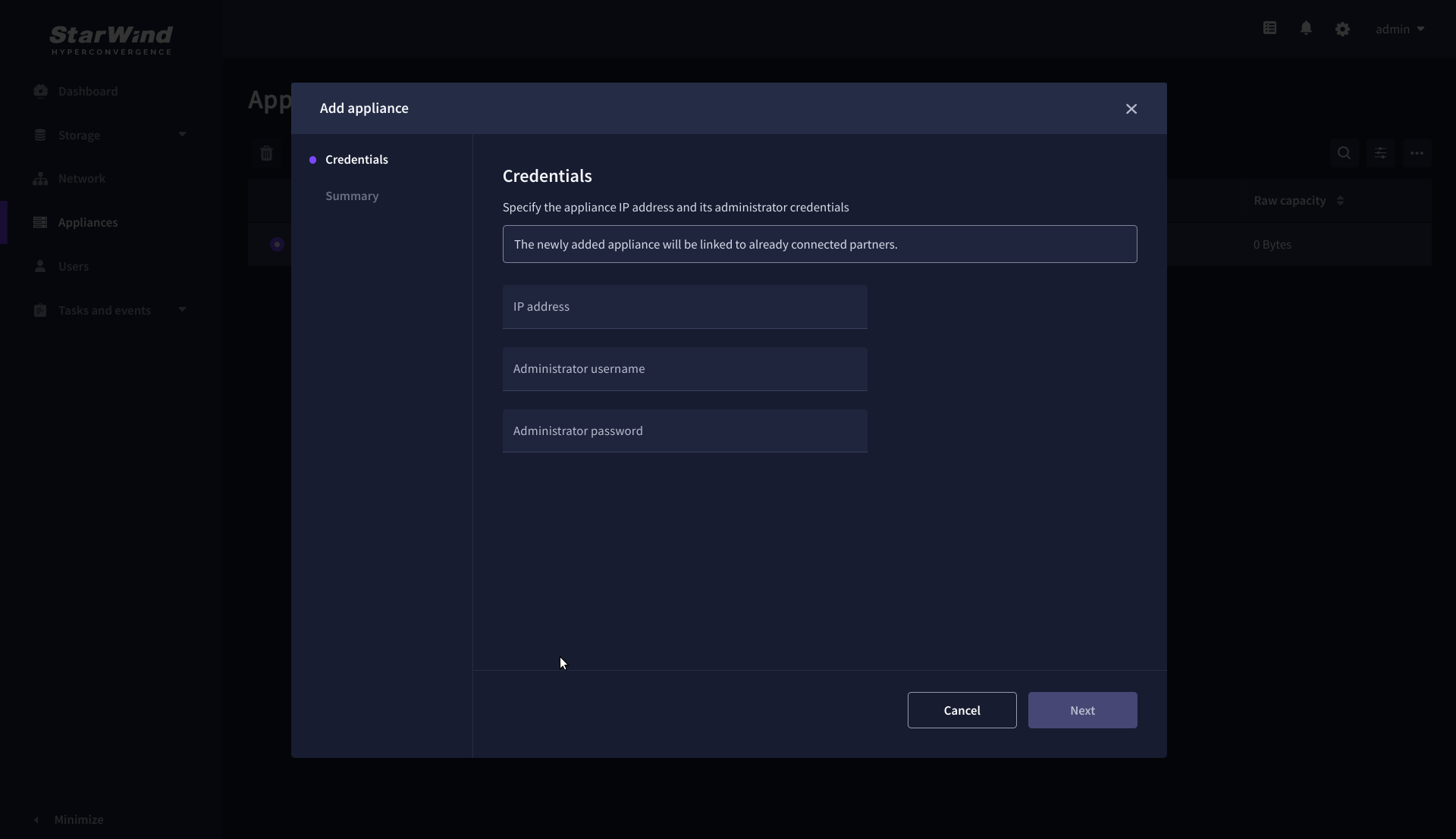
1. Navigate to the Appliances page and click Add to open the Add appliance wizard.
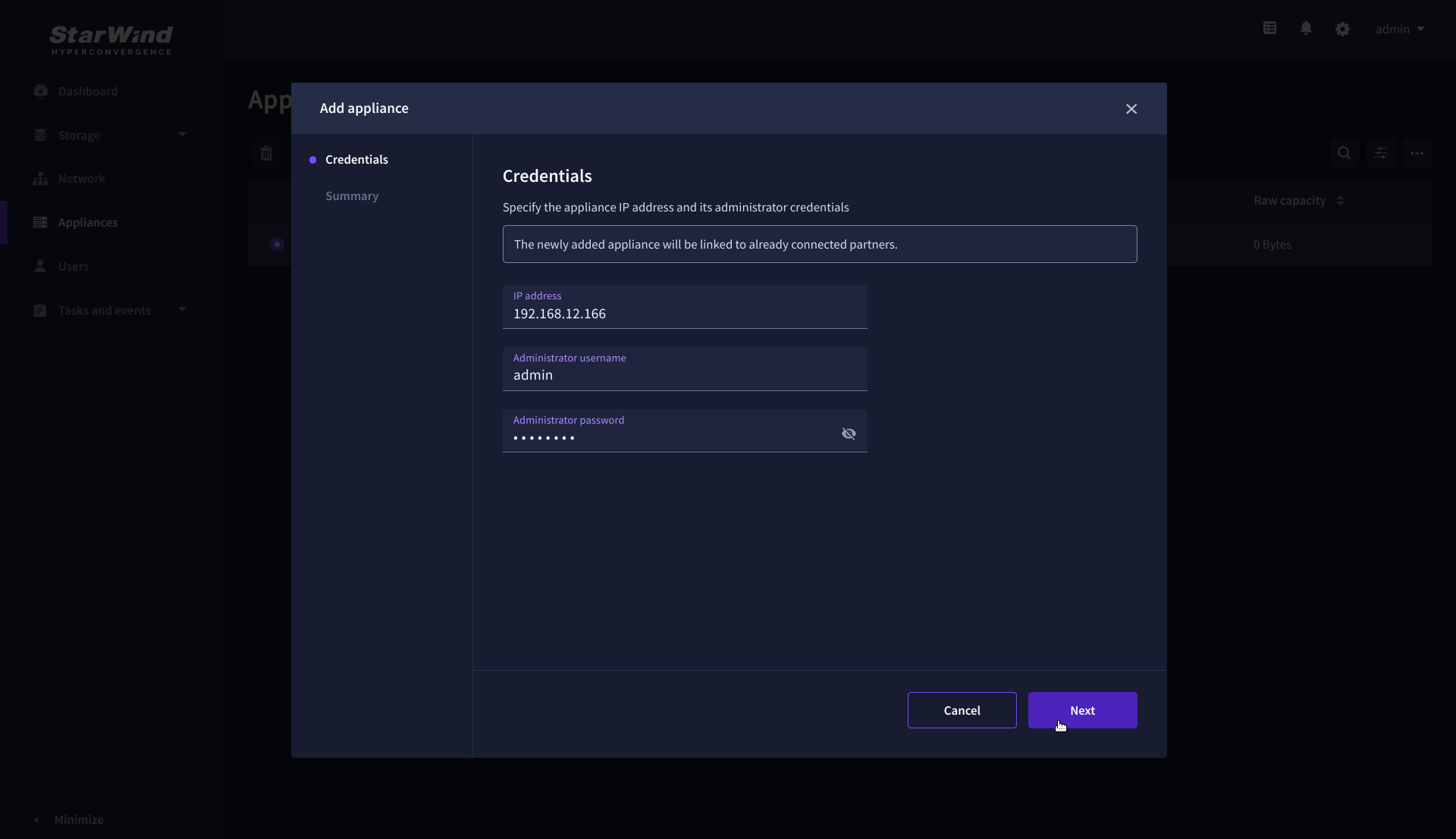
2. On the Credentials step, enter the IP address and credentials for the partner StarWind Virtual SAN appliance, then click Next.
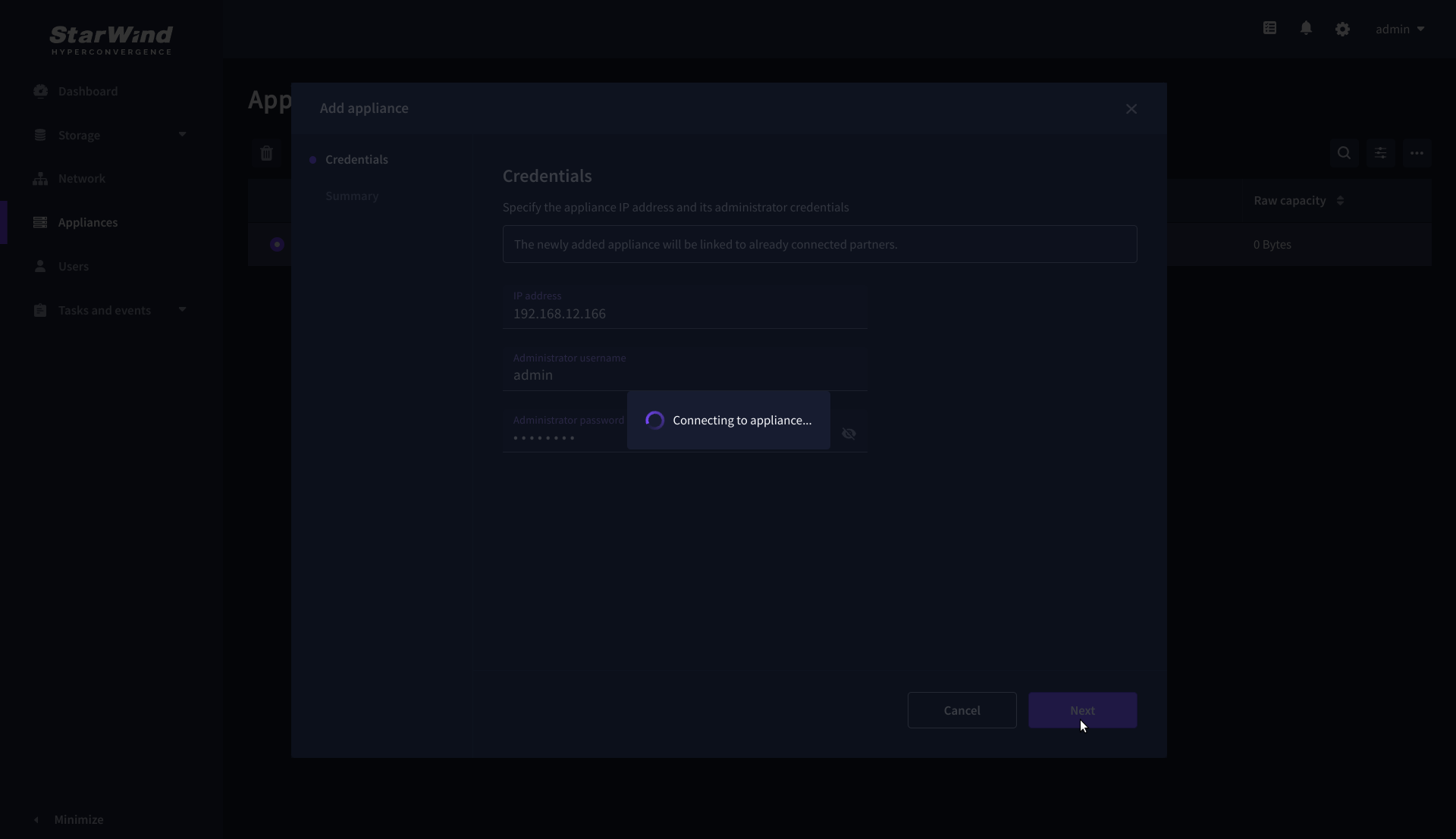
3. Provide credentials of partner appliance.
3. Wait for the connection to be established and the settings to be validated
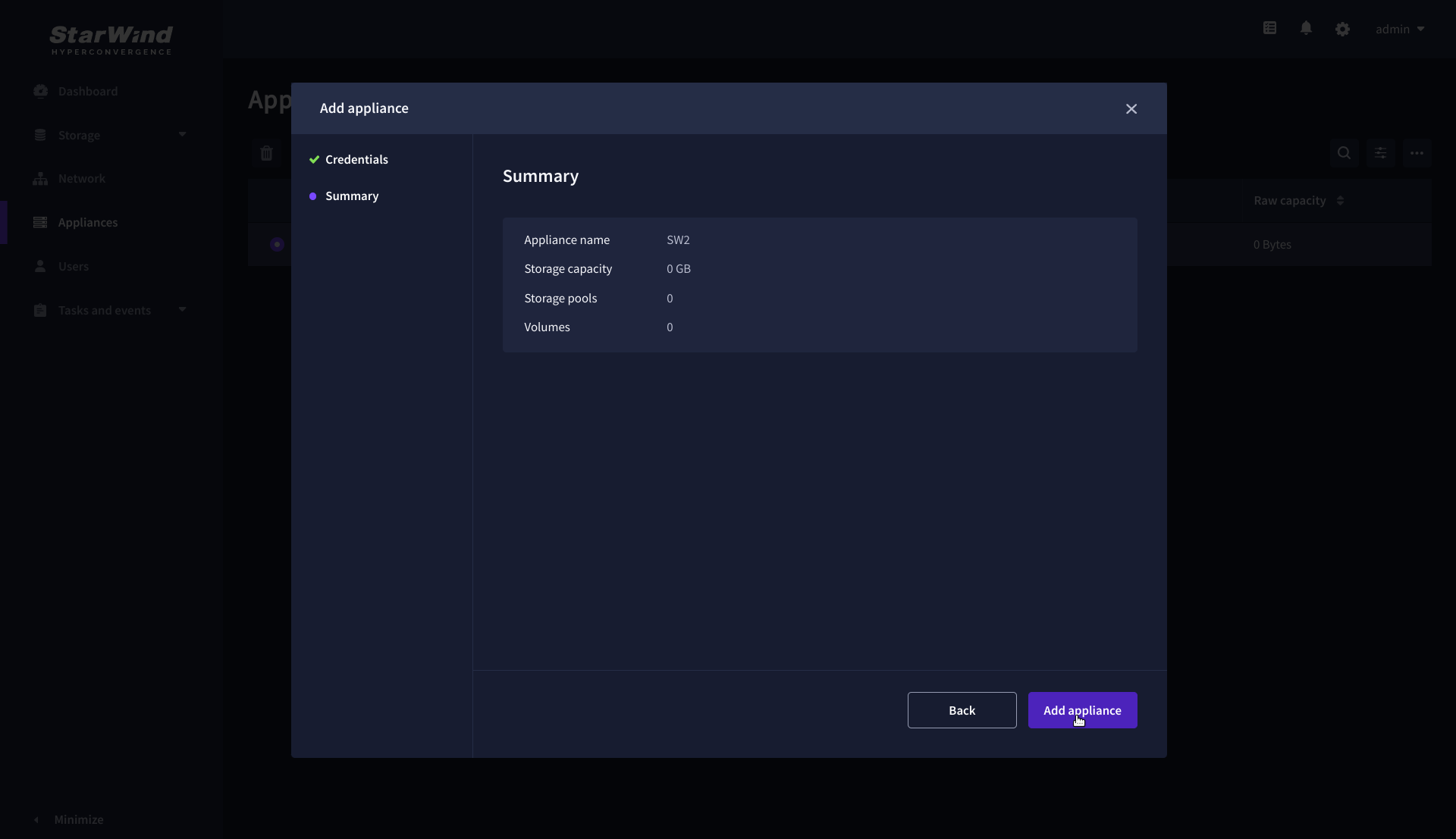
4. On the Summary step, review the properties of the partner appliance, then click Add Appliance.
Configure HA networking
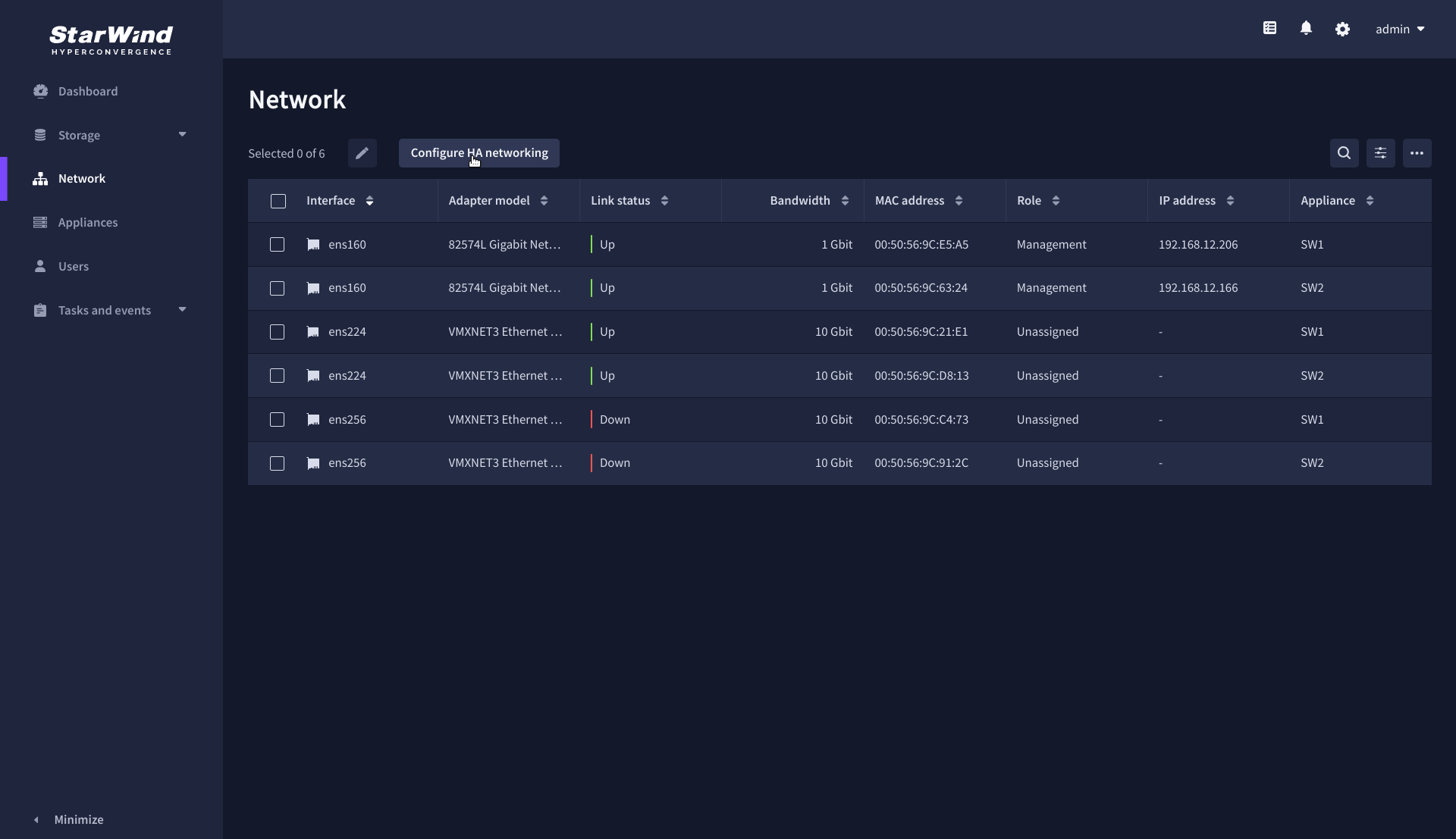
1. Navigate to the Network page and open Configure HA networking wizard.
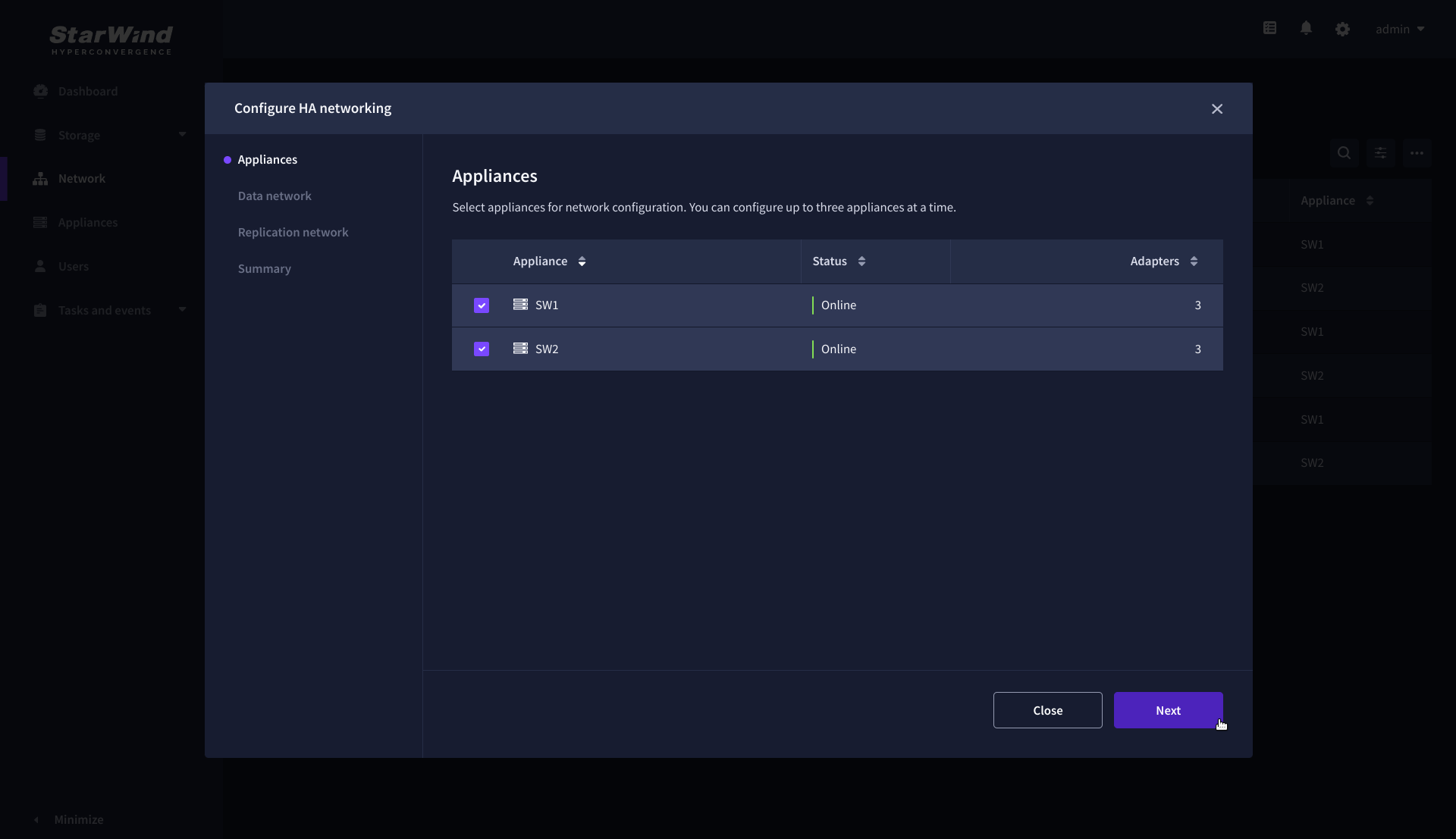
2. On the Appliances step, select either 2 partner appliances to configure two-way replication, or 3 appliances for three-way replication, then click Next.
NOTE: The number of appliances in the cluster is limited by your StarWind Virtual SAN license.
3. On the Data Network step, select the network interfaces designated to carry iSCSI or NVMe-oF storage traffic. Assign and configure at least one interface on each appliance (in our example: 172.16.10.10 and 172.16.10.20) with a static IP address in a unique network (subnet), specify the subnet mask and Cluster MTU size.
IMPORTANT: For a redundant, high-availability configuration, configure at least 2 network interfaces on each appliance. Ensure that the Data Network interfaces are interconnected between appliances through multiple direct links or via redundant switches.
4. Assign MTU value on all selected network adapters, e.g. 1500 or 9000 bytes. If you are using network switches with the selected Data Network adapters, ensure that they are configured with the same MTU size value. In case of MTU settings mismatch, stability and performance issues might occur on the whole setup.
NOTE: Setting MTU to 9000 bytes on some physical adapters (like Intel Ethernet Network Adapter X710, Broadcom network adapters, etc.) might cause stability and performance issues depending on the installed network driver. To avoid them, use 1500 bytes MTU size or install the stable version of the driver.
5. Once configured, click Next to validate network settings.
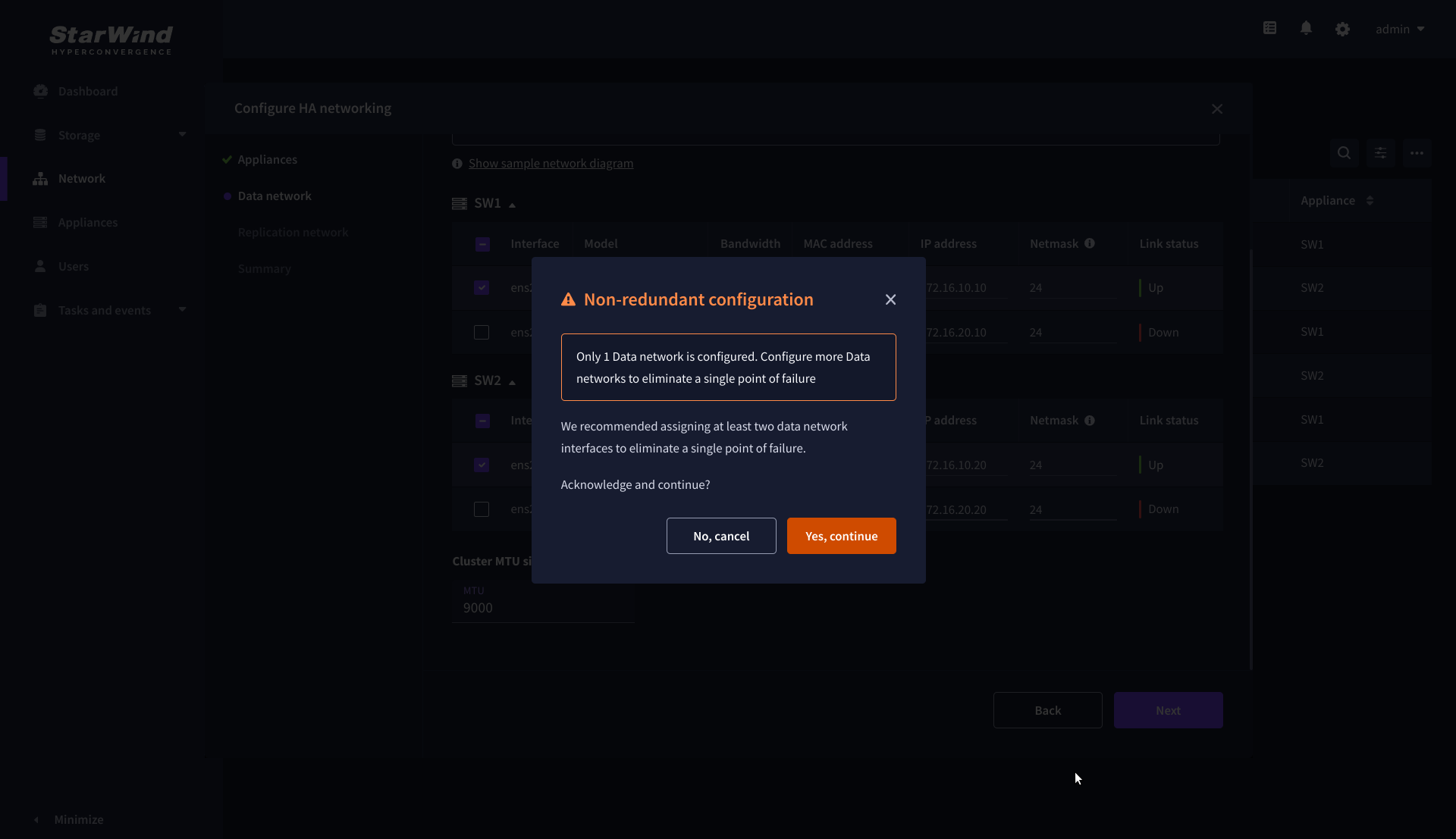
6. The warning might appear if a single data interface is configured. Click Yes, continue to proceed with the configuration.
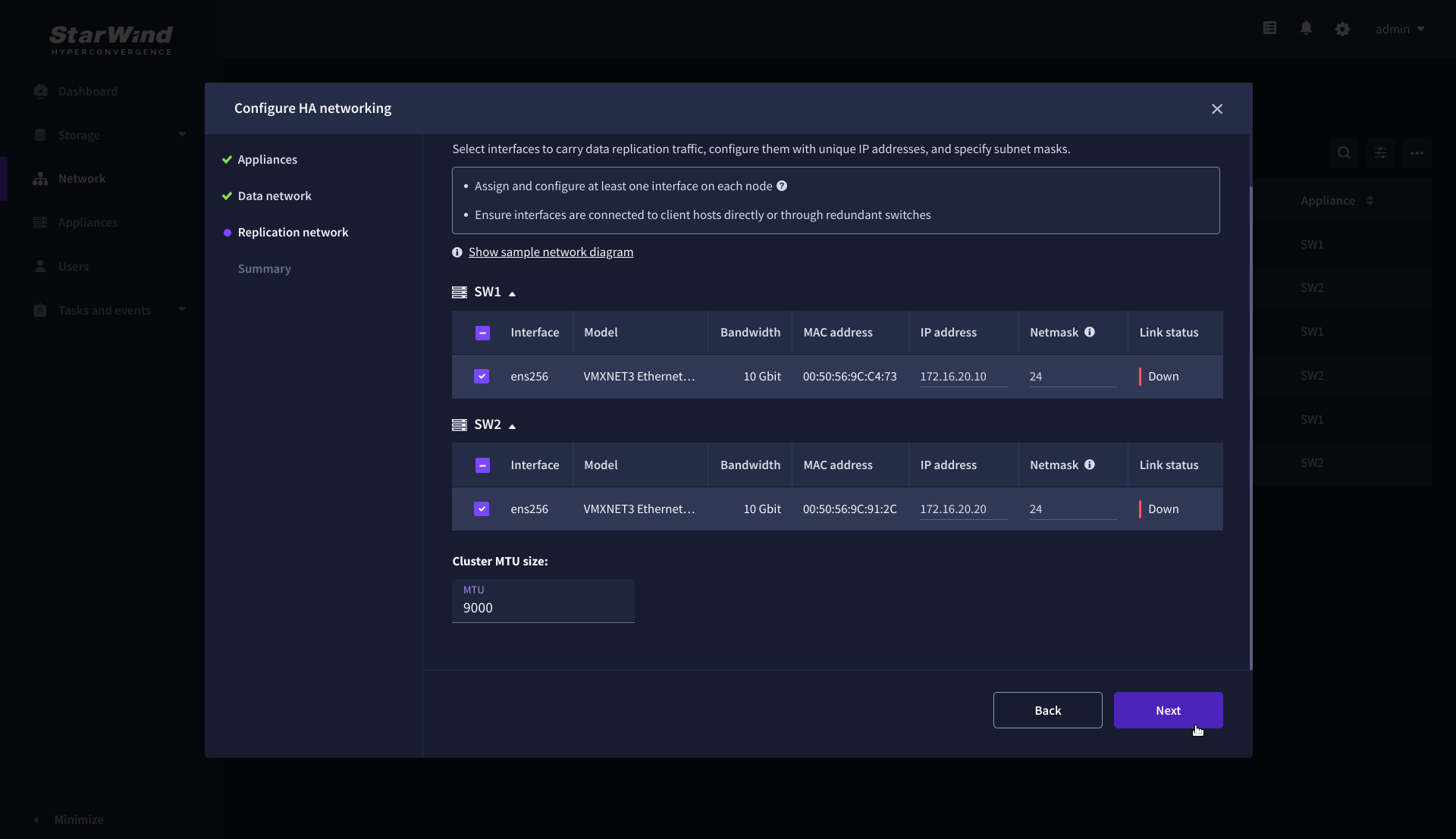
7. On the Replication Network step, select the network interfaces designated to carry the traffic for synchronous replication. Assign and configure at least one interface on each appliance with a static IP address in a unique network (subnet), specify the subnet mask and Cluster MTU size.
IMPORTANT: For a redundant, high-availability configuration, configure at least 2 network interfaces on each appliance. Ensure that the Replication Network interfaces are interconnected between appliances through multiple direct links or via redundant switches.
8. Assign MTU value on all selected network adapters, e.g. 1500 or 9000 bytes. If you are using network switches with the selected Replication Network adapters, ensure that they are configured with the same MTU size value. In case of MTU settings mismatch, stability and performance issues might occur on the whole setup.
NOTE: Setting MTU to 9000 bytes on some physical adapters (like Intel Ethernet Network Adapter X710, Broadcom network adapters, etc.) might cause stability and performance issues depending on the installed network driver. To avoid them, use 1500 bytes MTU size or install the stable version of the driver.
9. Once configured, click Next to validate network settings.
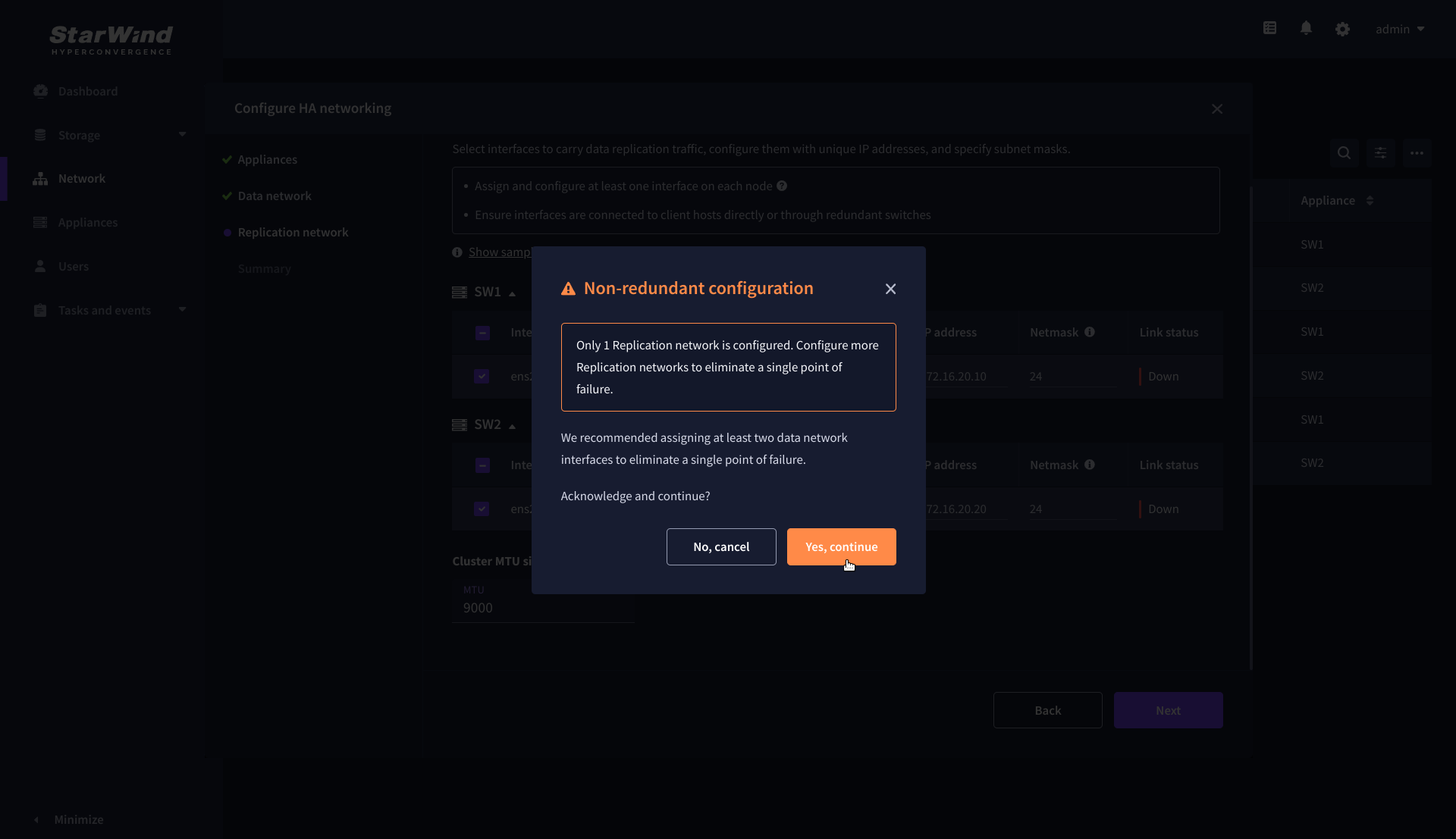
10. If only one Replication Network interface is configured on each partner appliance, a warning message will pop up. Click Yes, continue to acknowledge the warning and proceed.
11. Wait for the configuration completion.
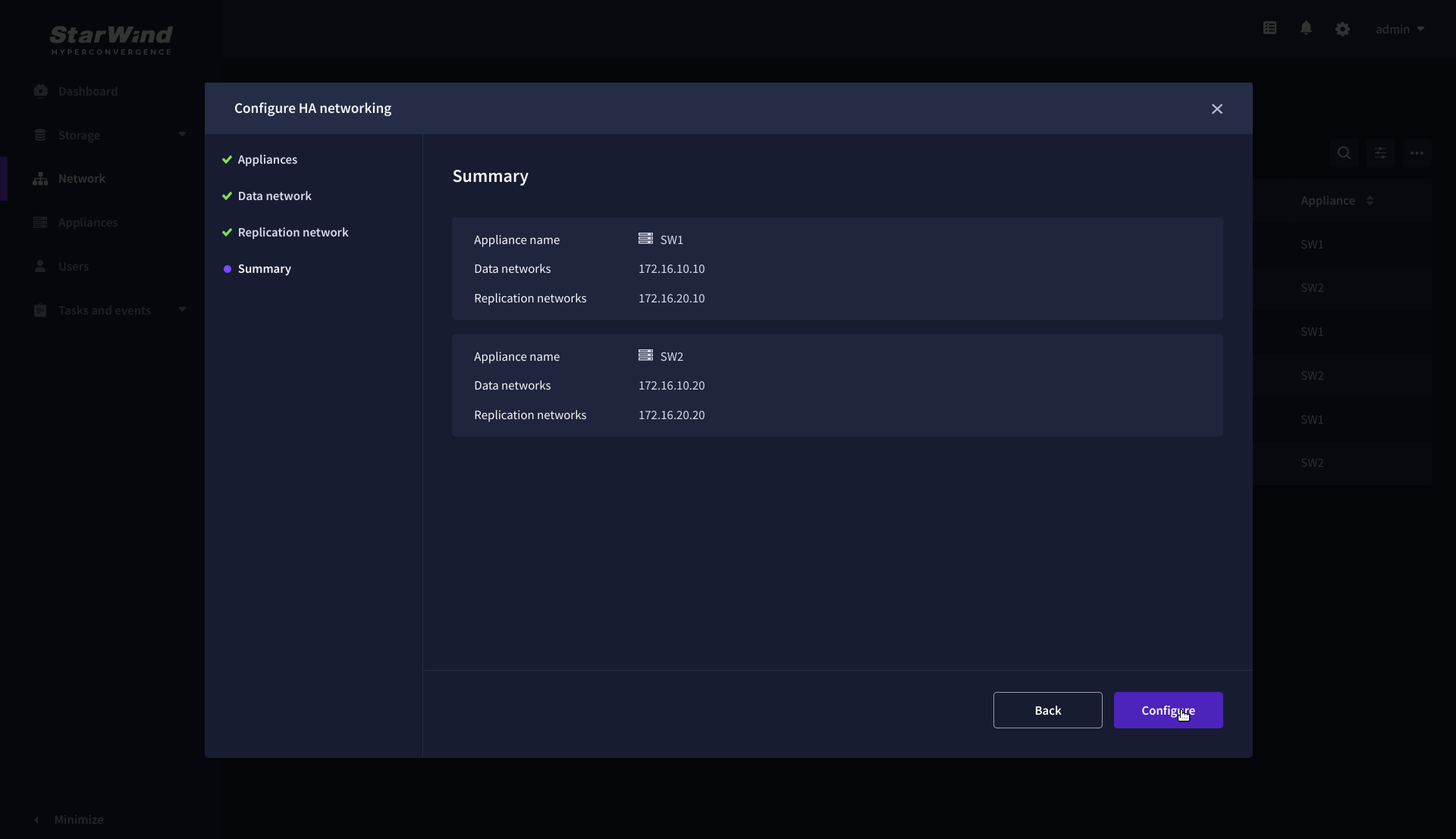
12. On the Summary step, review the specified network settings and click Configure to apply the changes.
Add physical disks
Attach physical storage to StarWind Virtual SAN Controller VM:
- Ensure that all physical drives are connected through an HBA or RAID controller.
- To get the optimal storage performance, add HBA, RAID controllers, or NVMe SSD drives to StarWind CVM via a passthrough device.
For detailed instructions, refer to Microsoft’s documentation on DDA. Also, find the storage provisioning guidelines in the KB article.
Create Storage Pool
1. Navigate to the Storage pools page and click the + button to open the Create storage pool wizard .
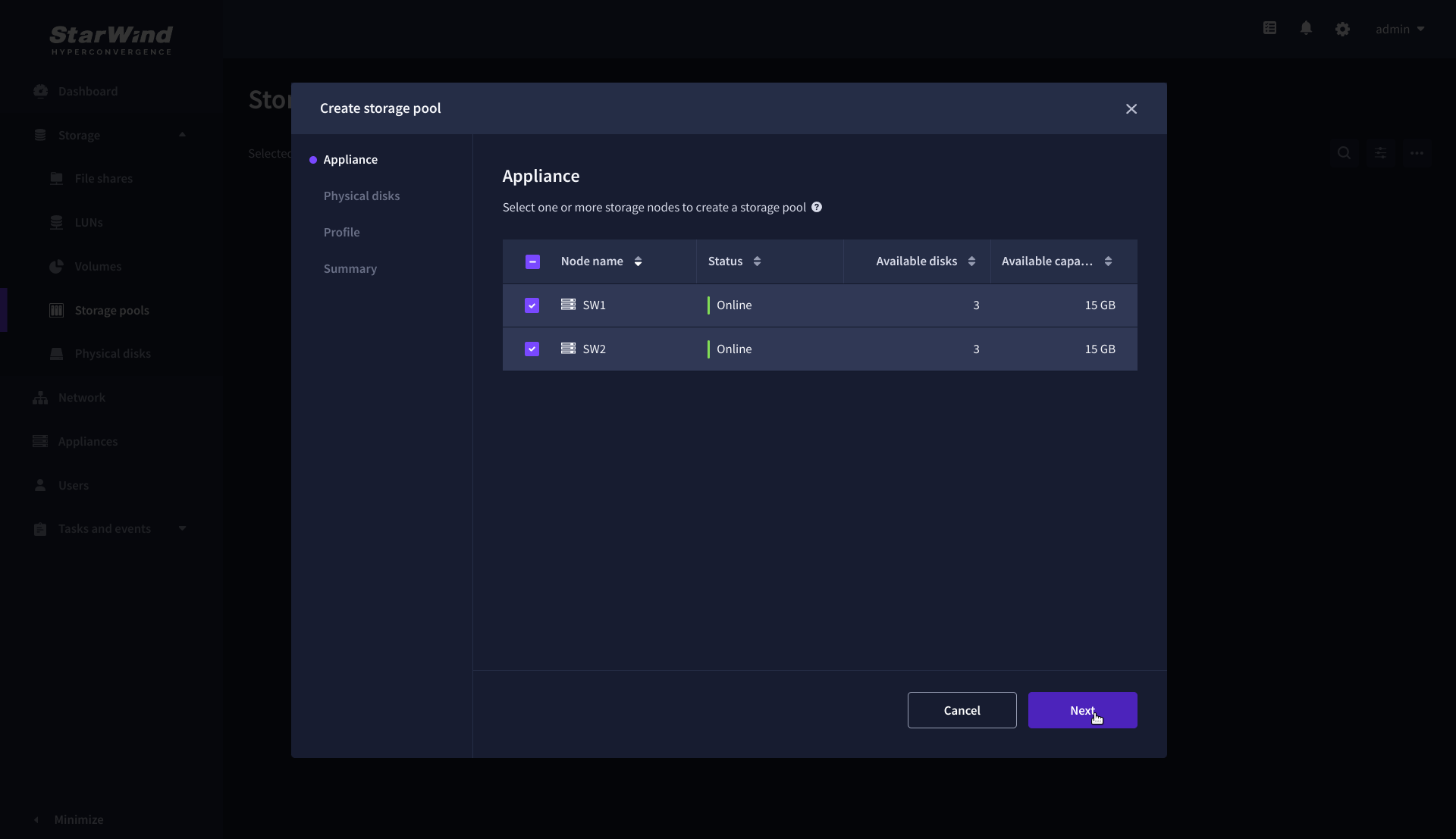
2. On the Appliance step, select partner appliances on which to create new storage pools, then click Next.
NOTE: Select 2 appliances for configuring storage pools if you are deploying a two-node cluster with two-way replication, or select 3 appliances for configuring a three-node cluster with a three-way mirror.
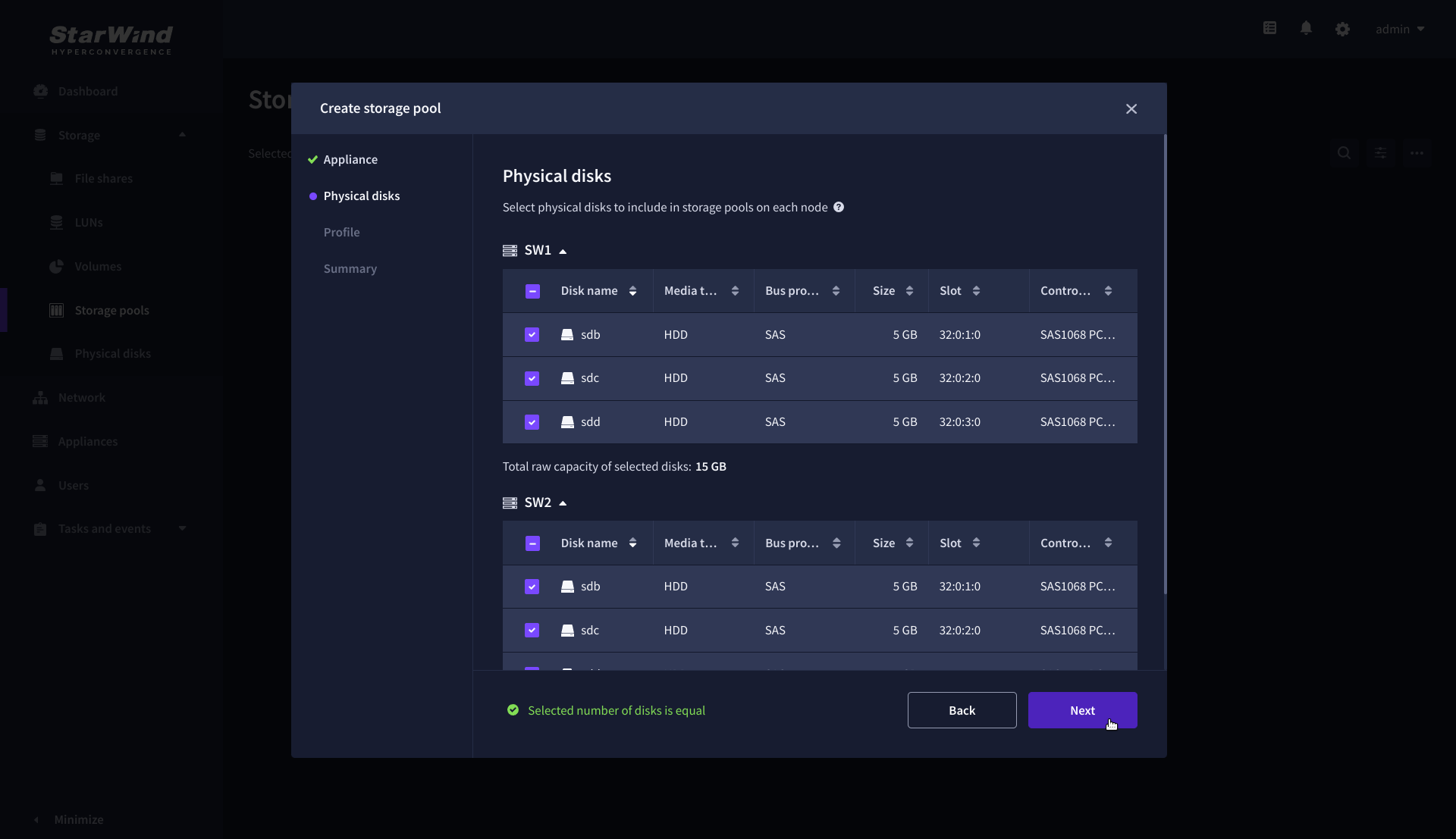
3. On the Physical disks step, select physical disks to be pooled on each node, then click Next.
IMPORTANT: Select an identical type and number of disks on each appliance to create storage pools with a uniform configuration.
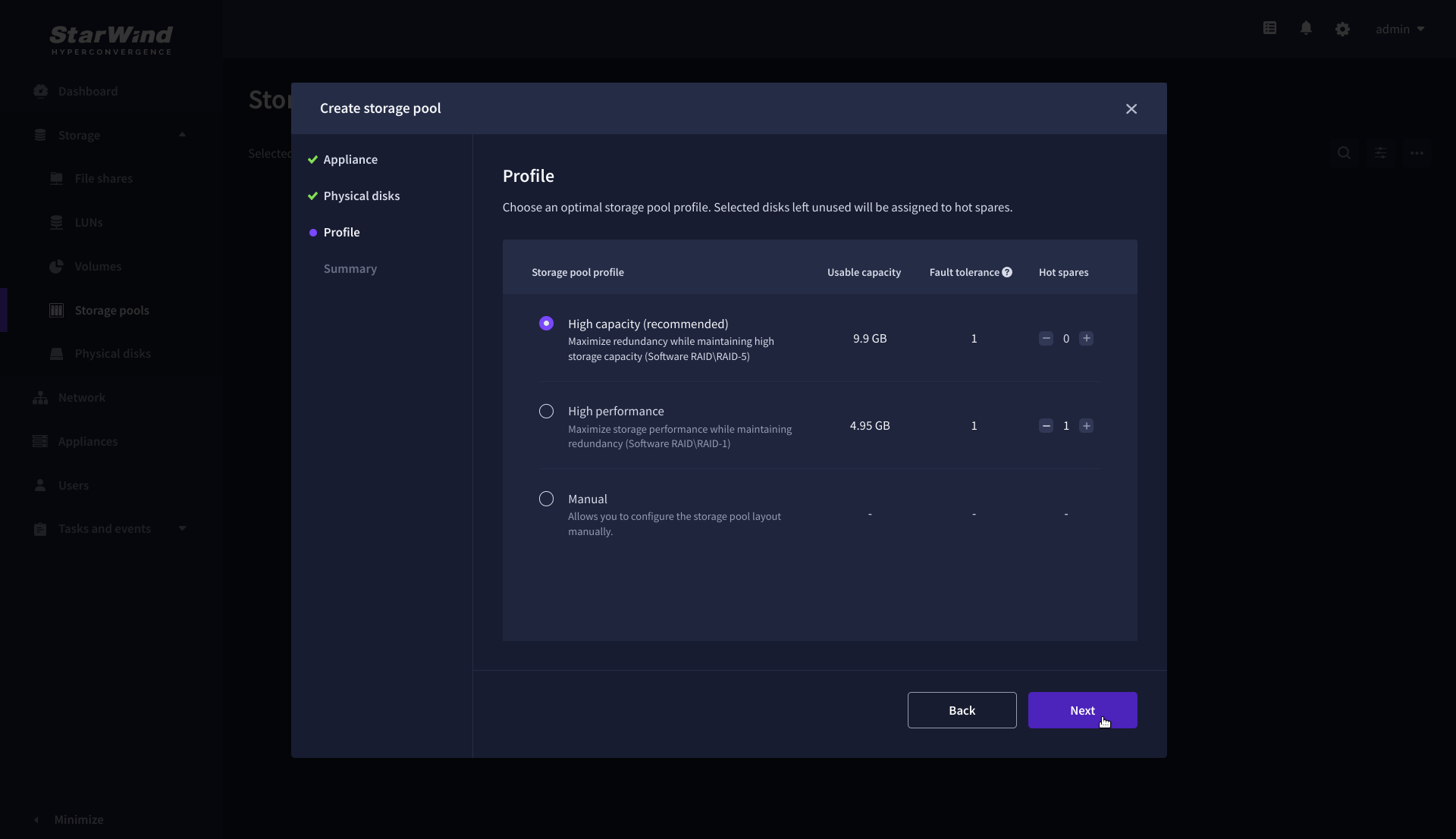
4. On the Profile step, select one of the preconfigured storage profiles, or choose Manual to configure the storage pool manually based on your redundancy, capacity, and performance requirements, then click Next.
NOTE: Hardware RAID, Linux Software RAID, and ZFS storage pools are supported. To simplify the configuration of storage pools, preconfigured storage profiles are provided. These profiles recommend a pool type and layout based on the attached storage:
- High capacity – creates Linux Software RAID-5 to maximize storage capacity while maintaining redundancy.
- High performance – creates Linux Software RAID-10 to maximize storage performance while maintaining redundancy.
- Hardware RAID – configures a hardware RAID virtual disk as a storage pool. This option is available only if a hardware RAID controller is passed through to the StarWind Virtual SAN.
- Better redundancy – creates ZFS Striped RAID-Z2 (RAID 60) to maximize redundancy while maintaining high storage capacity.
- Manual – allows users to configure any storage pool type and layout with the attached storage.
5. On the Summary step, review the storage pool settings and click Create to configure new storage pools on the selected appliances.
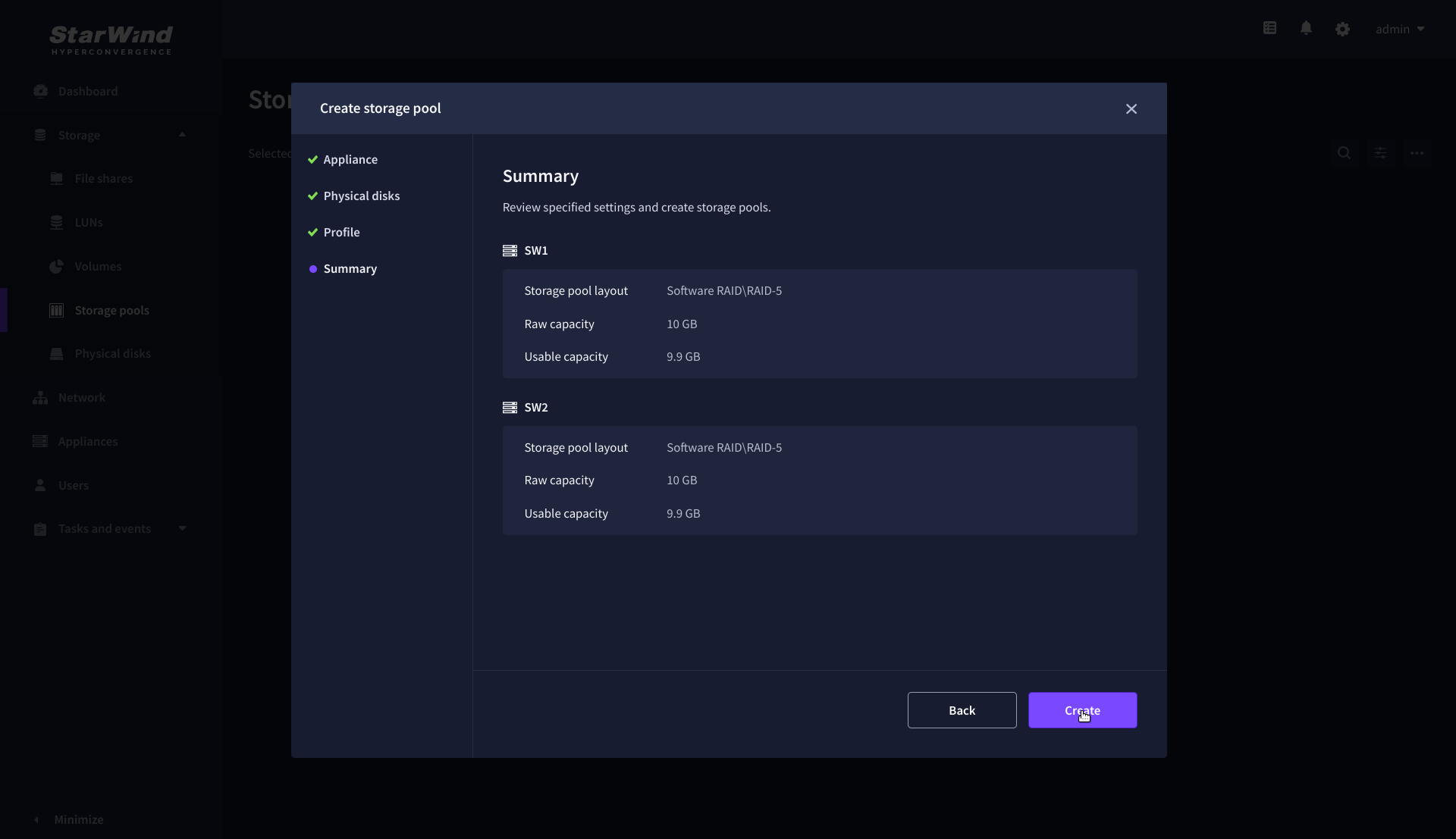
NOTE: The storage pool configuration may take some time, depending on the type of pooled storage and the total storage capacity. Once the pools are created, a notification will appear in the upper right corner of the Web UI.
IMPORTANT: In some cases, additional tweaks are required to optimize the storage performance of the disks added to the Controller Virtual Machine. Please follow the steps in this KB to change the scheduler type depending on the disks type: https://knowledgebase.starwindsoftware.com/guidance/starwind-vsan-for-vsphere-changing-linux-i-o-scheduler-to-optimize-storage-performance/
Create Volume
1. Navigate to the Volumes page and click the + button to open the Create volume wizard.
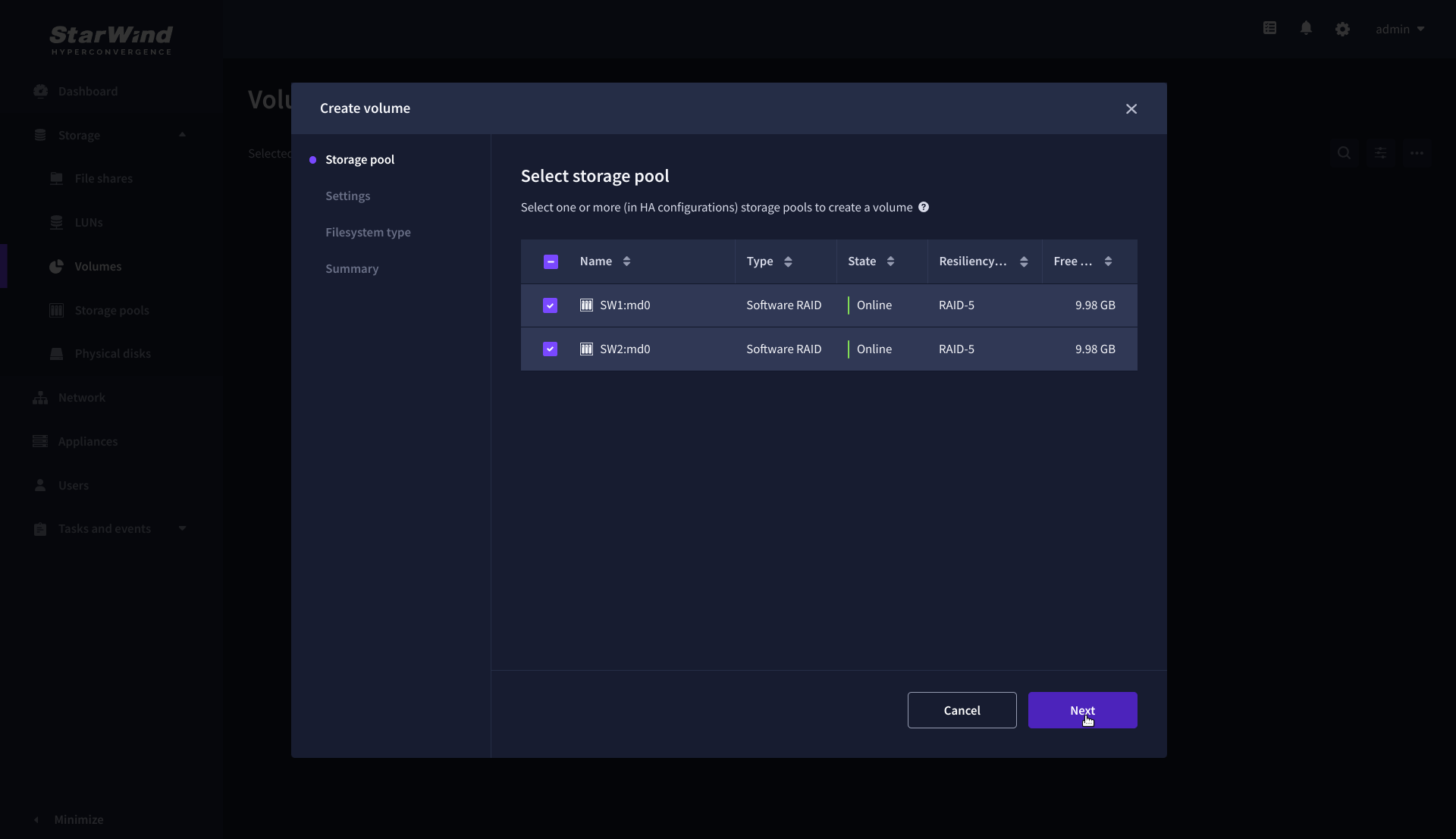
2. On the Storage pool step, select partner appliances on which to create new volumes, then click Next.
NOTE: Select 2 appliances for configuring volumes if you are deploying a two-node cluster with two-way replication, or select 3 appliances for configuring a three-node cluster with a three-way mirror.
3. On the Settings step, specify the volume name and size, then click Next.
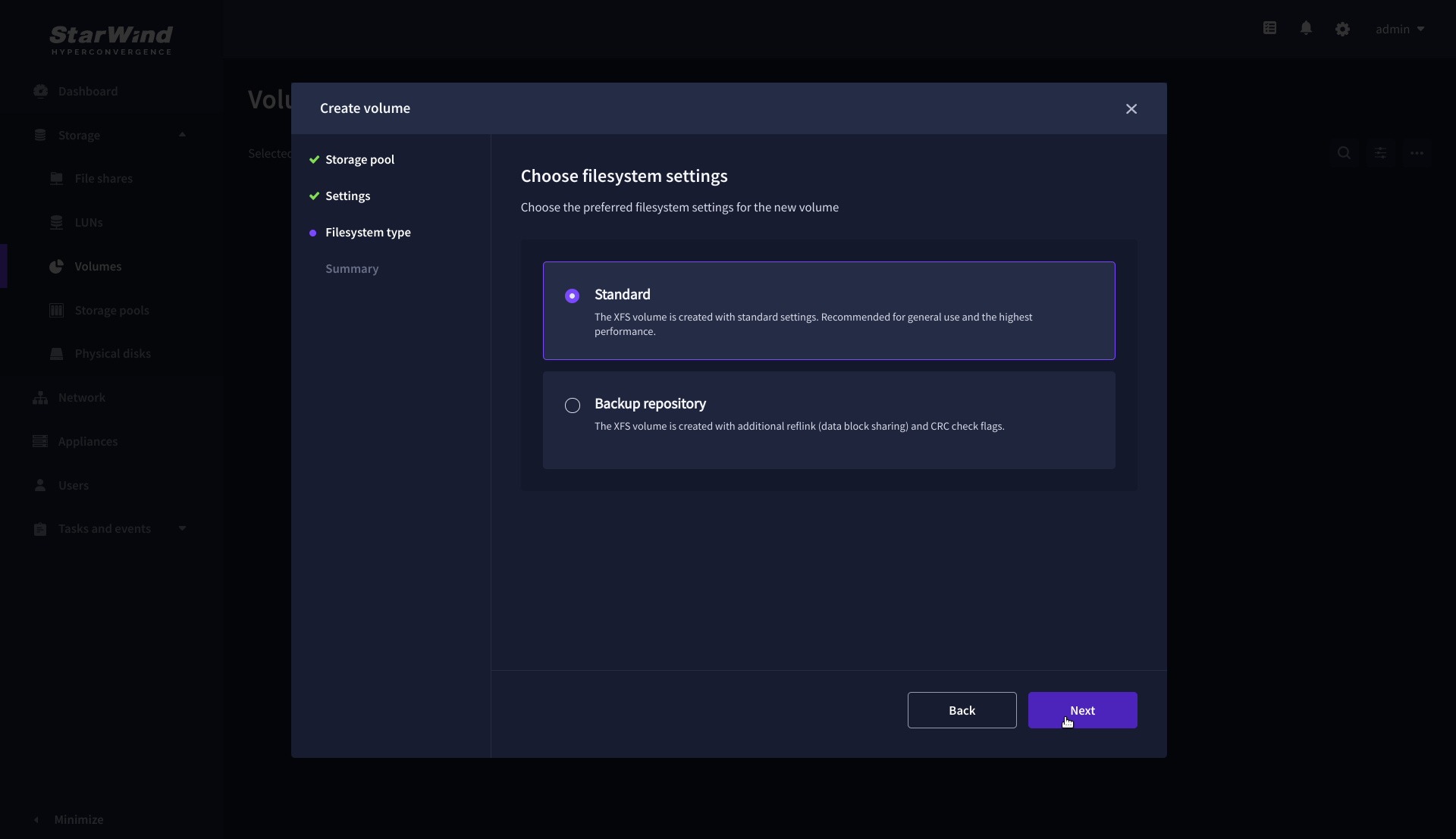
4. On the Filesystem type step, select Standard, then click Next.
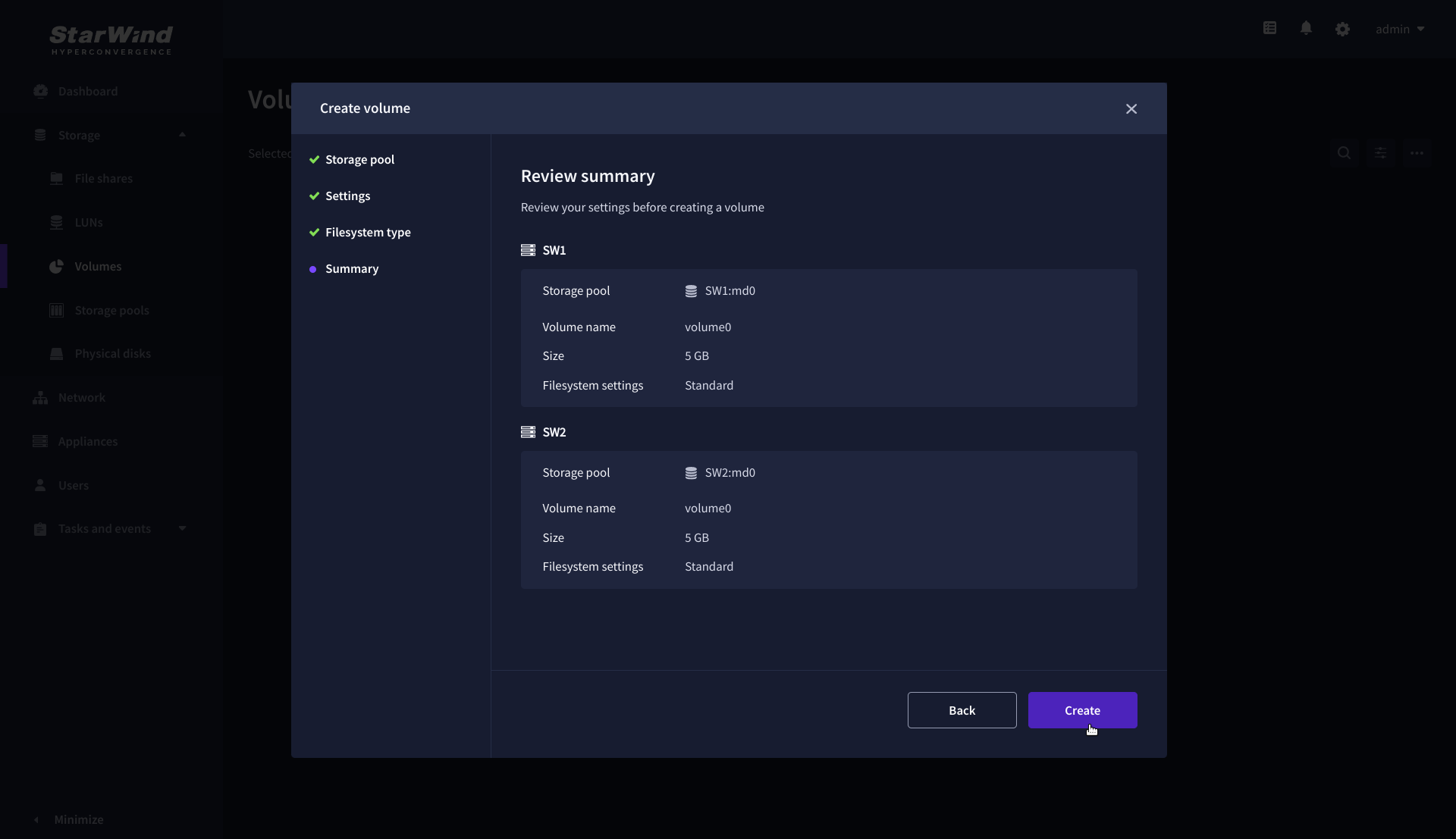
5. Review Summary and click the Create button to create the pool.
Create HA LUN using WebUI
This section describes how to create LUN in Web UI. This option is available for the setups with Commercial, Trial, and NFR licenses applied.
For setups with a Free license applied, the PowerShell script should be used to create the LUN – please follow the steps described in the section: Create StarWind HA LUNs using PowerShell
1. Navigate to the LUNs page and click the + button to open the Create LUN wizard.
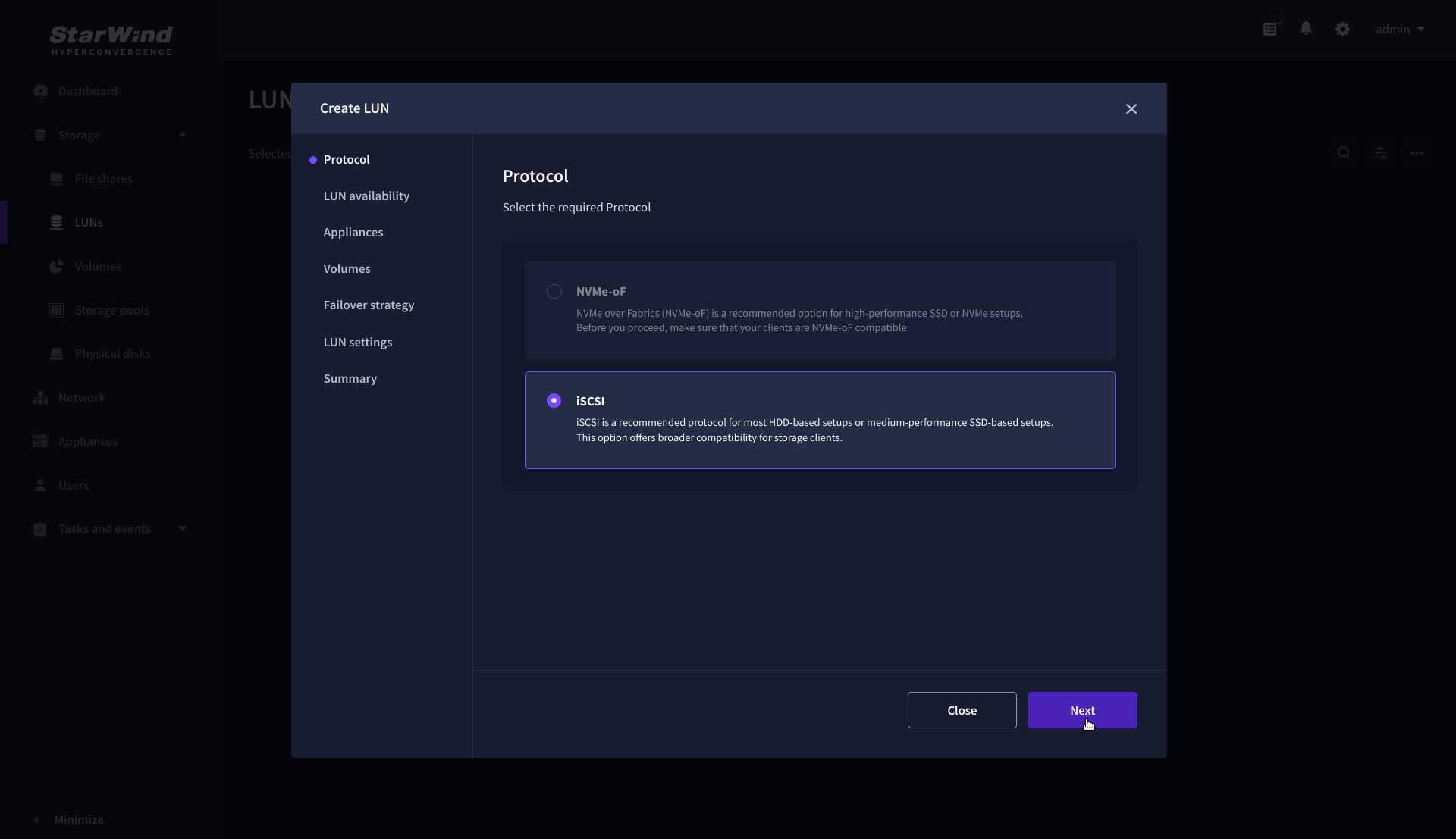
2. On the Protocols step, select the preferred storage protocol and click Next.
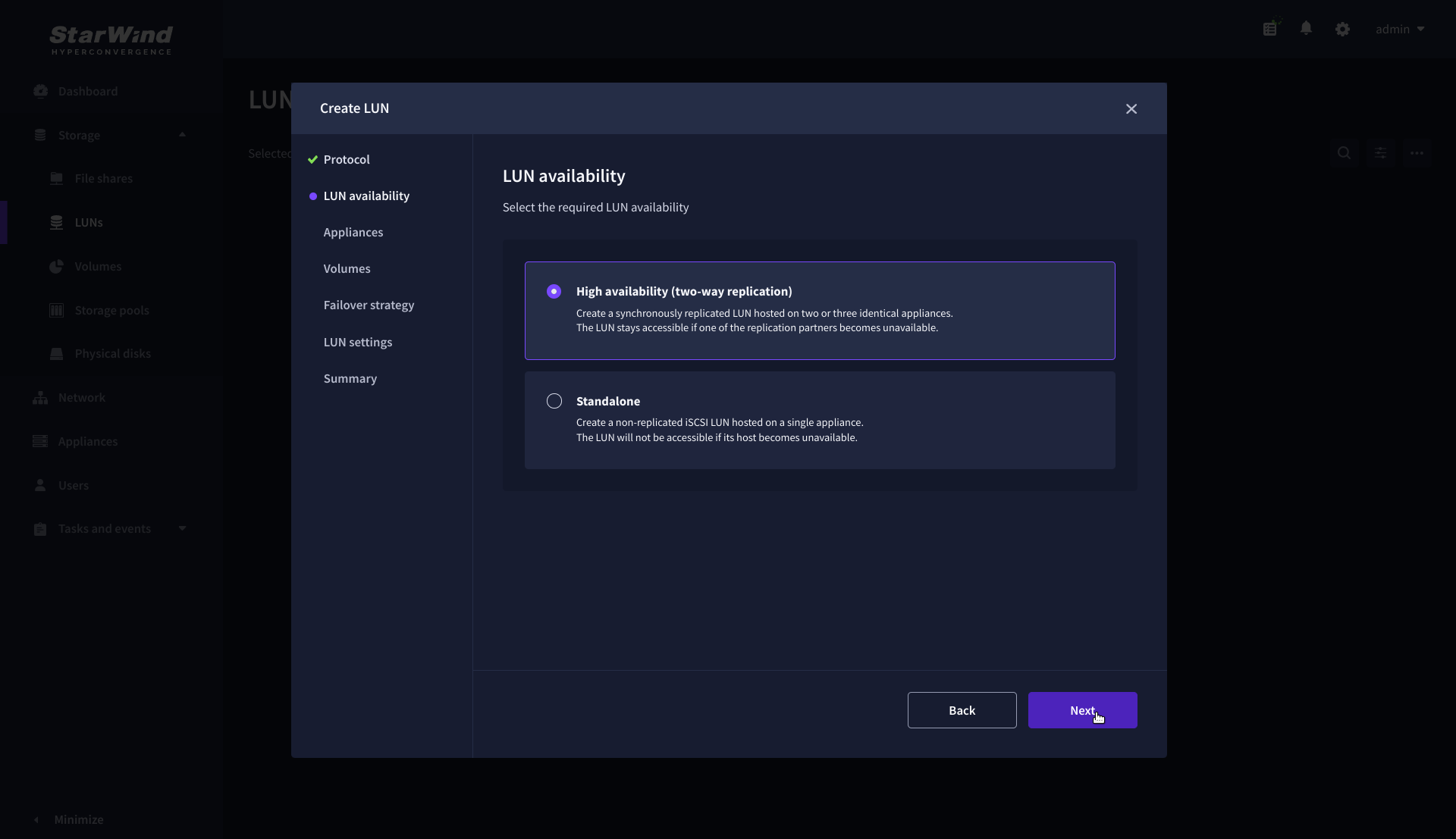
3. On the LUN availability step, select the High availability and click Next.
NOTE: The availability options for a LUN can be Standalone (without replication) or High Availability (with 2-way or 3-way replication), and are determined by the StarWind Virtual SAN license.
Below are the steps for creating a high-availability iSCSI LUN.
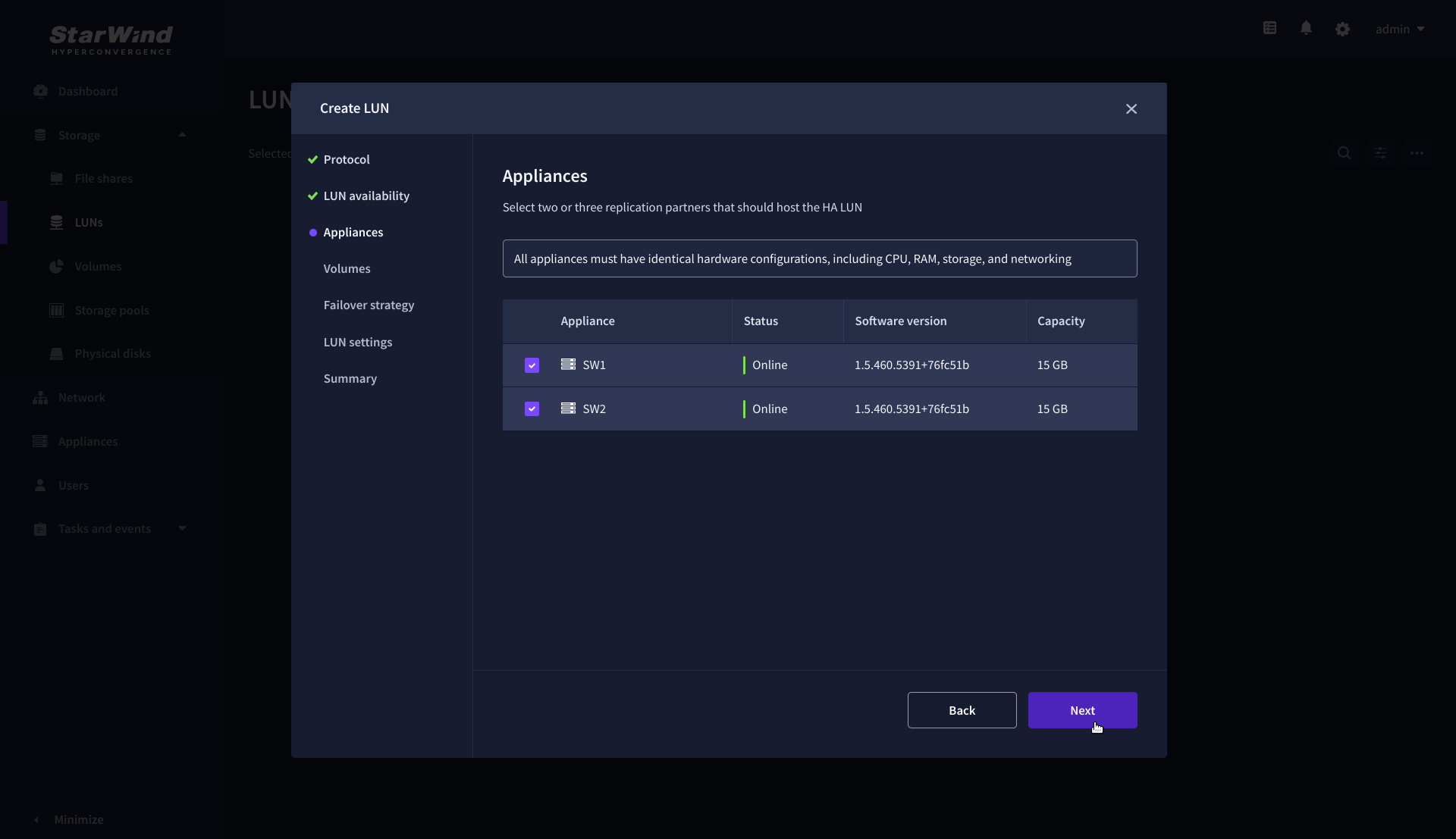
4. On the Appliances step, select partner appliances that will host new LUNs and click Next.
IMPORTANT: Selected partner appliances must have identical hardware configurations, including CPU, RAM, storage, and networking.
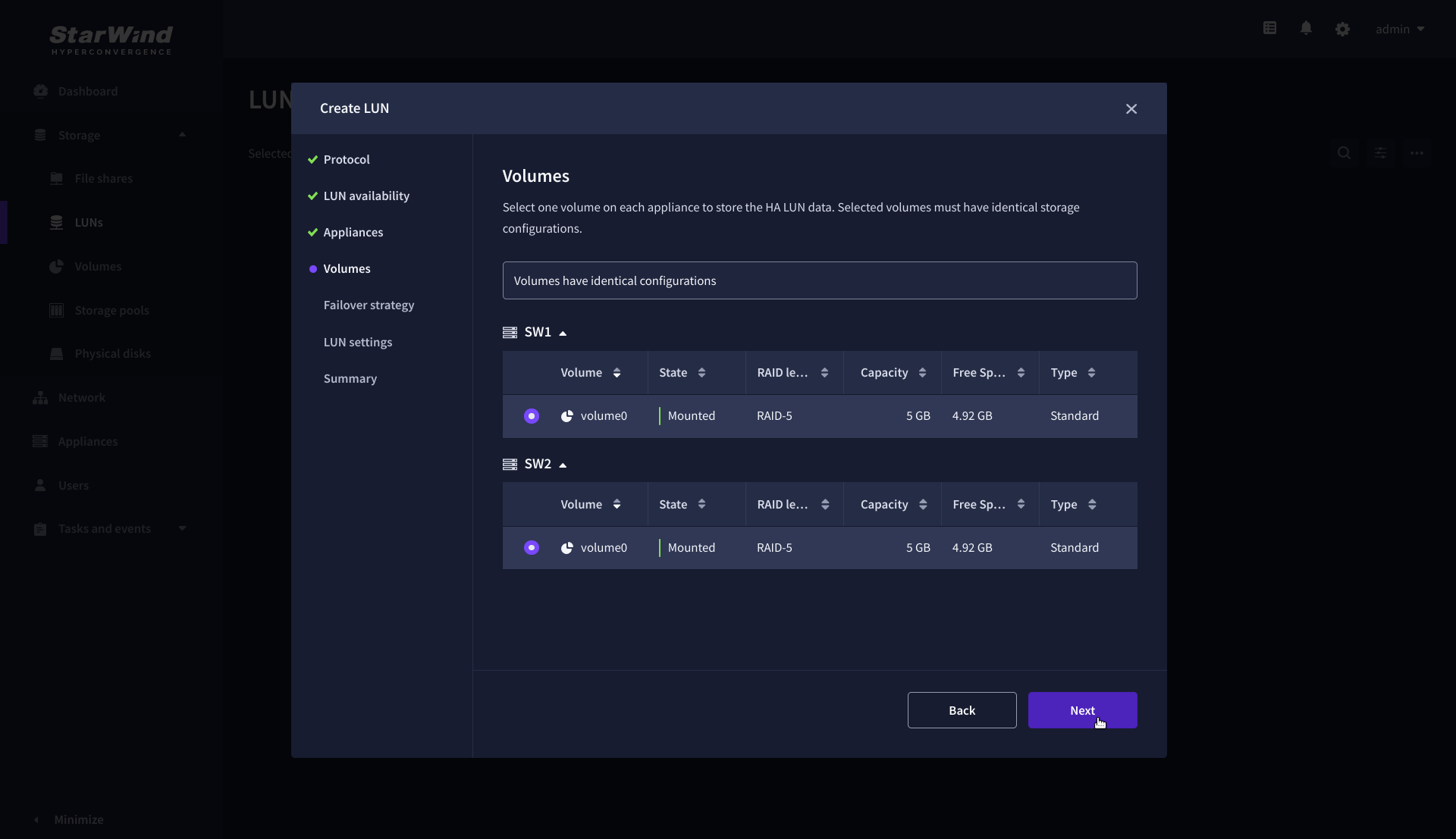
5. On the Volumes step, select the volumes for storing data on the partner appliances and click Next.
IMPORTANT: For optimal performance, the selected volumes must have identical underlying storage configurations.
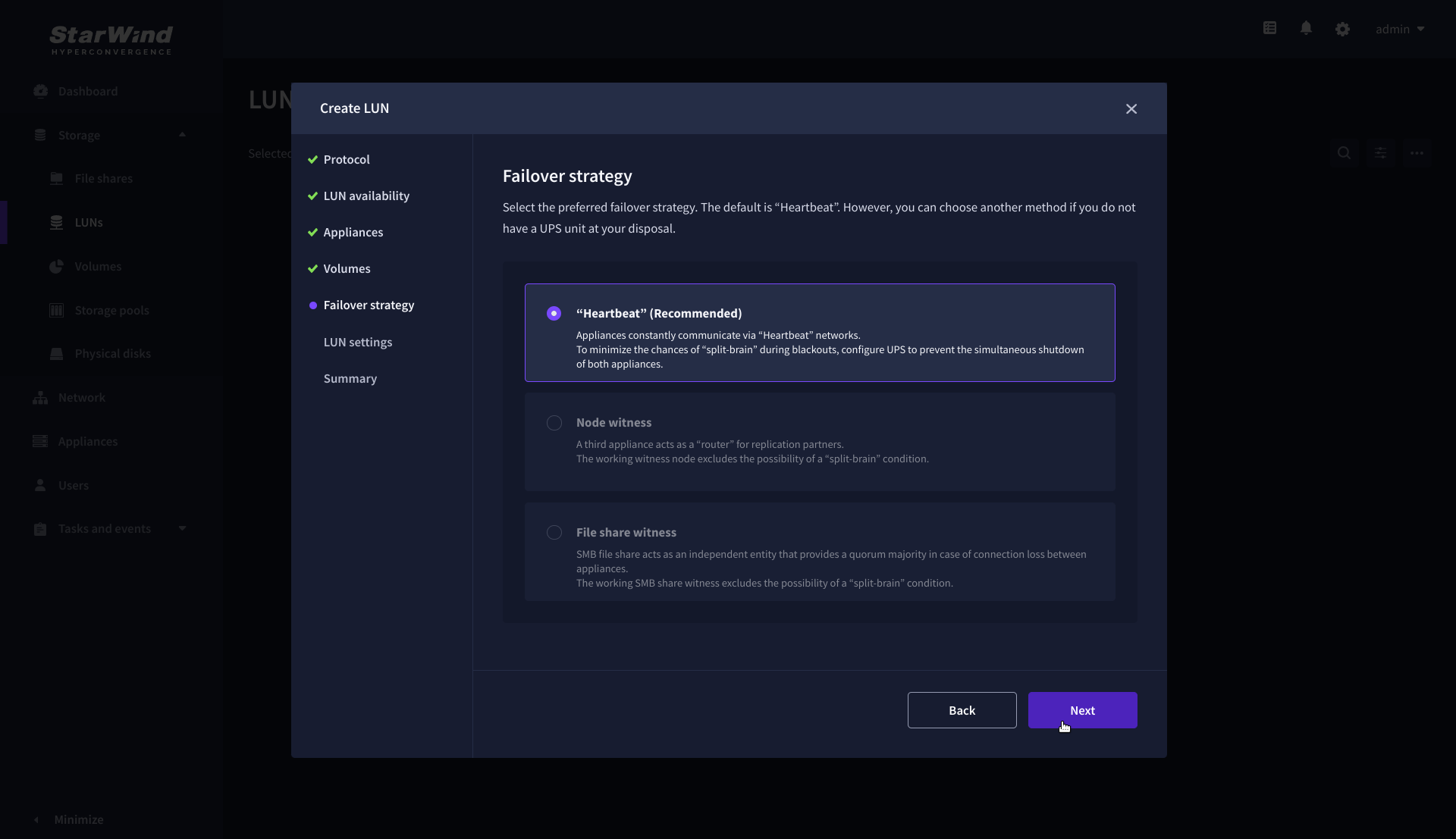
6. On the Failover strategy step, select the preferred failover strategy and click Next.
NOTE: The failover strategies for a LUN can be Heartbeat or Node Majority. In case of 2-nodes setup and None Majority failover strategy, Node witness (requires an additional third witness node), or File share witness (requires an external file share) should be configured. These options are determined by StarWind Virtual SAN license and setup configuration. Below are the steps for configuring the Heartbeat failover strategy in a two-node cluster.
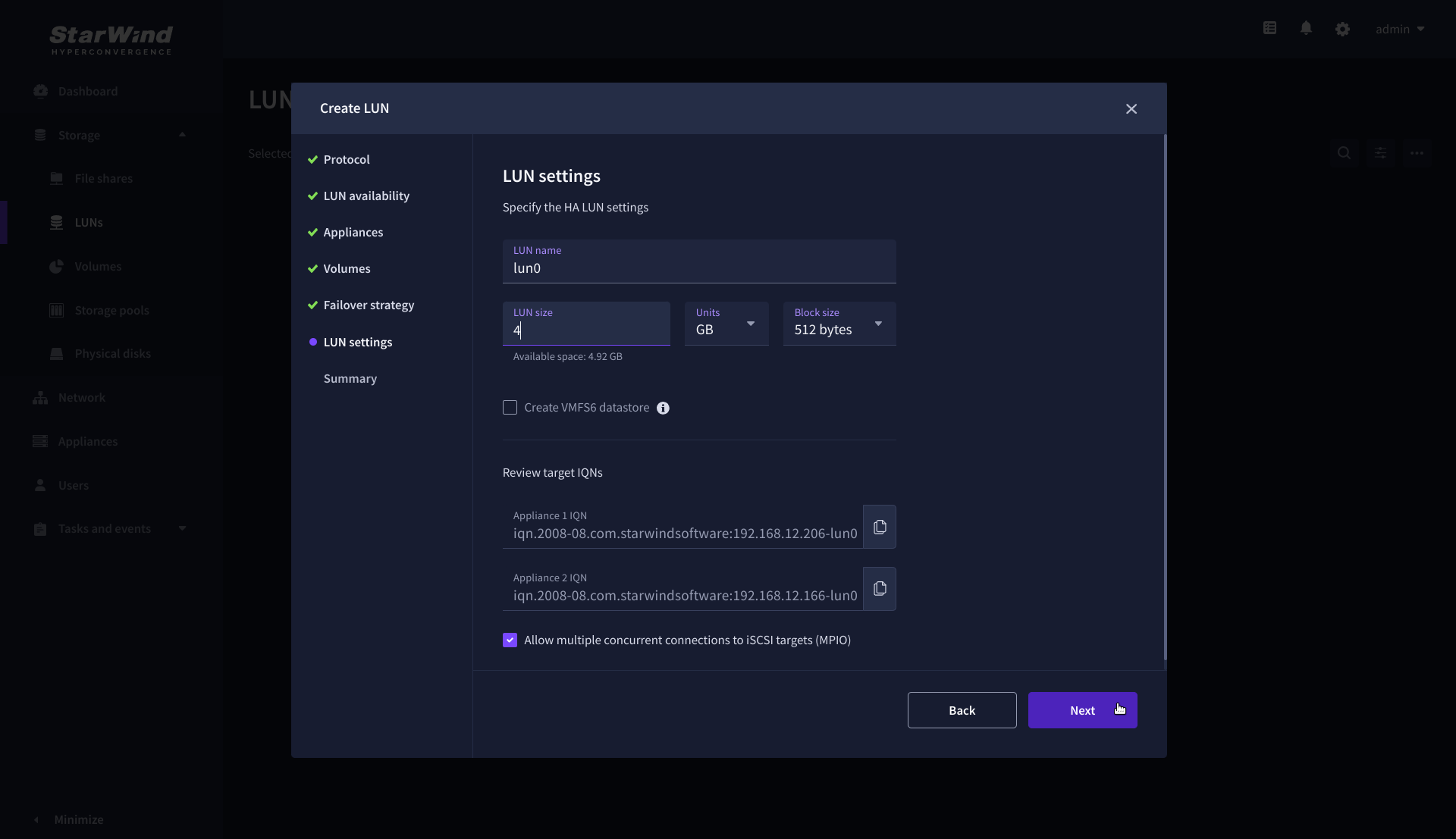
7. On the LUN settings step, specify the LUN name, size, block size, then click Next.
NOTE: For high-availability configurations, ensure that MPIO checkbox is selected.
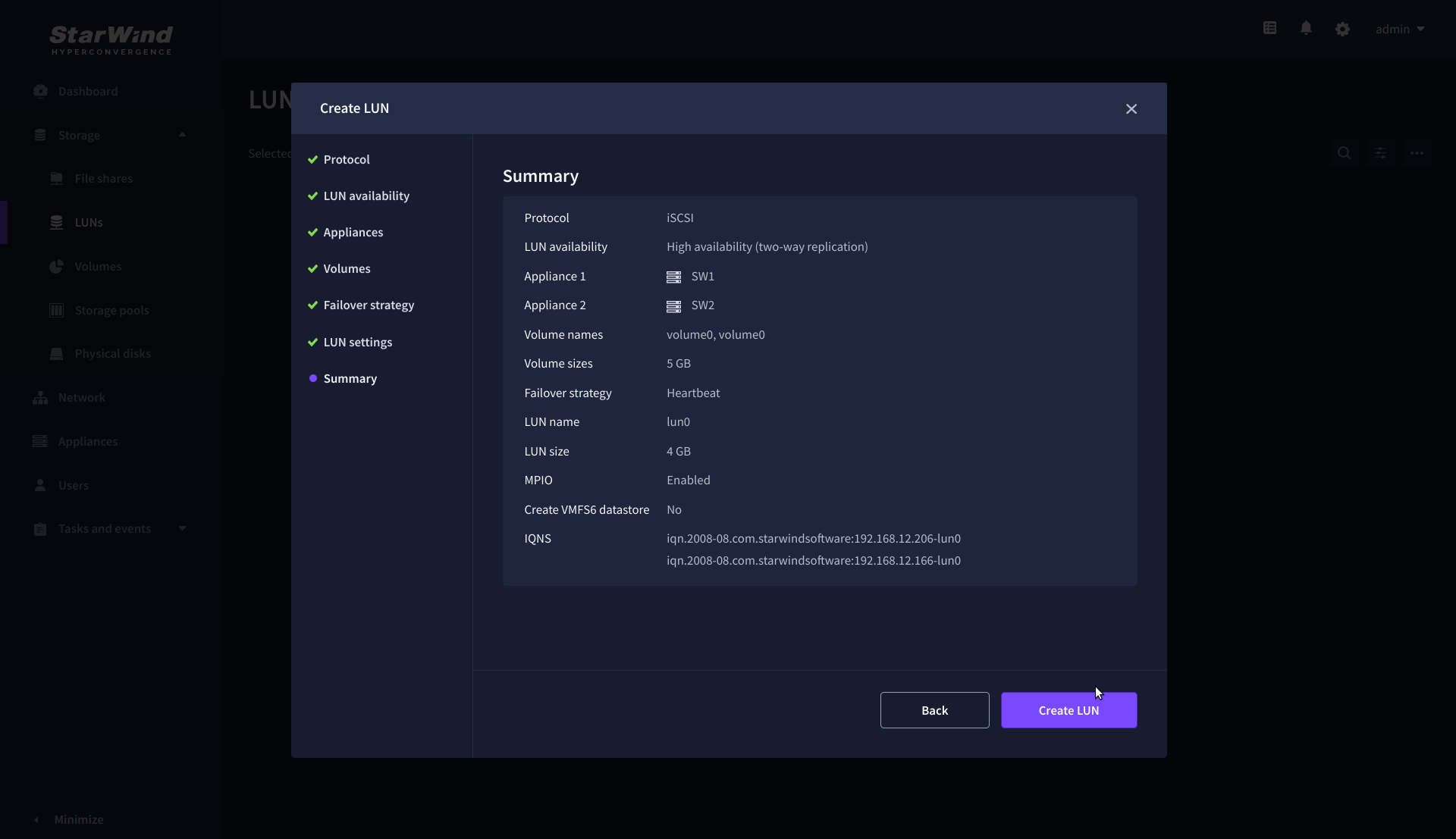
8. On the Summary step, review the LUN settings and click Create to configure new LUNs on the selected volumes.
Connecting StarWind LUNs to VMware vSphere servers
1. Log in to VMware vSphere Client.
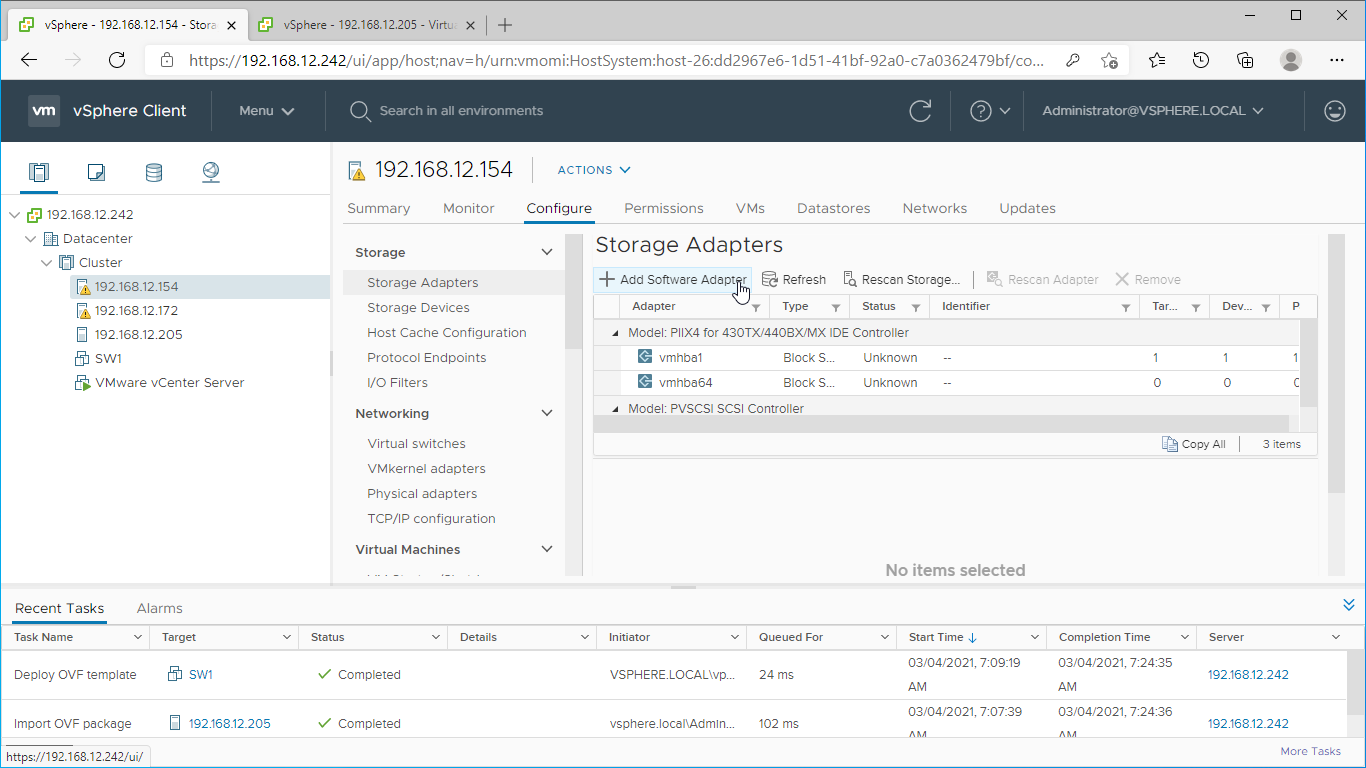
2. Select the ESXi server in the sidebar-menu, then navigate to the “Configure” tab and open the “Storage Adapters” submenu page.
3. Click the “+Add Software Adapter” button to launch the corresponding wizard.
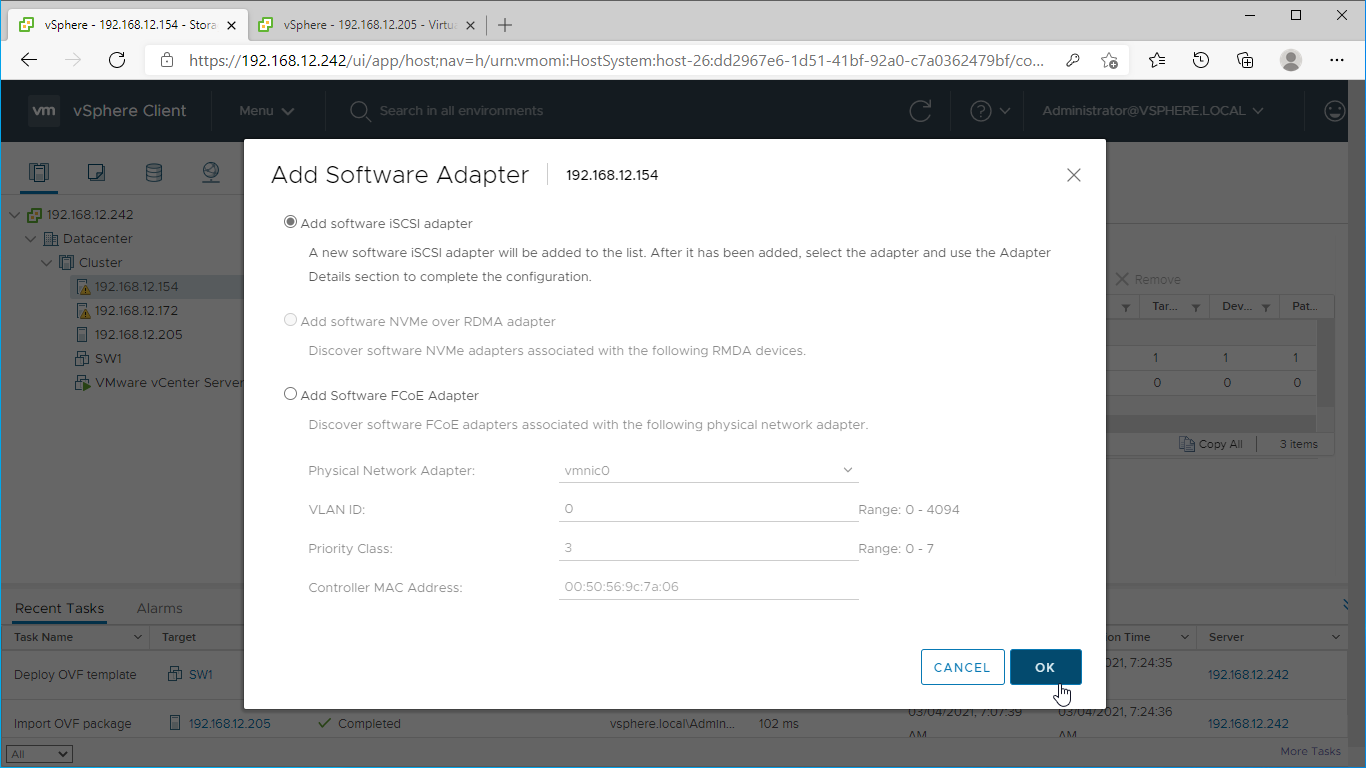
4. Mark the “Add software iSCSI adapter” option and click OK.
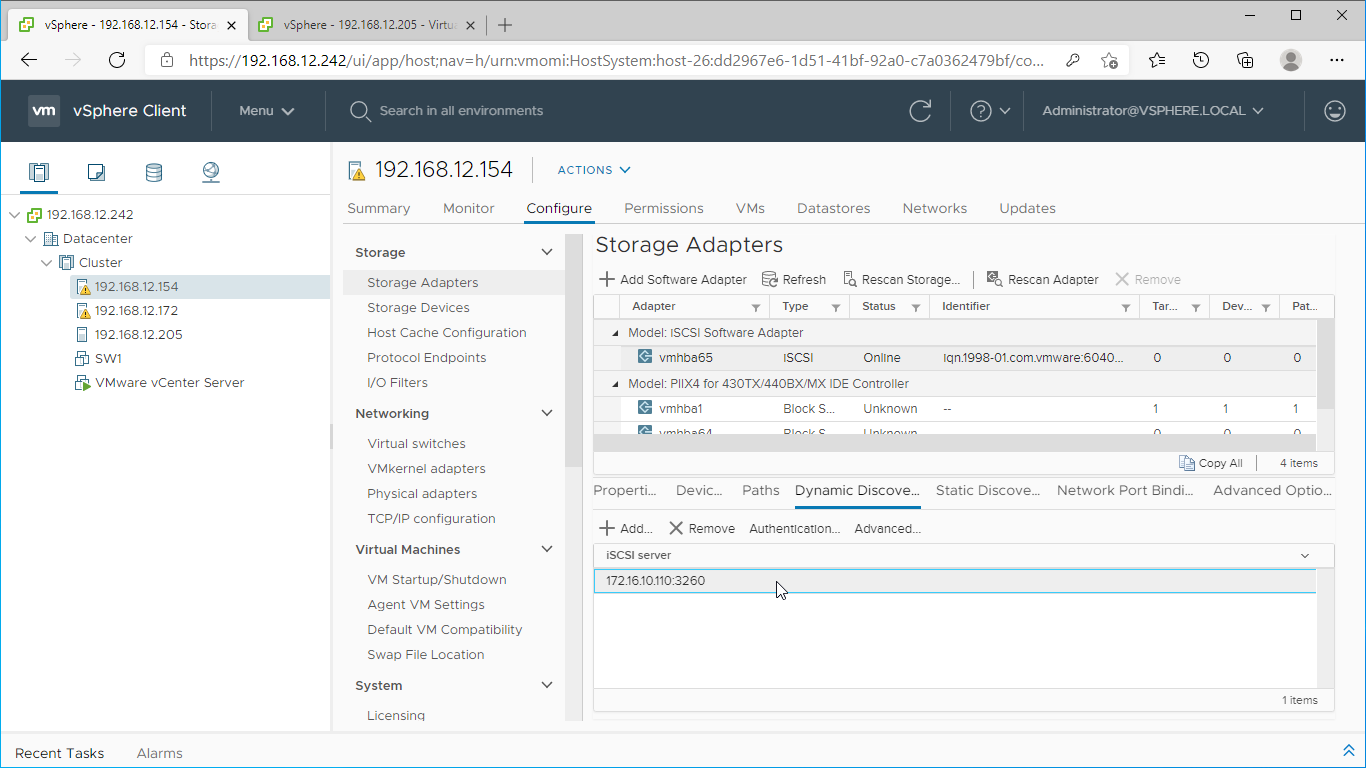
5. Add the IPv4 address of StarWind CVM Data\iSCSI network interface to the “Dynamic Discovery“. Save the configuration
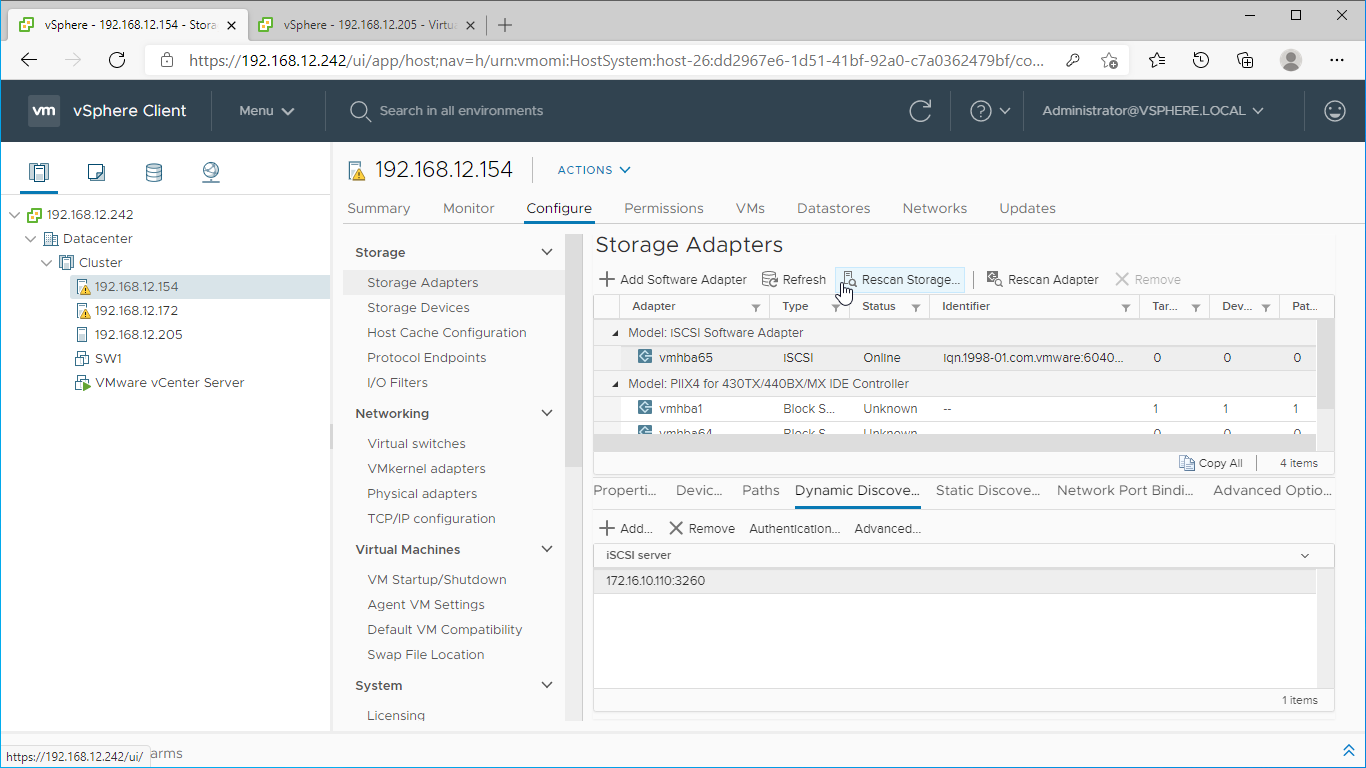
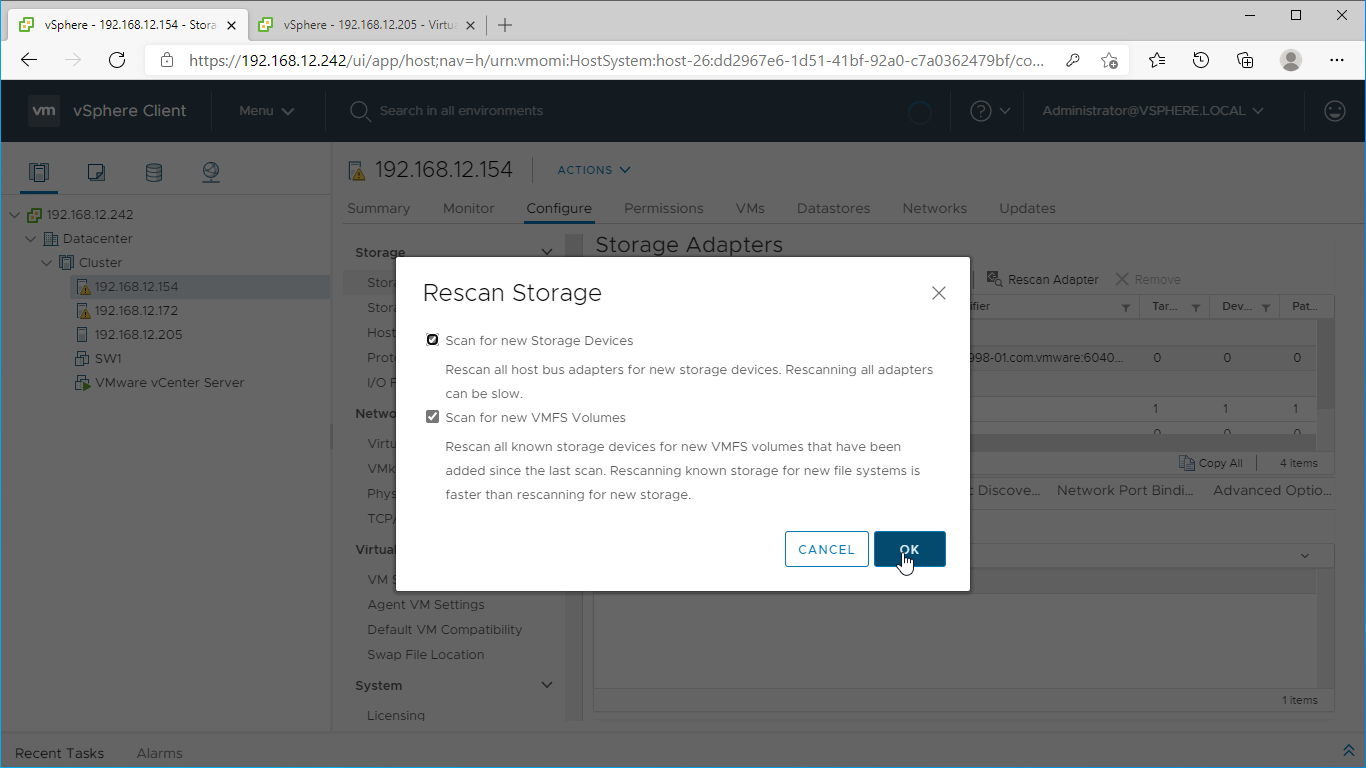
6. Click on the “Rescan” button to discover StarWind virtual disk.
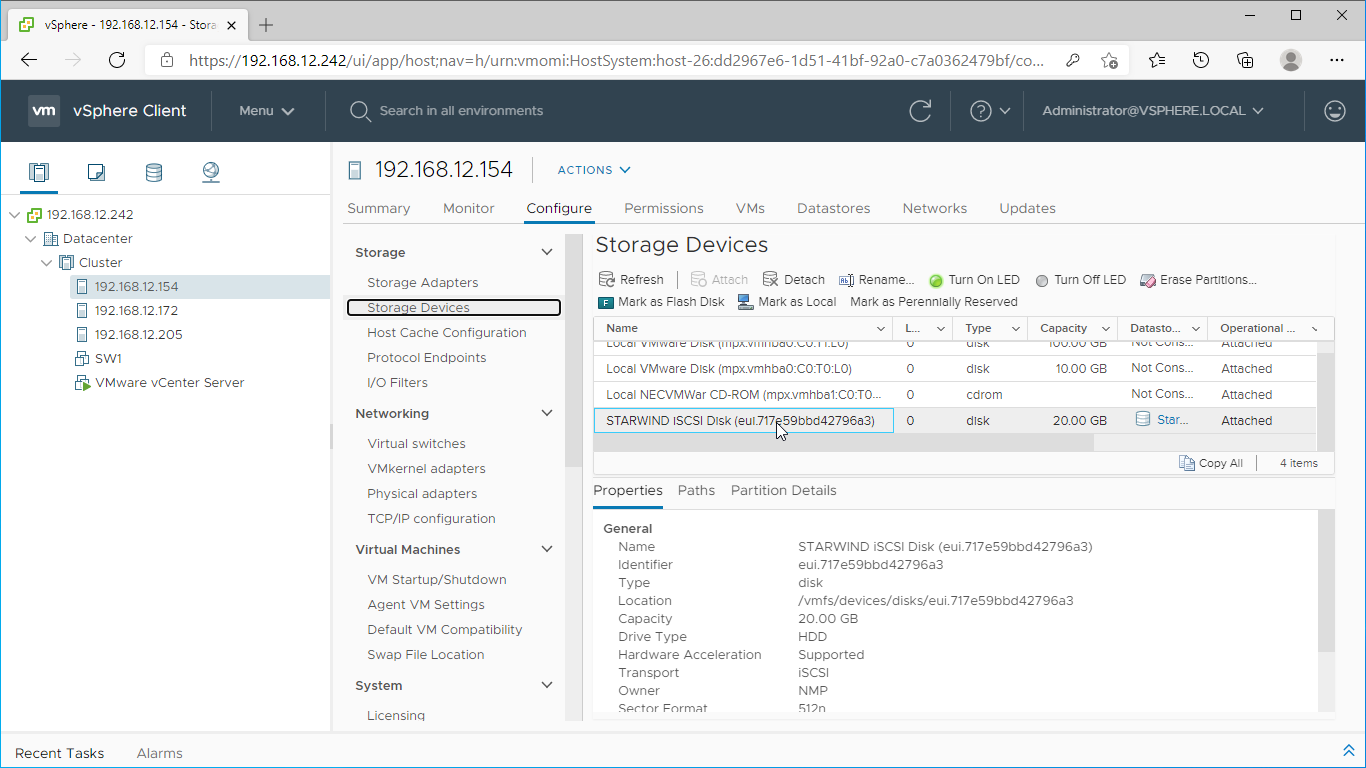
7. Once scanned, the created StarWind LUNs appear on the “Storage Devices” submenu page.
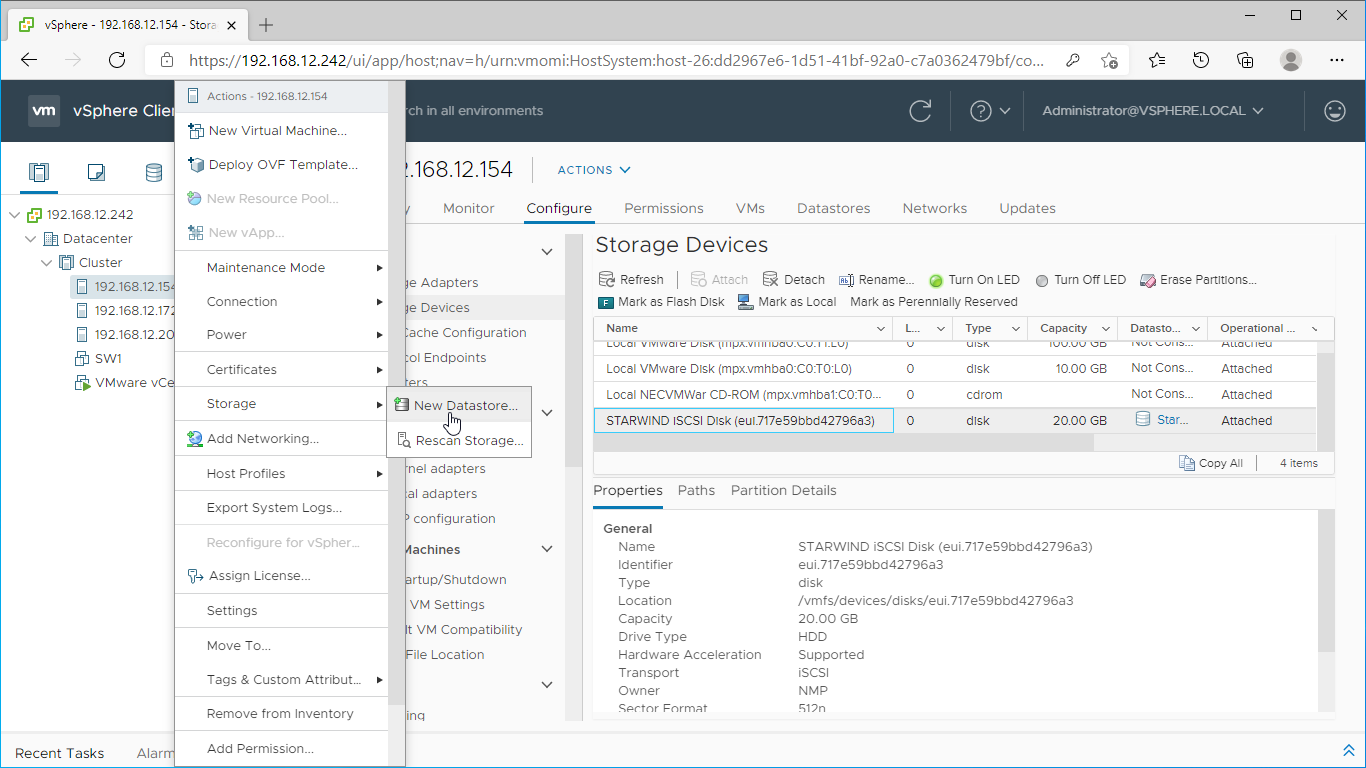
8. Right-click on the ESXi server to open the “Actions” menu, click on “Storage” and click the “New datastore” button.
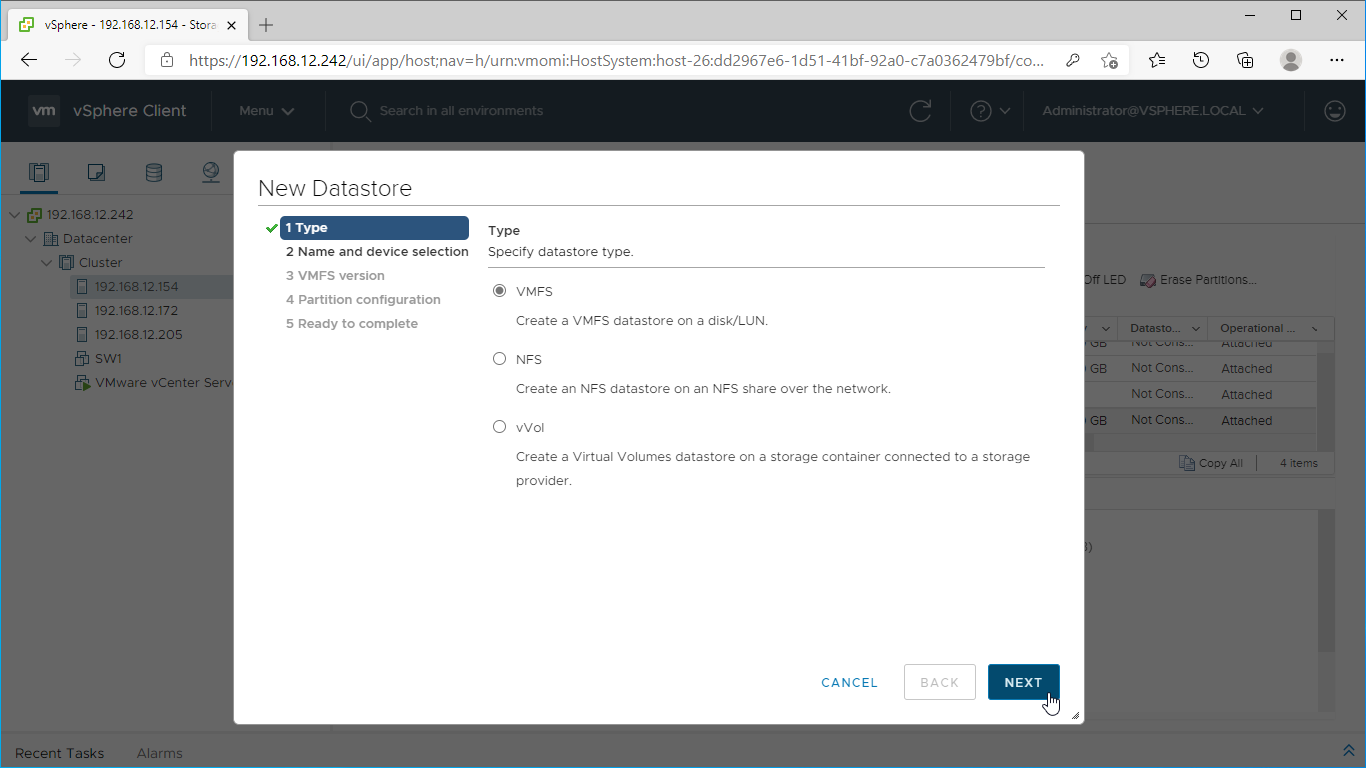
9. The Datastore creation wizard appears. Specify the Datastore type as VMFS.
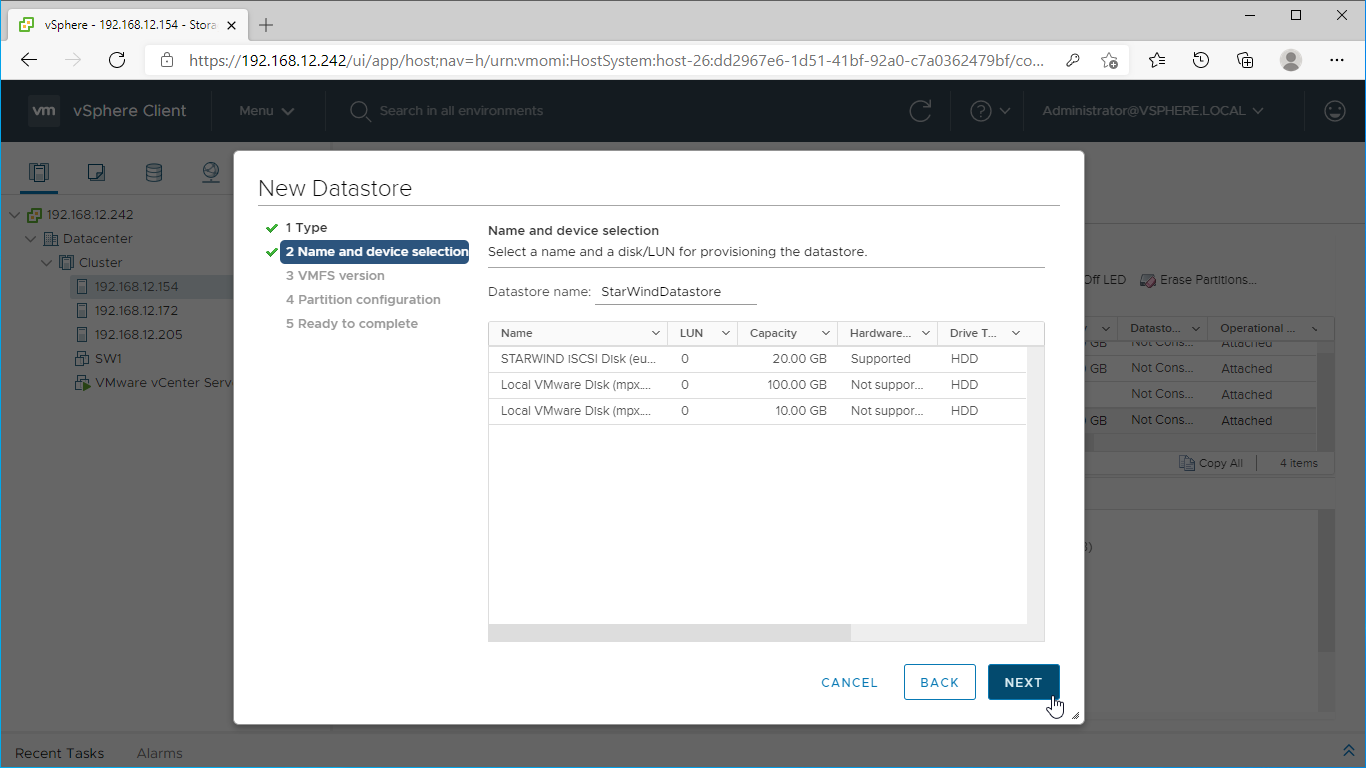
10. Specify the datastore name. Select the StarWind virtual disk.
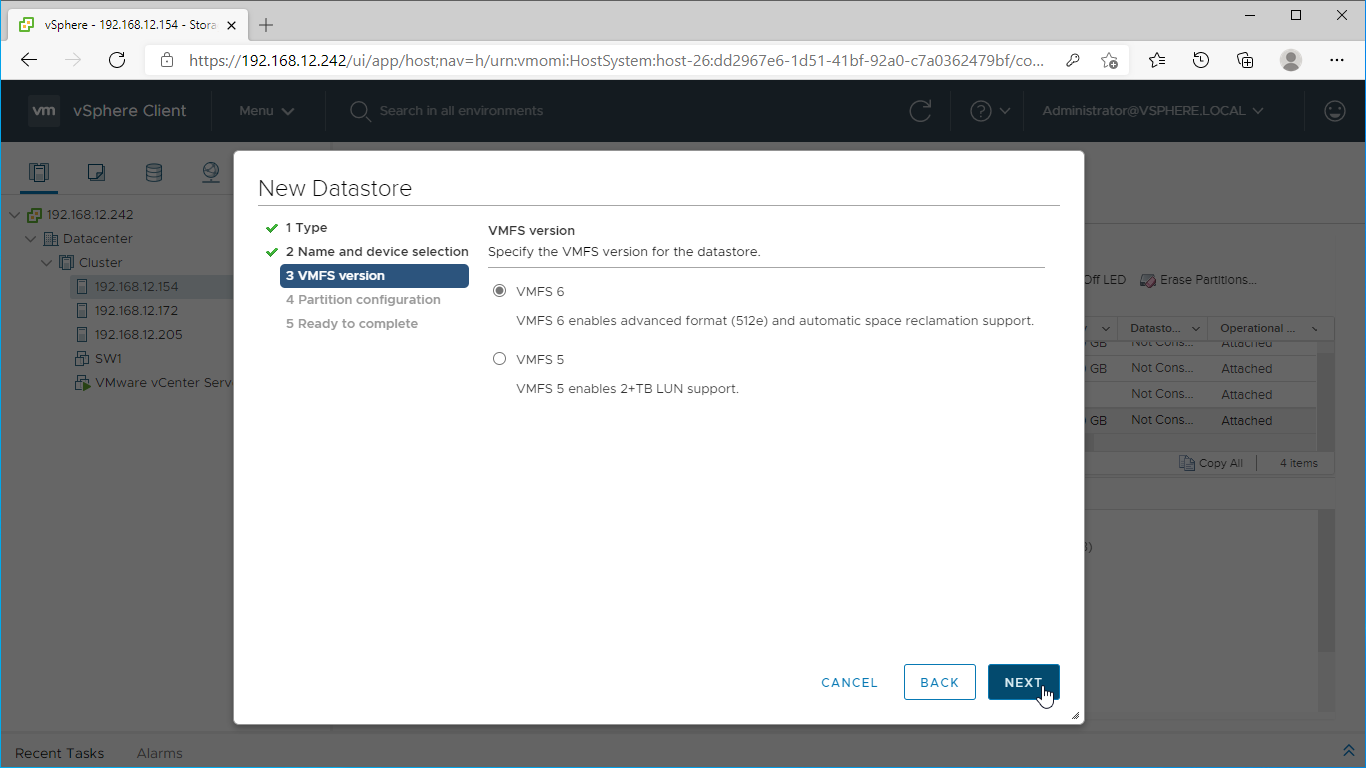
11. Specify the VMFS6 version for the datastore.
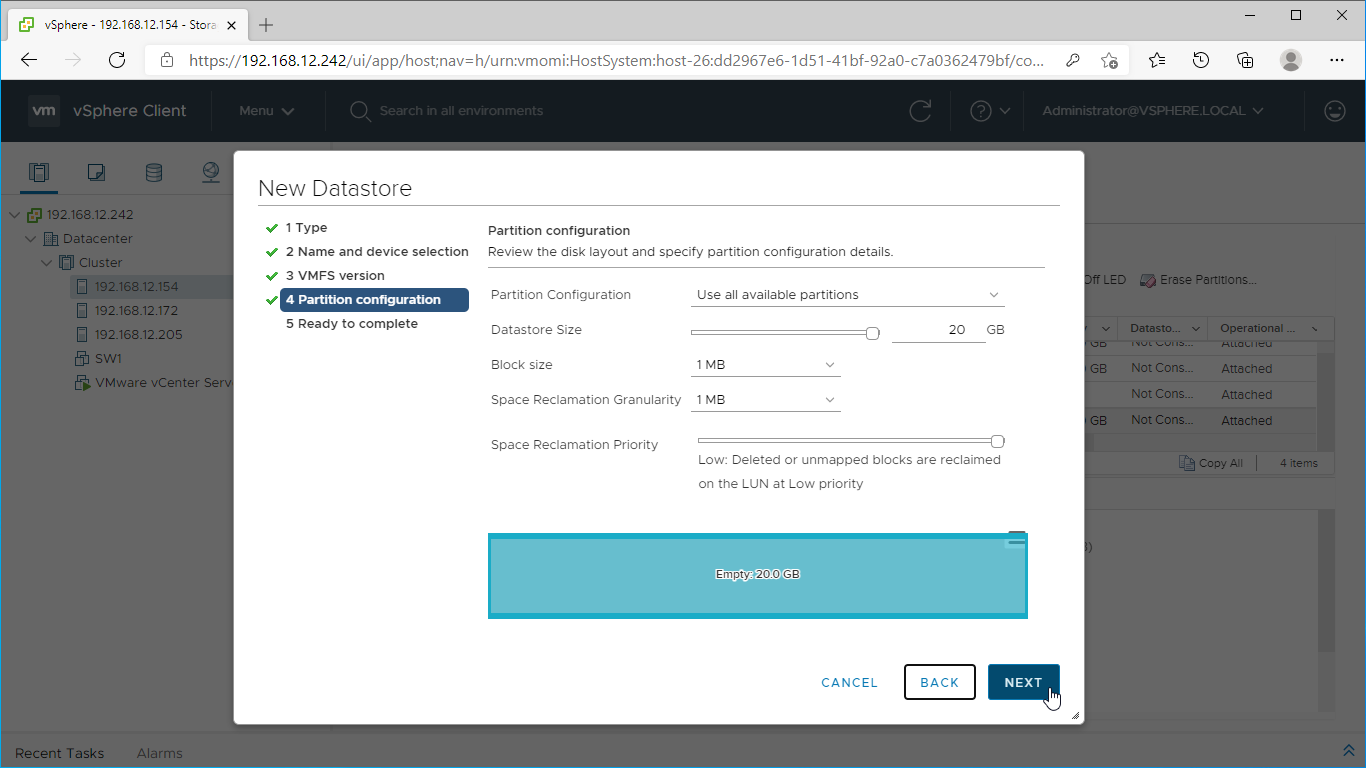
12. Specify the datastore size using the entire disk capacity.
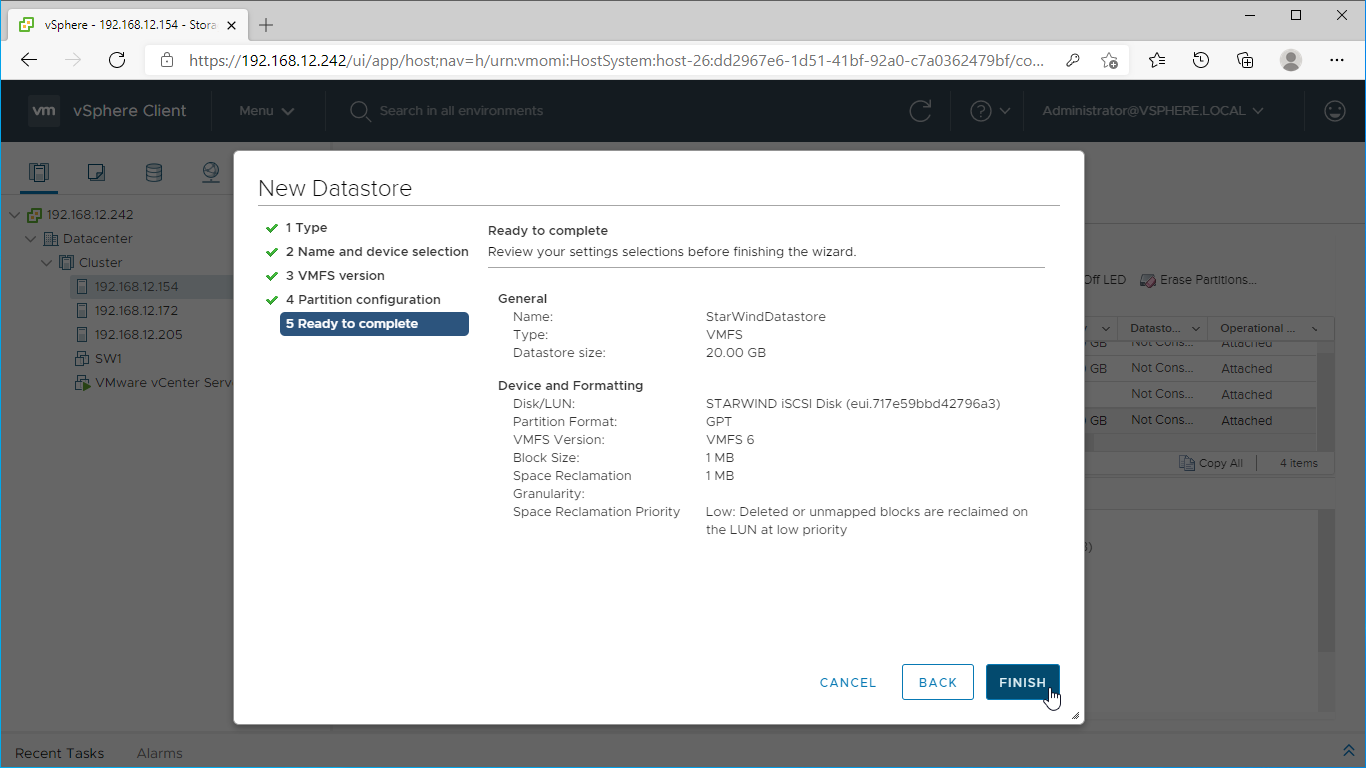
13. Review the configuration summary and click “Finish” to create the datastore.
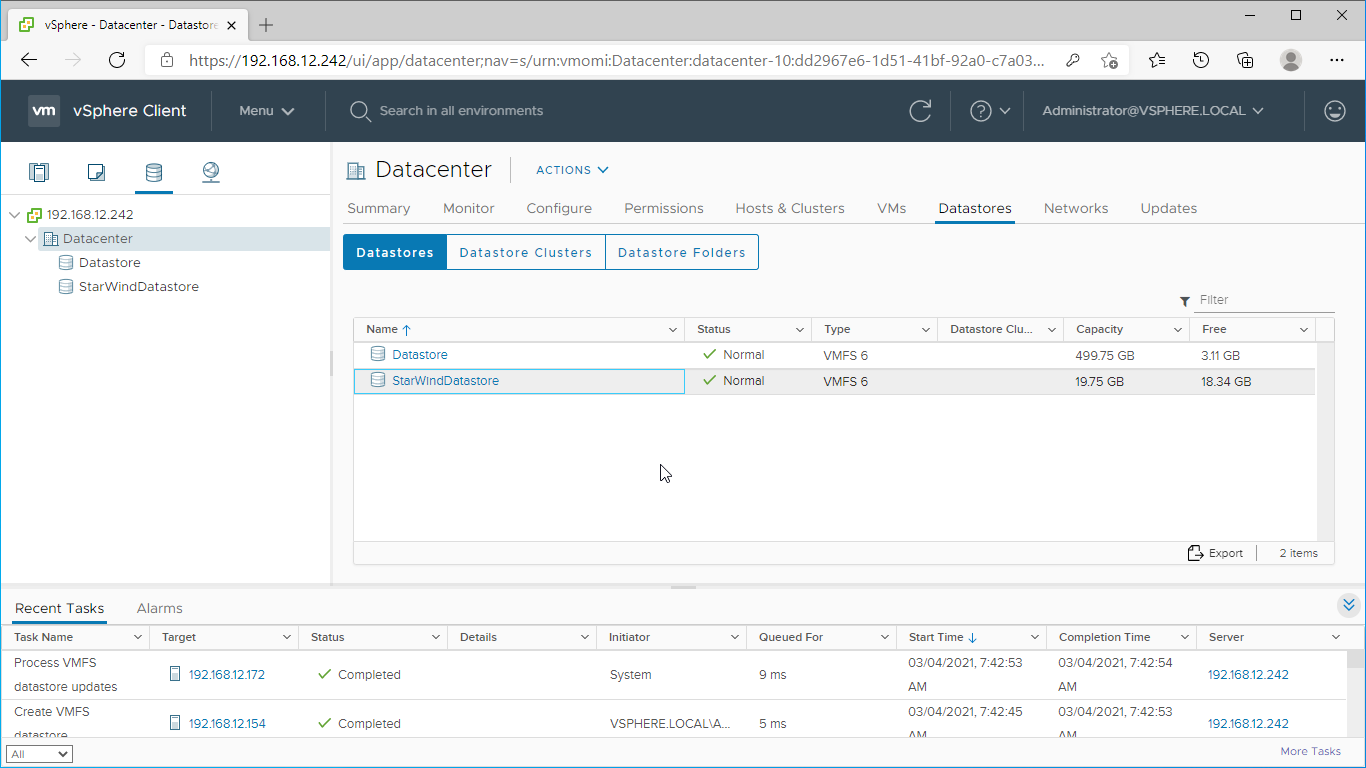
14. Check the StarWind datastore in the Datastores tab.
15. Repeat the configuration steps 6-13 to add newly created StarWind LUNs as datastores on your VMware vSphere cluster.
Configuring an Automatic Storage Rescan
1. Connect to the appliance via Shell Terminal in a Text-based User Interface (TUI) or using a remote SSH terminal.
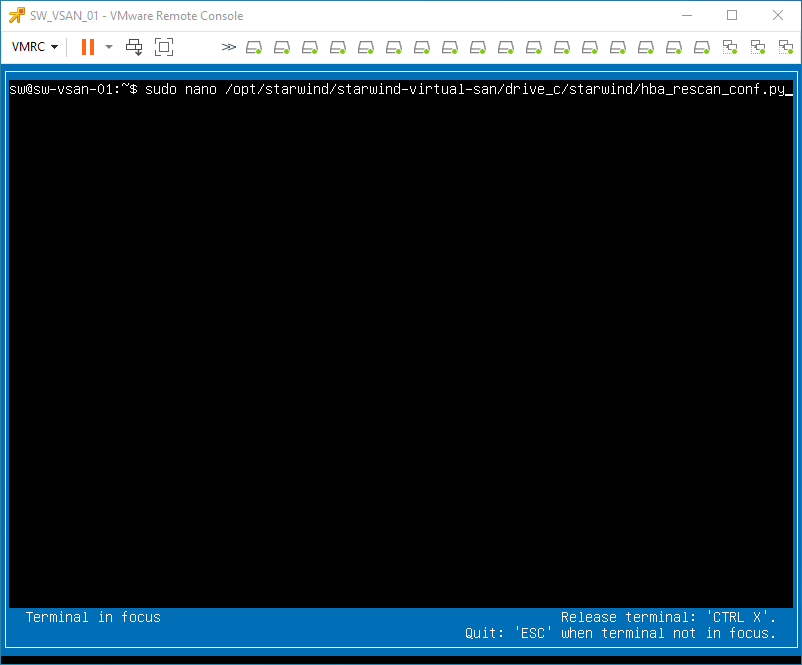
2. Edit file /opt/starwind/starwind-virtual-san/drive_c/starwind/hba_rescan_config.py with the following command: sudo nano /opt/starwind/starwind-virtual-san/drive_c/starwind/hba_rescan_config.py
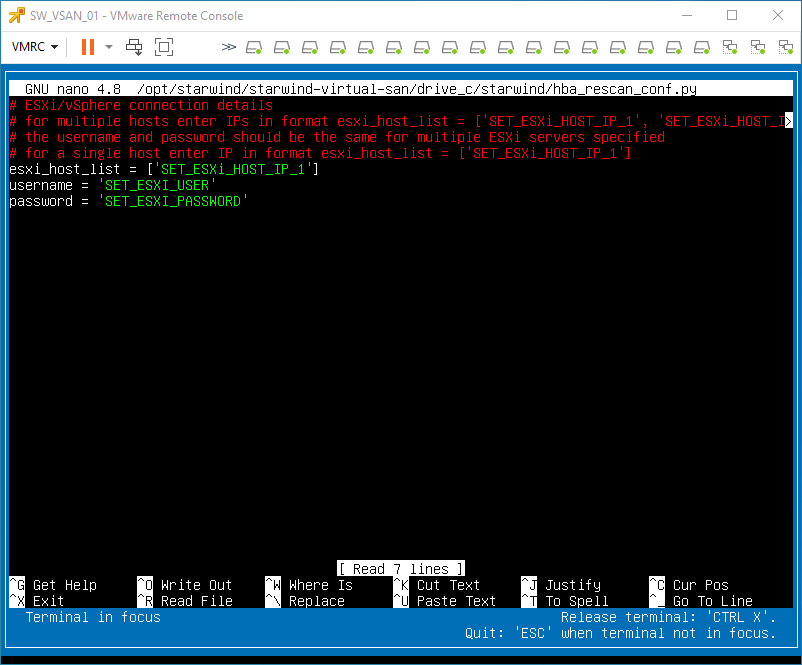
3. In the appropriate lines, specify the IP address and login credentials of the single or multiple ESXi hosts (see NOTE below) on which the current StarWind VM is stored and will trigger the storage rescan task:
$esxi_host_list = [‘IP address’]
$username = ‘Login’
$password = ‘Password’
NOTE: In some cases, it makes sense to create a separate ESXi user for storage rescans. To create the user, please follow the steps below:
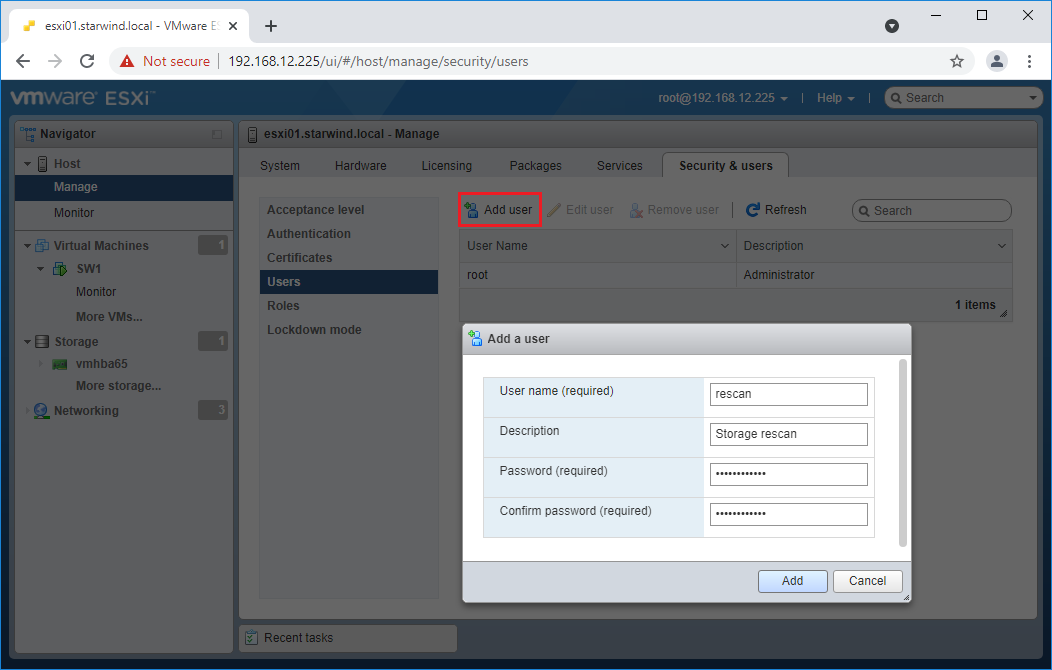
4. Log in to ESXi with the VMware Host Client. Click Manage, and under Security & users tab, in the Users section click Add user button. In the appeared window, enter a user name, and a password.
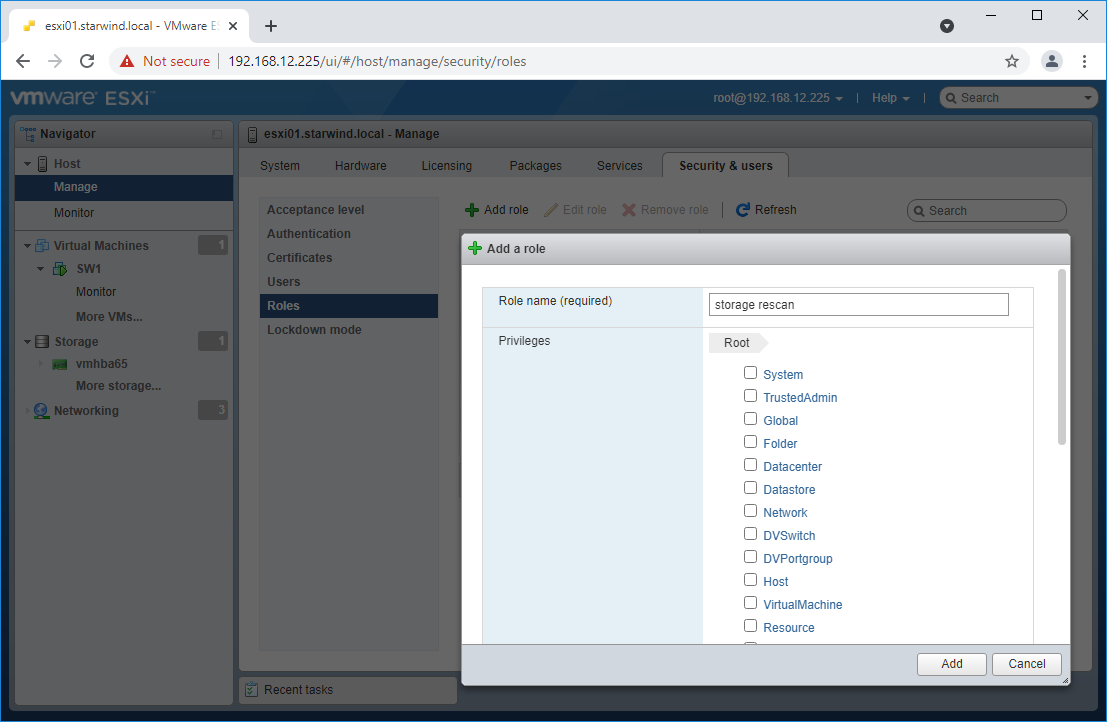
5. Create a new Role, under Roles section, and click New Role button. Type a name for the new role. Select privileges for the role and click OK.
The following privileges might be assigned: Host – Inventory, Config, Local Cim, and Global – Settings.
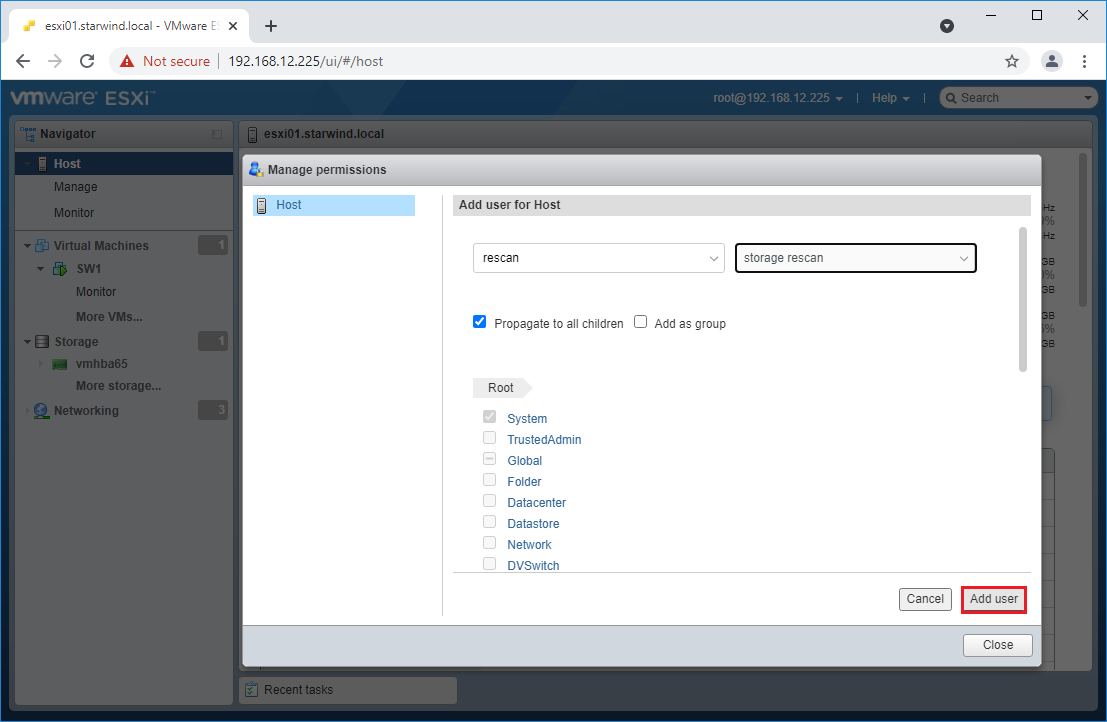
6. Assign permission to the storage rescan user for an ESXi host – right-click Host in the VMware Host Client inventory and click Permissions. In the appeared window click Add user.
7. Click the arrow next to the Select a user text box and select the user that you want to assign a role to. Click the arrow next to the Select a role text box and select a role from the list.
(Optional) Select Propagate to all children or Add as group. Click Add user and click Close.
Make sure that rescan script is working and execute it from the VM: sudo python3 /opt/starwind/starwind-virtual-san/drive_c/starwind/hba_rescan.py
4. Repeat all steps from this section on the other ESXi hosts.
Performance Tweaks
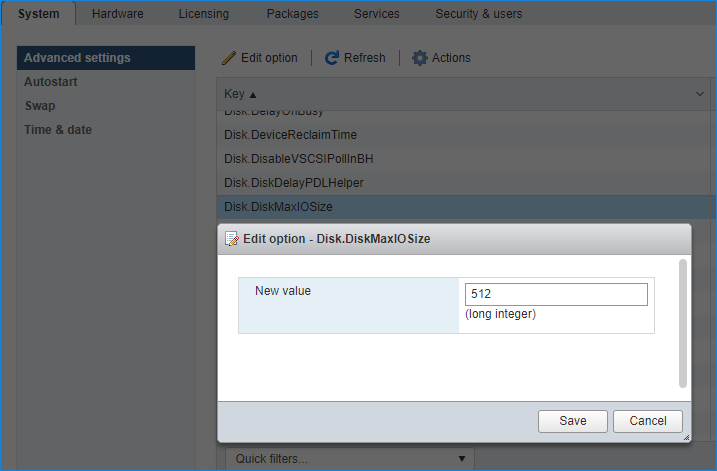
1. Click on the Configuration tab on all of the ESXi hosts and choose Advanced Settings.
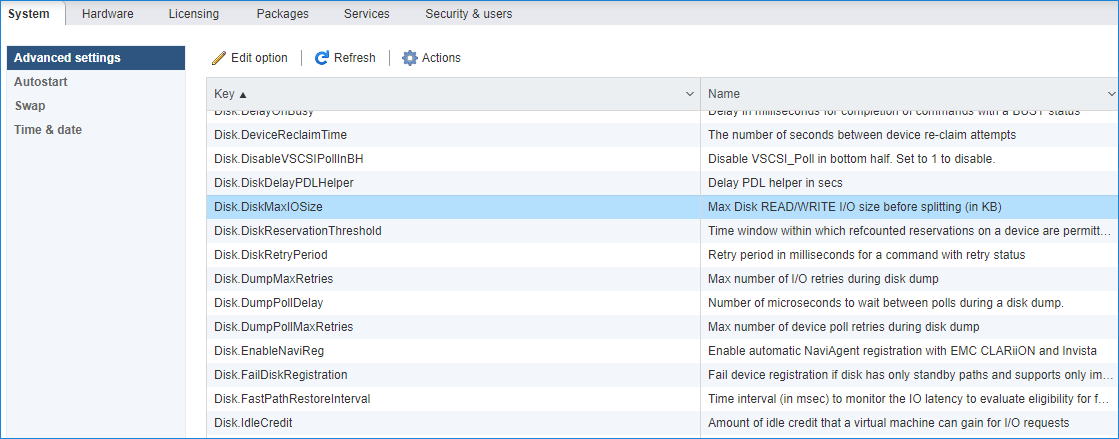
2. Select Disk and change the Disk.DiskMaxIOSize parameter to 512.
3. To optimize performance change I/O scheduler options according to the article below:
https://knowledgebase.starwindsoftware.com/guidance/starwind-vsan-for-vsphere-changing-linux-i-o-scheduler-to-optimize-storage-performance/
NOTE: Changing Disk.DiskMaxIOSize to 512 might cause startup issues with Windows-based VMs, located on the datastore where specific ESX builds are installed. If the issue with VMs start appears, leave this parameter as default or update the ESXi host to the next available build.
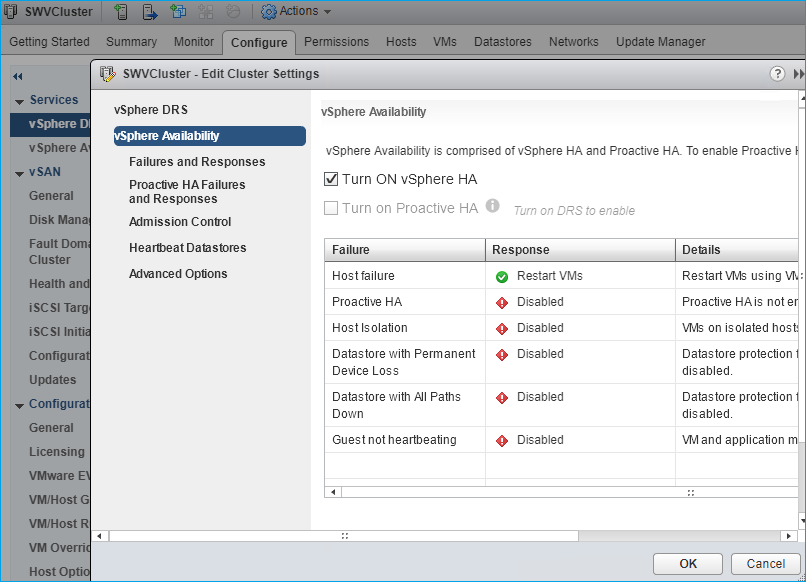
NOTE: To provide high availability for clustered VMs, deploy vCenter and add ESXi hosts to the cluster.
Click on Cluster -> Configure -> Edit and check the turn on vSphere HA option if it’s licensed.